Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Entamoeba Histolytica – Protozoa (GI Infection)
-
03-51 Entamoeba histolytica.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
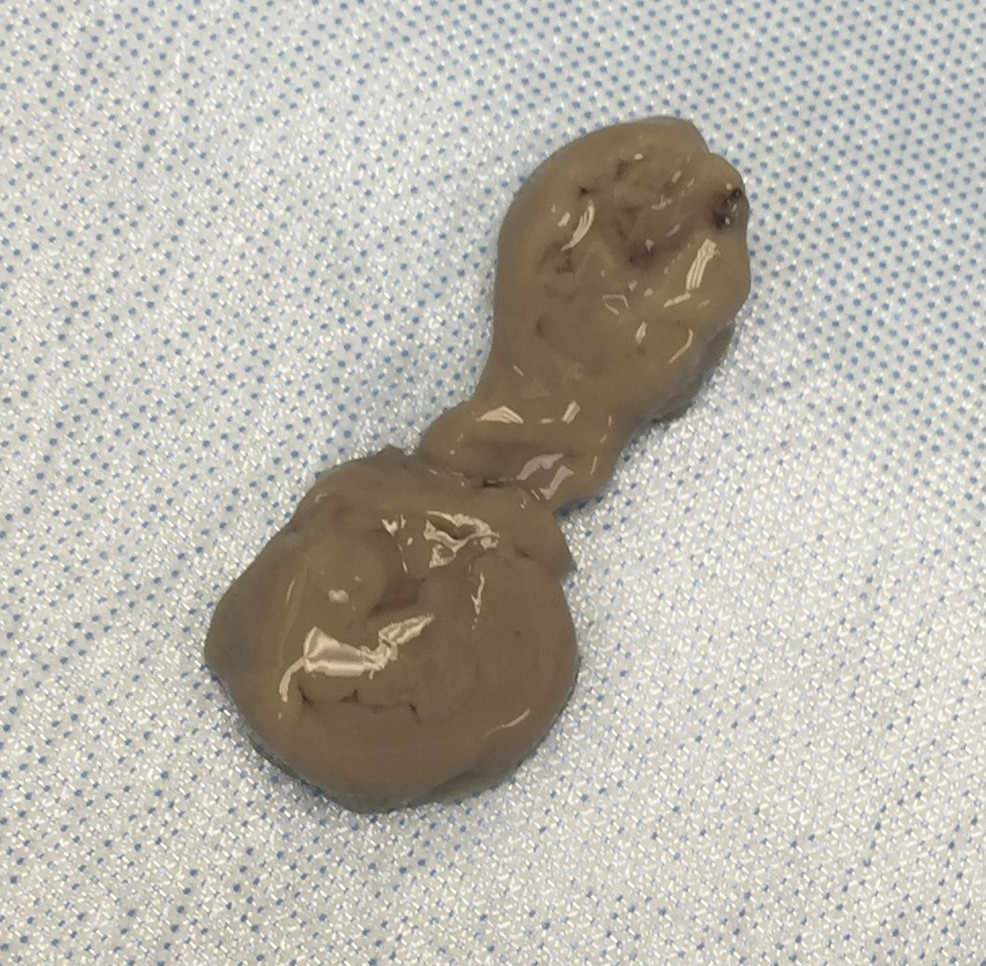
00:01 Entamoeba histolytica, a parasite. 00:04 Entamoeba histolytica is an anaerobic protozoan parasite such as you see on the picture in front of you. 00:11 It is transmitted via fecal-oral spread of the cysts and this is the very common mechanism of transmission for many of the parasites we talk about. 00:21 Incubation for those who are affected with the cyst is from two all the way up to four weeks or so. 00:28 The identification of the Entamoeba histolytica once one is looking for it can be obtained by looking at stool specimens or biopsy specimens which will identify either, or perhaps and, the trophozoites with engulfed erythrocytes, red blood cells, and the cytoplasm or cysts with up to four nuclei such as you see on the image on the slide. 00:52 For the diagnosis of E.histolytica, the most commonly used test is a stool antigen detection using the enzyme-linked-immunosorbent assay, or ELISA method. It is an easy and rapid test to use and can detect early infections as well as differentiate among the different species of amebae. The sensitivity is very good with the best commercial assays having 90% sensitivity and specificity, that is better than microscopy. 01:17 Other tests which can be used include stool microscopy, PCR, serology and colonoscopy with a tissue diagnosis. Stool microscopy is not ideal because it is labour intensive and has limited sensitivity. It also requires specialized expertise to differentiate the different types of amebae. However, in some situations, this may be the only test available. The best but costliest test is a stool polymerase chain reaction or PCR. Most of the commercial PCR assays have 100% sensitivity and specifity, and they are about 100 times more sensitive than stool antigen tests. Serology can be used as well with the antibodies detectable 5 to 7 days after infection, but it cannot distinguish between acute and prior infection. So, it is a problem in endemic areas where up to 35% of the population may have antiamebic antibodies. 02:13 Colonoscopy with biopsy is another way to diagnose cases of active infection and if there are lesions, the cecum and colon are the most commonly involved sites. 90% percent of infections are asymptomatic after this occurs, however, in the remaining 10% of cases, they have had a colonization of the large bowel. 02:34 After that colonization occurs, an invasion via the intestinal mucosa may occur and it’s associated with cellular necrosis via apoptosis, sort of a programmed cell death of those target cells. 02:47 Lytic enzymes are then are released which allow further penetration through the intestinal wall into the blood vessels and now one can have dissemination of the cysts, the Entamoeba histolytica, into other organs. 03:03 A primary target for Entamoeba histolytica is the liver. 03:07 There is then a chain reaction, a sort of tissue destruction, further inflammation, chain reaction of lytic enzymes of tissue destruction, etc., and ultimately one gets flasked-shaped ulcers or abscesses with many fistulas connecting them either to other abscesses or to the external surface of the affected organ. 03:30 There are several clinical manifestations of infection with Entamoeba histolytica, one is amebic dysentery if the infection remains limited to the gut. 03:41 Such patients will have a watery diarrhea which may actually be somewhat foul-smelling and they may also be blood or mucus in the stool. 03:50 In addition, patients that have further progression may develop right upper quadrant pain and they’ll have flask shaped intestinal ulcers so the pain comes from getting edema related to the ulcers and stretching the intestinal capsule. 04:07 Pain fibers are typically in the pleura, or the covering, the skin if you will of internal organs and it’s when those become inflammed that pain can be referred to any part of the quadrant. 04:20 Perhaps the most common or commonly found infection with Entamoeba histolytica is or are liver abscesses. 04:30 amebic liver abscesses and when they are drained which is one of the proper mechanisms of treatment, an anchovy paste exudate is described. 04:39 The specimen which you see is a biopsy material with anchovy paste material present within it. 04:46 Treatment then, if the patient has amebic dysentery, then treatment with antibiotics alone should be sufficient and the antibiotic of choice is metronidazole. 04:58 One can also follow that up with paromomycin or iodoquinol for patients who have a asymptomatic passage of the cyst. 05:08 For those patients with then amebic liver abscess, the metronidazole is not sufficient. 05:14 There must be a percutaneous drainage of the liver abscess to remove that anchovy paste material that is typically accomplished by interventional radiology. 05:25 There is however a risk and that is having chronic fistula formation between that abscessed liver and the external abdominal wall. 05:35 So small abscesses may be treated medically; larger require intervention with drainage and then followed by the antibiotic. 05:45 So Entamoeba histolytica is absolutely one of the more common parasites that we see in terms of causing amebic dysentery in underdeveloped parts of the world and then liver abscesses surprisingly and maybe in your backyard, beware the Entamoeba histolytica.
About the Lecture
The lecture Entamoeba Histolytica – Protozoa (GI Infection) by Sean Elliott, MD is from the course Parasites.
Included Quiz Questions
If a patient presents with bloody diarrhea and flask-shaped intestinal ulcers, which of the following is the most likely mode of transmission of the causative organism?
- Feco-oral route
- Animal vector
- Sexual contact
- Droplet sprays
- Blood transfusion
If the percutaneous drainage of a liver abscess reveals "anchovy paste" exudate, the most likely organism is a/an...?
- ...anaerobic parasitic protozoan.
- ...aerobic parasitic protozoan.
- ...aerobic gram-positive bacteria.
- ...aerobic gram-negative bacteria.
- ...helminth parasite.
Which of the following is the most common extra-intestinal manifestation of an invasive infection by Entamoeba histolytica?
- Liver abscess
- Peritonitis
- Pleuropulmonary disease
- Pericarditis
- Brain abscess
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |