Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Immunoassays: ELISA, RIA and Luminex™
-
17 Slides Immunodiagnostics.pdf
-
Reference List Immune System.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
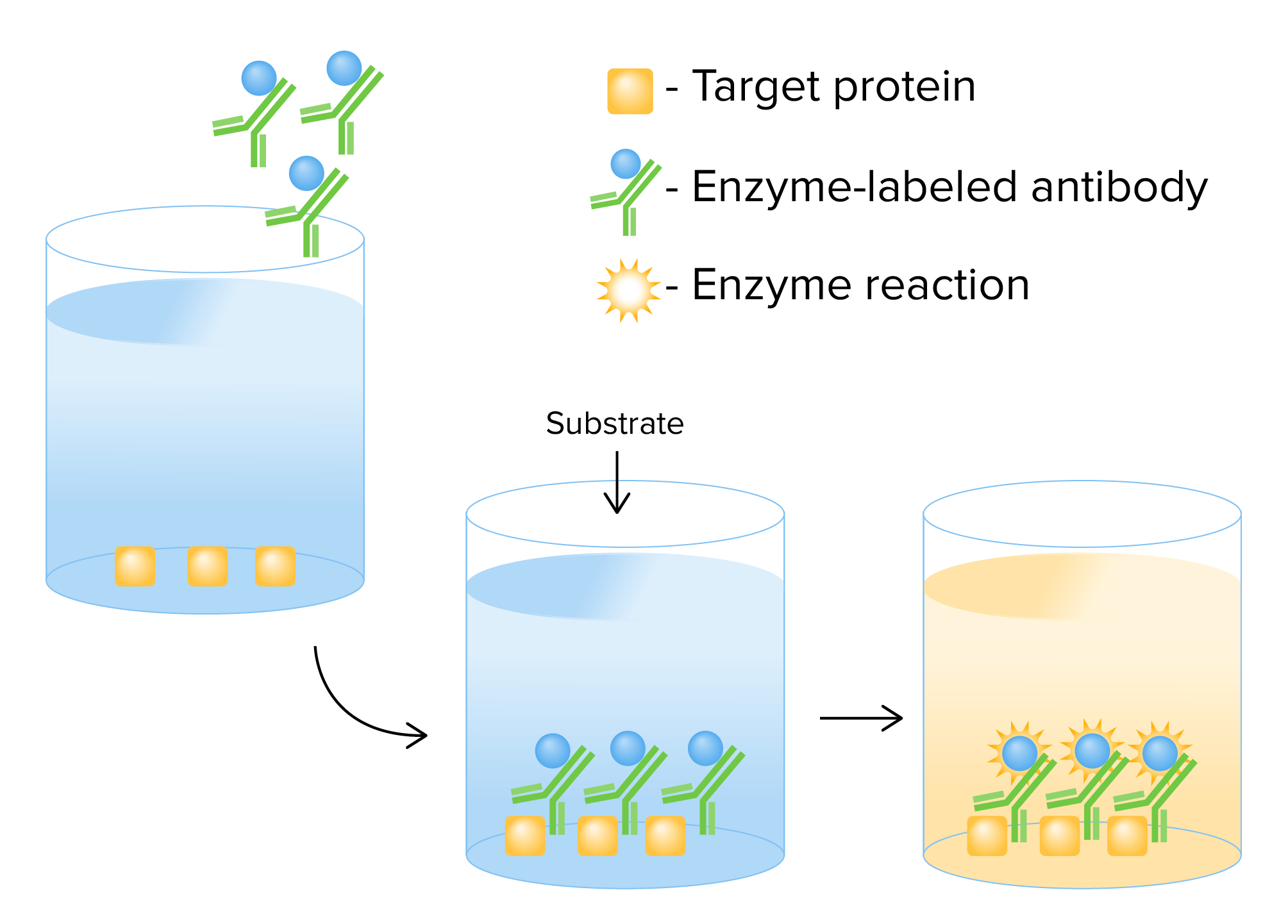
00:01 ELISA - Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a very, very commonly employed analytical method in immunology. 00:16 Plastic plates are coated with an antigen. 00:20 They can be coated with an antibody as well, but in this particular example we are coating the plates with an antigen. 00:27 Very often one will purchase already coated plates from a manufacturer. 00:36 The excess antigen is washed off. 00:41 Test antibody is then added. 00:44 So maybe this is an autoantigen that is coated on the plate. 00:48 And we want to discover whether a patient has autoantibodies against that autoantigen. 00:57 If they do, then they will bind, those autoantibodies will bind to the autoantigen. 01:04 Following a period of incubation, the plate is washed. 01:09 And then a ligand to the test antibody is added. 01:13 In this case the ligand is another antibody coupled to the enzyme horseradish peroxidase. 01:23 The plate is again washed and a substrate, a chromagen is added and a colored product is produced by the enzyme reaction. The amount of color is proportional to the amount of antibody bound to the antigen. In a sandwich immunoassay, first of all antibody is bound to the well of a microtitre plate, which is typically a 96 well plate. 01:56 Varying amounts of antigen are added. 02:00 Any unbound antigen is then removed by washing. 02:06 So for example, maybe we want to measure the amount of a particular substance in the serum of a patient. 02:17 This will be detected by a specific antibody. 02:25 Following washing, a labeled second antibody is added that is specific for a non-overlapping epitope of the antigen. 02:36 So let’s say we are trying to measure a cytokine. 02:42 The first antibody coating the plate would be for one epitope on that particular cytokine. 02:49 The other antibody would be for a different epitope, a different part of the same cytokine. 02:56 Labels include radioactive isotopes or an enzyme that causes a substrate to change color or emit light. 03:09 This would be in a chemiluminescence assay. 03:15 The unbound labeled second antibody is removed by washing. 03:21 And then the amount of second antibody bound is measured. 03:28 What is able to determine the amount of bound second antibody as a function of the concentration of antigen added with construction of a standard curve. 03:40 In the fluorescent microsphere Luminex assay, there are beads that are coated with particular antigens. 03:50 Patient’s serum is added to the coated beads and then incubated. 03:57 There is a reporter tag, for example fluorescently labeled anti-human IgG antibody added to detect the binding of the patient’s antibody to the antigen coating the bead. 04:12 These beads are then subject to a technique called flow cytometry, and signals that identify each bead are emitted and detected. 04:24 There is also a second signal that identifies the reporter tag. 04:31 The amount of signal is proportional to in this example, anti-hepatitis A antibody in the patient’s serum. 04:39 So in this particular example, we have beads coated with different antigens from Hepatitis A, B and C and one can detect that the patient has antibodies to Hepatitis A.
About the Lecture
The lecture Immunoassays: ELISA, RIA and Luminex™ by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Immunodiagnostics. It contains the following chapters:
- ELISA
- Sandwich Immunoassay
- Fluorescent Microsphere (Luminex™) Assay
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is one of the most commonly used enzymes in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay?
- Horseradish peroxidase
- Lysozyme
- Caspase 3
- Activated-induced cytidine deaminase
- C3 convertase
Which of the following best describes a sandwich immunoassay?
- Binding of a labeled antibody to the target antigen, which is bound to a monoclonal antibody on a microtiter plate.
- Binding of a labeled antibody to 2 antigens of different origins which are coated on to a microtiter plate.
- Binding of 2 antigen coated red blood cells to a labeled antibody on a microtiter plate
- Precipitating red blood cells using antibodies that specifically bind to their membranes
- Isolating an antigen from a solution using an antibody that specifically binds to that particular antigen
Fluorescent microsphere assays most often involve which of the following?
- Antigen-coated beads
- Horseradish peroxidase
- A radioactive isotope
- Chromagen
- Caspase 3
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |