Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Molimina, PMS and PMDD
-
Slides Molimina PMS and PMDD.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
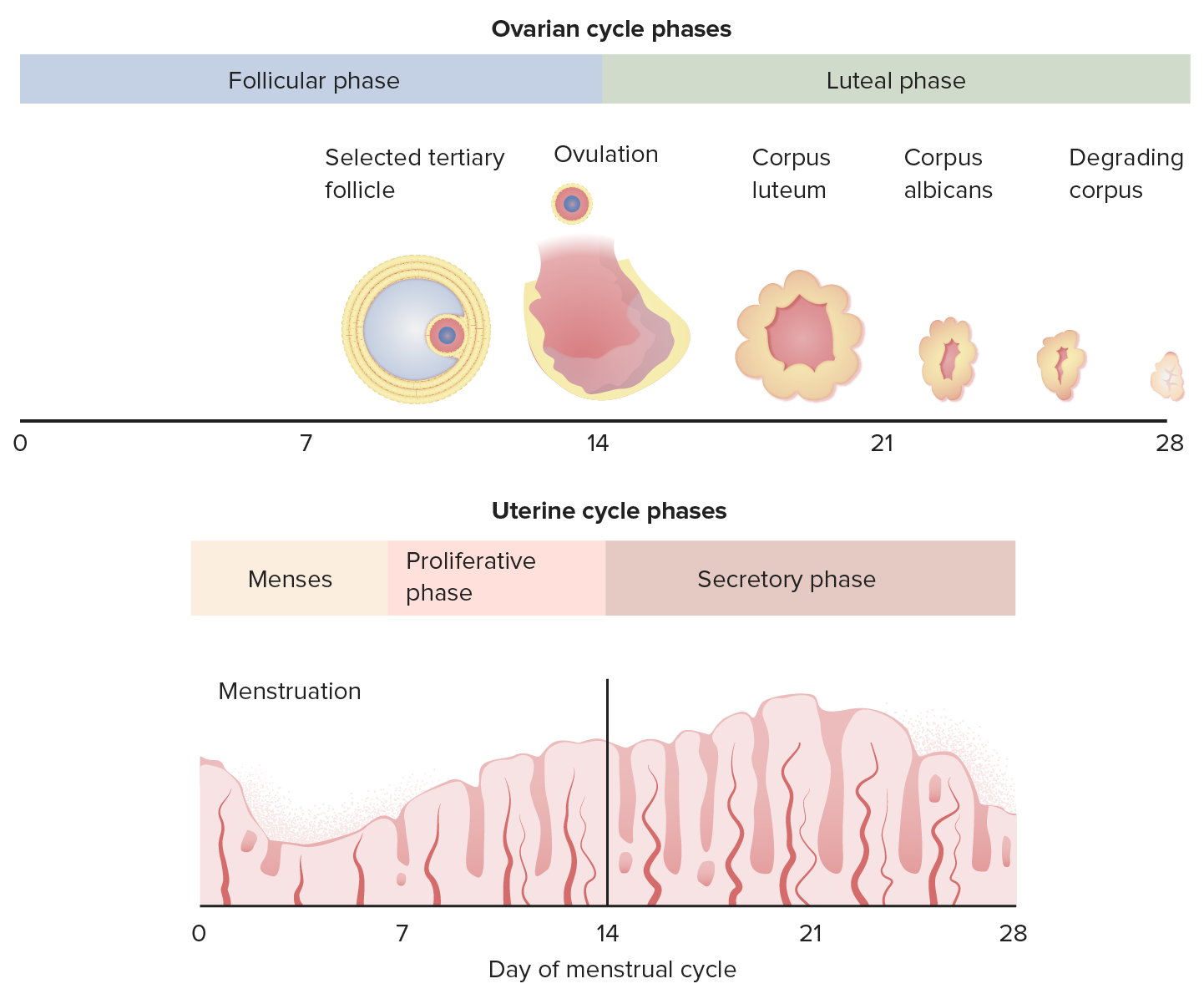
00:01 So today I'd like to talk to you about molimina, premenstrual syndrome and premenstrual dysphoric disorder. 00:07 These are three different clinical scenarios that will be helpful in you taking your step two. 00:12 So during the reproductive years, a lot of women about 80-90% of menstruating women will experience some symptoms. 00:21 They’ll have breast pain, bloating, acne, or constipation, that will forewarn them of an impending menstruation. 00:28 This is called molimina. 00:29 This is a normal natural process that happens prior to your period, and it can alert women that their period is coming. 00:37 Premenstrual syndrome, however, is a bit different. 00:42 It encompasses a wide range of severity with more than 100 physical and psychological symptoms reported. 00:49 Over 60% of women report some swelling or bloating. 00:53 And some women have cyclical breast pain and about 22% of those women express moderate to extreme discomfort. 01:01 30%-40% of women are sufficiently bothered to ask their health care provider about how to relieve symptoms. 01:09 Usually these symptoms with PMS appear the week before menstruation and resolve within one week of the onset of menses. 01:17 This is different though than premenstrual dysphoric disorder, which is abbreviated PMDD. 01:26 This diagnosis should be reserved for a more severe constellation of symptoms. 01:31 And they are mostly psychiatric. 01:34 These symptoms can lead to periodic interference with the day-to-day activities and interpersonal relationships that the patient may experience. 01:43 PMDD has a 3%-5% incidence during their reproductive years. 01:49 There are different causes for PMS and PMDD. 01:55 We think that it could be ovarian fluctuation, ovarian steroid fluctuation. 02:00 It could be a lack of CNS neurotransmitters. 02:04 It could be a genetic predisposition, or it could be the suicidal and social expectations place on a woman. 02:13 There is a distinct diagnostic criteria for PMDD. 02:18 Recall that these diagnoses is mostly a psychiatric diagnosis. 02:24 So the diagnosis is based on a, the timing of symptoms. 02:28 In the majority of menstrual cycles, at least 5 symptoms must be present in the final week before the onset of menses. 02:35 And they then start to improve after the onset of menses. 02:39 The symptoms that one can experience with PMDD include marked lability, marked irritability, depression and anxiety. 02:51 However, you can also experience decrease interest in your usual daily activities and that can also lead to fatigue, difficulty concentrating and change in your whole appetite. 03:05 It can also lead to sleep abnormalities and feeling overwhelmed or out of control. 03:11 Breast tenderness, swelling, joint pain; also make up this constellation of symptoms. 03:18 The symptoms are usually severe enough that they interfere with the daily activities that the woman may experience. 03:25 However, the most important thing with PMDD is that we not forget to consider other psychiatric disorders and you can actually have a presentation of PMDD at the same time that you have co-occurring psychiatric and mental disorders. 03:44 The confirmation of the disorder is made by criterion A, should be confirmed by a prospective daily rating during two symptomatic cycles. 03:52 And we must not forget that you have to exclude other medical explanations. 03:58 So the diagnostic criteria for PMDD include a daily listing of symptoms, rating of symptoms throughout the month that are severe. 04:09 Timing of symptoms that lead in relationship rather to menstruation. 04:14 And rating the baseline symptoms during the follicular phase which is the first half of the menstrual cycle. 04:20 Clinically we sometime use a tool called PRISM Menstrual Calendar. 04:26 And PRISM stands for Perspective Record of Impact and Severity of Menstrual symptoms. 04:31 It’s a menstrual calendar that allows the woman to record their symptoms accurately. 04:35 In actual practice, we don't use this, however it’s something good to know for your exam. 04:41 There are some laboratory test that we typically send on a woman who is experiencing these symptoms. 04:49 TSH or thyroid-stimulating hormone, is a test that we would use to make sure the woman doesn't have hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. 04:57 In terms of management of PMDD, the first thing we wanna do is encourage healthy communication strategies, so that during times of irritability and anger, the patient can communicate effectively with the people around her. 05:13 We also counsel patients that improving their diet during this time can help with their overall symptoms, especially bloating. 05:21 So we encourage them to eliminate salt, sugar, processed food that would encourage more bloating. 05:28 Exercise is a really good treatment strategy and that it helps relieve stress which can also exacerbate the symptoms that a woman might be suffering from. 05:39 However, if those management strategies do not work, medical options are an alternative. 05:47 Medical ovarian suppression with oral contraceptive pills has been shown to be very effective and usually those pills are prescribed continuously. 05:57 Another medication is Danazol. 05:59 Danazol is an androgenic medication that causes oily skin, male pattern hair growth, and breast atrophy. 06:08 So most women don’t desire these symptoms. 06:11 Another method of ovarian suppression are GnRH agonists. 06:15 GnRH agonists shut down the hypothalamic, pituitary-ovarian access and cause vasomotor symptoms such as hot flashes or hot flushes as they are known medically and they can also lead to bone loss. 06:29 Another proven strategy to treat PMDD are luteal phase SSRIs. 06:35 Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, which increase serotonin levels. 06:40 So in your checklist, remember to take accurate and thorough gynecologic history. 06:47 Rule out other psychiatric disorders and rule out other medical causes. 06:54 Ask the patient to keep a menstrual calendar if you're having trouble making the diagnosis. 07:00 Thank you.
About the Lecture
The lecture Molimina, PMS and PMDD by Lynae Brayboy, MD is from the course Abnormal Menstruation. It contains the following chapters:
- Definitions of Molimina, PMS and PMDD
- PMDD Treatment
Included Quiz Questions
Which symptom has the highest frequency of occurrence in patients with premenstrual syndrome?
- Breast tenderness
- Bloating or swelling
- Psychiatric symptoms
- Constipation
- Fatigue
Which of the following is NOT a cause of premenstrual syndrome?
- Backflow of menses
- Ovarian steroid fluctuation
- CNS neurotransmitters
- Genetic predisposition
- Social expectations
A 25-year-old woman has breast pain, bloating and constipation about 2 weeks before menstruation. She doesn't complain of any mental changes. There is no history of bleeding between the menses. Which of the following is a possible diagnosis?
- Molimina
- Premenstrual syndrome
- Premenstrual dysmorphic disorder
- Menses
- None of the options are correct
Which of the following is NOT a treatment option for PMDD?
- Anti-thyroid drugs
- GnRH agonists
- Danazol
- Oral contraceptive pills
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Concise and Clear first introduction to menstrual disorders, presentation, definitions, guidelines and salient information for management,