Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Histoplasmosis: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention – Endemic Mycoses
-
Slides 07 FungalDiseases MicrobiologyAdvanced.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
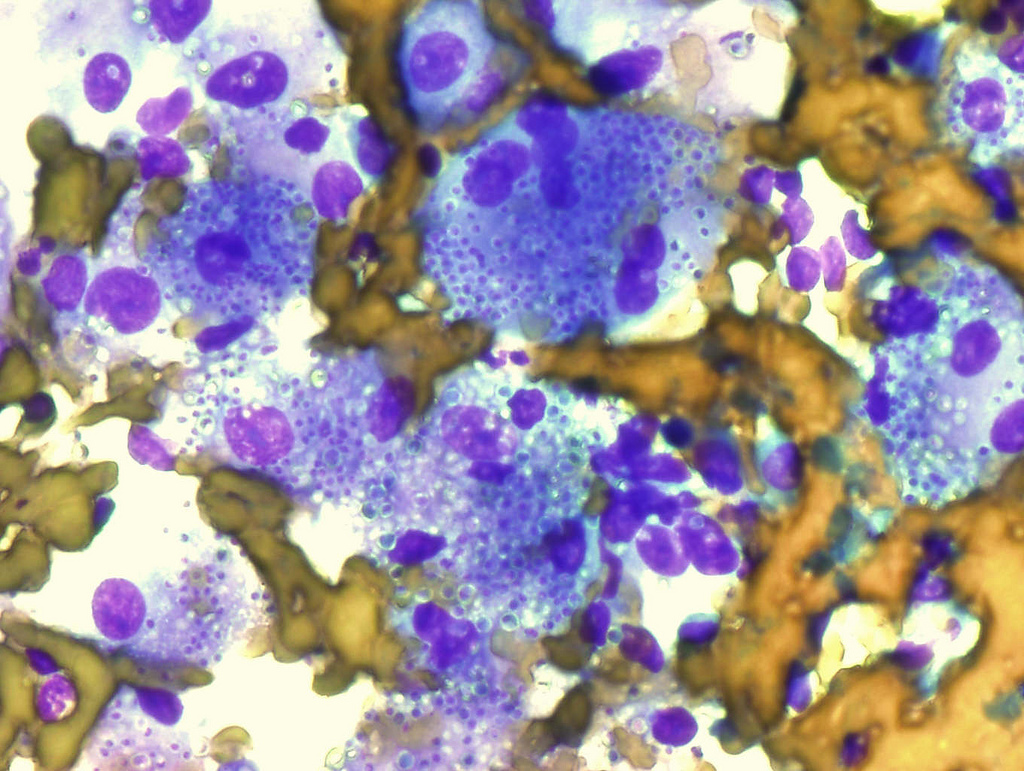
00:01 How do we diagnose histoplasmosis? One way to do so is to try and grow the organisms from clinical specimens, like sputum, blood, tissue samples or other body fluids. But this is a long process, it takes about six weeks and it's not always successful. You can demonstrate the presence of small intracellular yeasts in other clinical specimens and this is more rapid because you take the sample, you look at it under a microscope with the appropriate stain and you can rapidly confirm the diagnosis. You can get samples from bone marrow, liver, lung or lymph. Some of these are more invasive than others. Examine them under the microscope and confirm the diagnosis by the morphologic examination. You can also do enzyme linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA), and you can look for the polysaccharide antigen from the cell wall of the fungus. This can be done with urine or serum, in particular if the infection is disseminated, the fungus will appear in these fluids as well and it's relatively straightforward and quick to do an ELISA to look for the fungal antigen. You can also look for antibody against fungal components, again using an ELISA format and using serum from the patient. 01:25 So these are all rapid ways to diagnose it, in addition to the culture which takes a long time. Once diagnosis is established, which can often be done not only by the laboratory methods, but also considering where the individual has been. If it's in a place at risk for histoplasmosis, you can treat with drugs like itraconazole. This takes a while, it takes 3 to 12 months to eliminate the organisms, so the drug has to be taken continuously. This drug is good for mild to moderate pulmonary or disseminated histoplasmosis, as long as it's a moderate infection. If the infection is more severe, amphotericin B is initially given, followed by itraconazole. Now how do you prevent getting a histoplasma infection? Well if you're working in a contaminated area, if you're involved in construction or demolition, you really should be wearing a respirator. Now I pass construction sites all the time in New York City and nobody wears respirators, because they're a little bulky and annoying and it probably doesn't look very good to be wearing a respirator, but if you're an at risk person, in particular if you have lung disease, or you're on immunosuppressive treatments, you should be wearing a respirator if you're going to do this kind of work.
About the Lecture
The lecture Histoplasmosis: Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention – Endemic Mycoses by Vincent Racaniello, PhD is from the course Fungi.
Included Quiz Questions
How much time is required to culture histoplasmosis from a sample of sputum?
- 6 weeks
- 2 weeks
- 3 weeks
- 10 weeks
- 12 weeks
How does ELISA testing detect histoplasmosis infection?
- By detecting antigens on the fungal cell wall
- By reducing culture time
- By staining fungal cells
- By detecting macrophages in yeast cells
- By antibody–antibody complex formation
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |