Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hepatorenal Syndrome
-
Slides GD liver disease.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
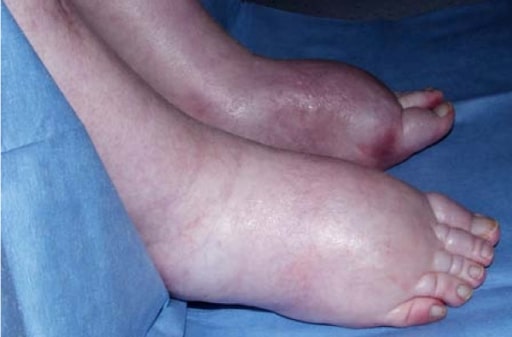
00:01 An important understanding of Hepatorenal Syndrome is required. 00:07 This is a functional renal failure without underlying renal pathology. 00:12 This is not nephralic syndrome, this is not nephrotic syndrome nor it is arteriosclerosis taking place at the renal artery. 00:19 The perfectly functional kidney, used to be the patient developed portal hypertension and now, there is a functional renal failure Is that clear? Very interesting. Important? Yes. 00:35 Hepatorenal syndrome-acute kidney injury (or HRS-AKI) is a serious condition defined as an acute rise in serum creatinine (typically of at least 2-fold). 00:46 This renal dysfunction does not respond to diuretic withdrawal or volume expansion with IV albumin administration. 00:52 HRS-non-AKI refers to renal dysfunction that is more insidious or otherwise does not meet criteria for AKI. It may also be defined by “diuretic-refractory ascites. 01:06 Diagnosis of exclusion. 01:07 Here, you'll find that urine sodium is less than 10mEq/L urine sodium is less than 10mEq/L It means to say, it is not able to properly take care of sodium handling. 01:16 Steps should be taken to improve liver function (where possible) so patients will be told to stop drinking, treating underlying HBV infections can also be helpful. 01:28 Treatment options include vasoconstrictors (such as terlipressin or norepinephrine) in combination with IV albumin. Octreotide plus midodrine is an alternative option. 01:39 Interventions may include dialysis or TIPS procedure. 01:42 Interestingly, in these patients, that do recieve the transplantation, renal function does seem to recover. 01:50 it seems as though the kidney actually comes back to life. 01:54 Fascinating. We don't know a whole lot about it but we know just enough, where that statistic of 100% mortality puts it on the radar, big time.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hepatorenal Syndrome by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Liver Diseases: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the treatment of choice for patients with hepatorenal syndrome?
- Liver transplantation
- Chemotherapy
- Steroids
- Antibiotics
- Antihypertensives
Which of the following factors determines the type of hepatorenal syndrome?
- Rapidity in the loss of renal function
- Amount of loss of renal function
- Severity of loss of renal function
- Severity of loss of hepatic function
- Rapidity of loss of hepatic function
Which of the following statements regarding hepatorenal syndrome is NOT true?
- HRS-NAKI (type 2 HRS) shows rapid loss of renal function.
- It includes HRS-AKI (type 1) and HRS-NAKI (type 2).
- It is defined as functional renal failure without underlying renal pathology secondary to portal hypertension.
- HRS-AKI (type 2 HRS) has a high mortality rate.
- It is usually a diagnosis of exclusion, with urine Na < 10 mEq/L.
Which of the following statements regarding hepatorenal syndrome is TRUE?
- HRS-AKI (type 1 HRS) is defined as at least a 2-fold increase in serum creatinine to a level > 2.5 mg/dL in less than 2 weeks.
- HRS-NAKI (type 2 HRS) shows rapid loss of renal function.
- It is treated with steroids and antihypertensives.
- It is usually diagnosed with certainty based on the renal function only.
- It does not improve after liver transplantation.
A patient is diagnosed with hepatorenal syndrome. Which of the following laboratory abnormalities would be expected in this patient?
- Serum creatinine – increased Urine Na – decreased Serum transaminases – increased
- Serum creatinine – normal Urine Na – decreased Serum transaminases – increased
- Serum creatinine – increased Urine Na – decreased Serum transaminases – normal
- Serum creatinine – increased Urine Na – increased Serum transaminases – increased
- Serum creatinine – decreased Urine Na – decreased Serum transaminases – decreased
A 48-year-old man with cirrhosis is admitted to the hospital with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. His lab values show: total bilirubin = 2.0 mg/dL, albumin level = 2.0 g/dL, creatinine = 1.2, and urine Na = 8 mEq/L on hospitalization. On day 6, the creatinine rises to 4.2, and the patient is anuric. What is the diagnosis of the patient?
- Type 1 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS-AKI)
- Type 2 hepatorenal syndrome (HRS-NAKI)
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome
- Non-alcoholic liver disease
- Cirrhosis with portal hypertension
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |