Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
IgA Nephopathy
-
Slides NephriticSyndrome IgA Nephropathy RenalPathology.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
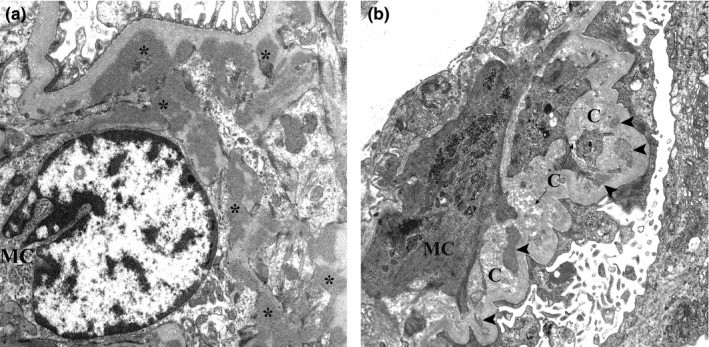
00:01 Now the first primary now for this type of glamor disease that we'll take a look at is AJ Glimmer Allopathy or AJ Nephropathy all the same thing a.k.a burger. 00:13 What I wish to bring to your attention is there's another condition in pathology that we call boogers disease and booger disease is going to be associated with small vessel disease or vasculitis. 00:25 Completely different discussion. 00:27 That's point number one. 00:29 Many students tend to get that confused between burgers and boogers. 00:33 There are two different conditions. 00:34 One has nothing to do with the other. 00:37 And burger has to has to be dealing with it. 00:42 This idea is then going to deposit. 00:44 I'll tell you in a second. 00:46 But before I get there, this idea could also be fun. 00:50 Another important disease that is an important differential that could also be associated with the kidney. 00:56 Do you remember which one? What if I told you there was IGF deposition in the kidney or the glomeruli? And there's also palpable purpura in a young child in the lower extremities or perhaps the buttocks. 01:08 That's called hanoch schon, line purpura. 01:11 And a better name now clinically and has been for quite some time called ECG vascular empathy. 01:17 Are we clear? Be careful. 01:19 This is only nephropathy, Berger. 01:23 Most common nephropathy worldwide. 01:26 Meaning to say majority of the critic. 01:28 And also take a look nephrotic 5% of the time. 01:31 So worldwide, this is the one that you definitely want to know. 01:34 Next for children and adults. 01:37 Next, increased mucosal synthesis and decreased clearance of IGA. 01:42 Thus, you'll find 50% of the population in which the IGA levels are elevated in the serum. 01:50 Next there is focal proliferative glimmer allopathy and this IGA is then going to deposit ornaments and you may ask you something. 01:58 So therefore, which one of the biopsy patterns would most come in handy here? Do you think it would be the minute fluorescence in which in the end you you find green pools mean you say many globulin is accumulating in the messenger result in green pool type of deposition. 02:16 So missing Jim ECG is what you're paying attention to these immune complexes deposit the granular immunofluorescence it ends up being in the messenger. 02:25 You're going to activate the complement pathway complement alternative overlapping features with home hanoch shoreline purpura may occur, but the differences with IgG here and hence action line you pay attention to PREPARA and HSP and action line the purpura representing involvement every blood vessel in Berger. 02:45 That is not the case. 02:47 But in HSP, could you involve the blood vessel in the kidney? Yes, you can. 02:51 What do we mean, a global than a episodic both of hematuria. 02:56 I need you to pay attention to description episodic that is big in medicine. 03:01 You can have episodic episodic type of events with hypertension that fear chromosome trauma. 03:07 You could have episodic events of a jaundice. 03:11 That's a Gilbert or Gilbert syndrome. 03:13 You have episodic bouts of hematuria high on the differential you should be thinking about ija nephropathy usually following a upper respiratory infection. 03:24 Highlight that in your head. 03:25 How hyper or upper respiratory infection you don't have this latent period. 03:31 For example, say that you had sore throat or pharyngitis 2 to 4 weeks later that would not be Berger. 03:39 2 to 4 weeks later would be PSTN with hematuria. 03:45 If we're talking days after a sore throat or pharyngitis, that would be Berger, IJA, nephropathy. 03:53 Did you hear what I just said and how important it is based on that history to come up with two differentials and which one would be a more likely differential if you had what's known as sin for angelic? Sin for angelic basically means days after a fair, energetic episode, upper right of your tract infection, your patient now has developed hematuria, slower progression of chronic renal failure only 40 50% of the time. 04:21 But it's slow progression. 04:22 Many times you can have kidney damage and not necessarily going into chronic renal failure. 04:27 Treatment of mild disease, those with normal renal function and minimal proteinuria, is typically not required. 04:35 For patients with significant proteinuria (at least 500 mg/day), ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and SGLT2 inhibitors may be used to decrease proteinuria and slow progression of the disease. 04:48 Blood pressure control is also an important aspect of angiotensin inhibition. 04:54 For patients at high risk of progressive disease, have severe disease, or have persistent disease despite the described therapies, immunosuppression with glucocorticoids is suggested. 05:08 Mycophenolate mofetil is an alternative for patients with contraindications to glucocorticoids. 05:15 The dual endothelin and angiotensin II receptor antagonists, sparsetan, may also be considered in these cases.
About the Lecture
The lecture IgA Nephopathy by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Glomerulonephritis.
Included Quiz Questions
A 12-year-old boy presents to your office with blood in his urine for the past few days. His mother who accompanies him says that he passes "bloody urine" frequently. He was diagnosed with an upper respiratory tract infection a few days ago and seems to be recovering from that condition. A physical examination shows edema around his eyes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- IgA nephropathy
- Buerger's disease
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
- IgA vasculitis
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of Berger's disease?
- Episodic bouts of hematuria
- Episodic bouts of periorbital puffiness
- Episodic bouts of hypertension
- Episodic bouts of proteinuria
- Episodic bouts of vasculitis
What is the likely cause of generalized edema and periorbital puffiness in nephrotic syndrome?
- Decreased oncotic pressure
- Increased hydrostatic pressure due to salt retention
- Decreased hydrostatic pressure due to salt retention
- Increased oncotic pressure
- Decreased hydrostatic pressure due to proteinuria
Which of the following statements is false regarding nephritic syndrome?
- Proteinuria greater than 3.5 g/day
- RBC casts are a key finding indicating glomerular damage.
- Proteinuria greater than 150 mg/day but less than 3500 mg/day
- The tubular function is intact in acute disease.
- GFR is decreased due to glomerular inflammation.
What is the most likely site of immune complex deposition in IgA glomerulopathy?
- Mesangium
- Subendothelium
- Subepithelium
- Epithelium
- Vascular
Which of the following is the most important feature that distinguishes IgA nephropathy from post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis?
- Length of time between infection and clinical manifestation
- Vasculitis
- Immune complex deposition
- Amount of hematuria
- Amount of proteinuria
What is the differentiating factor between Henoch-Schonlein purpura and IgA nephropathy?
- Vasculopathy
- Immune complexes
- Neuropathy
- Proteinuria
- Hematuria
Which of the following is least likely seen in a patient presenting with IgA nephropathy?
- Proteinuria > 3.5 g/day
- Increased serum IgA
- Granular pattern on immunofluorescence
- Decreased clearance of IgA
- Increased mucosal synthesis of IgA
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |