Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Glaucoma: Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
-
Slides Optic Pathology Glaucoma.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
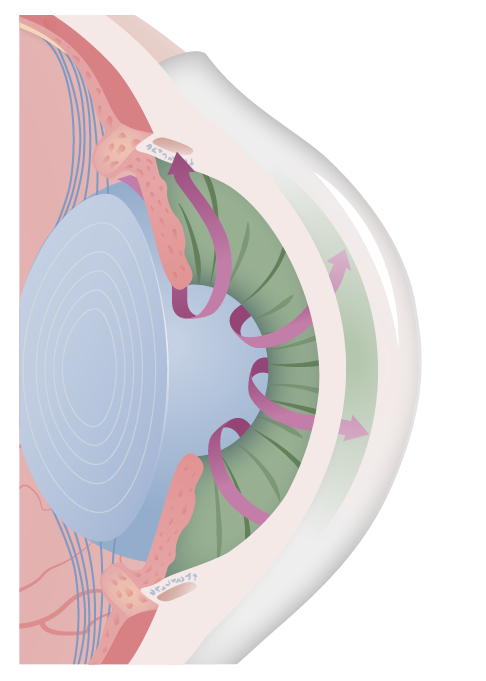
00:01 So overall, for open-angle Glaucoma and normal-pressure glaucoma signs and symptoms, it's usually asymptomatic, it's not painful and most people walking around glaucoma don't know that they have it. 00:14 In fact, that's why we have to do a very thorough eye exam and screen for it. 00:20 So when you go for your ophthalmologic exam, they'll puff their little puffer in your eyeball, and they will get a sense of the pressure. 00:28 It's an important part of the exam. 00:30 And there are other ways that we can do this called tonometry that we'll talk about shortly. 00:36 As we get progressive compression of the optic nerve at the back of the eye, with all of these pressures, kind of differentials being eventually translocated to the posterior portion of the eye, you'll get a gradual loss of peripheral vision. 00:48 And then late in the process, you'll get loss of central vision. 00:53 And if it's untreated, you will go blind. 00:56 So that's open-angle glaucoma. 00:59 Closed-angle glaucoma. 01:02 Chronic closed-angle glaucoma can be a very slow motion way of developing glaucoma, so that you have much less symptomatology. 01:13 So, chronic closed-angle glaucoma, as indicated here in the title will overall be less severe and may be completely asymptomatic. 01:23 But again, you'll have gradual loss of peripheral vision and then a decrease in central vision. 01:27 And eventually you can go blind. 01:29 Conversely, acute closed-angle glaucoma is an ophthalmologic emergency. 01:35 And in this setting, we have now acutely change the geometry for a variety of reasons, things that we talked about previously. 01:42 And there will be an abrupt, acute increase in intraocular pressure that can be manifested by a number of symptoms and signs. 01:52 So that's what's shown here. 01:53 In acute closed-angle glaucoma you can have in fact, relatively severe eye pain, you can have headache. 01:59 Photophobia, because in fact, you're not getting the normal relaxation, the mydriasis of the pupil, so that you have too much light getting through. 02:10 The vision may be blurred, because we have in fact increased pressure. 02:15 There will be halos around bright lights and because of the increased intraocular pressure, in fact that can be acutely felt and manifested as nausea and vomiting. 02:24 So it can be quite severe. 02:26 The signs are those that you see right here, it'd be a red eye. 02:30 So there is conjunctivitis associated with this as we are compromising the outflow of blood out of the conjunctiva. 02:39 So the vessels look dilated and the cornea can look steamy because of then increases in edema fluid that's actually getting into our cornea. 02:49 The pupil is mid dilated and nonreactive light. 02:52 This is part of the photophobia and there will be an absence of accommodation in the light reflex because the various sphincter muscles of the iris will not function appropriately. 03:04 This is an ophthalmologic emergency. 03:08 So how do we diagnose glaucoma? One of the major elements, the major tools that we use are devices that will measure the intraocular pressure, the tonometry devices, and couple are shown here. 03:22 That's not enough though, because you can have normal pressure glaucoma as we talked about, and you may have completely normal pressures as measured with those devices. 03:32 So you need to evaluate the rest of the eye. 03:36 In terms of deciding whether you have closed-angle or open-angle glaucoma, looking at the anterior chamber angle is an important element. 03:43 And that's the visualization as is shown here. 03:47 You also want to look for optic disc changes. 03:51 As the pressures change, we will see on fundoscopic exam differences in the appearance of the back of the eye. 03:59 And that's shown on this slide were normal around the optic disc, you can see the vessels, you can see a normal area of power where we don't have such a high density of microvasculature but you can see that there are vessels there. 04:16 In glaucoma as we get progressive nerve atrophy and compressed the vessels going in and out at the optic disc, you'll see this large area of yellow power and so that is a real sign of optic disc atrophy. 04:31 And then finally, you will assess for visual field changes, cuts in the visual field and they will be all over the place from complete cut out to little tiny dots scotoma throughout depending on how the nerves are being compressed at the back of the eye as they exit through the optic desk. 04:54 The management overall for glaucoma focuses primarily on lowering intraocular pressure. 05:00 Even in normal pressure, glaucoma, we still may want to try to reduce the intraocular pressure. 05:06 And we'll use either pharmacologic means remember we can modify parasympathetic and sympathetic tone, which will affect intraocular pressure or we can use surgical methods if the sewer grate is blocked, we can open that up. 05:20 So there are a variety of things that we can do. 05:22 But we do need to intervene so that the patient doesn't go completely blind. 05:27 And with that, we finished our discussion on glaucoma.
About the Lecture
The lecture Glaucoma: Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosis by Richard Mitchell, MD, PhD is from the course Diseases of the Anterior Chamber and Uvea.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the characteristic symptom of open-angle glaucoma?
- Loss of bilateral peripheral vision
- Myopia
- Photophobia
- Mydriasis
- Diplopia
What is a sign of acute closed-angle glaucoma?
- Red-eye with a "steamy cornea"
- Purulent discharge from the medial canthus
- Bell's sign
- Strabismus
- Nystagmus
On what exam can the optic disc changes be visualized?
- Fundoscopy
- Slit-lamp
- Schirmer's test
- Rose bengal dye test
- Tonometry
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
I really enjoy this series of lectures, they are very nicely broken down, explained and the visuals are amazing