Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Definition, Function & Basic Principles – Electrocardiogram
-
Slides CV Physiology-Electrocardiogram.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
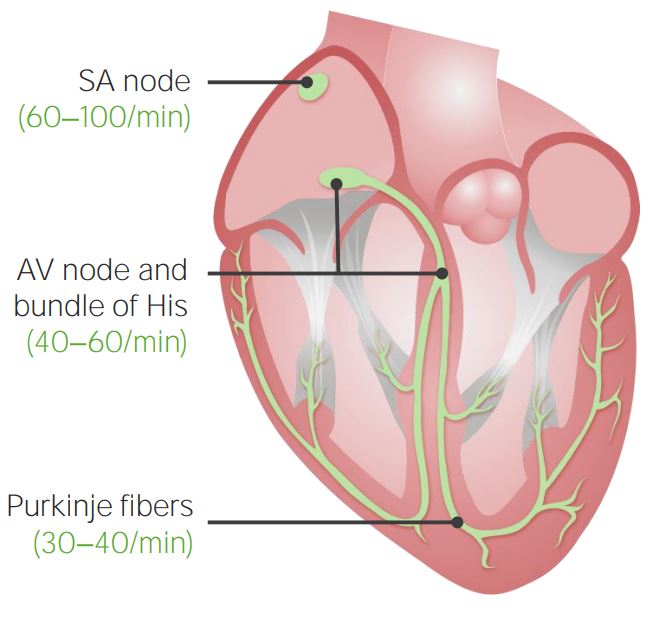
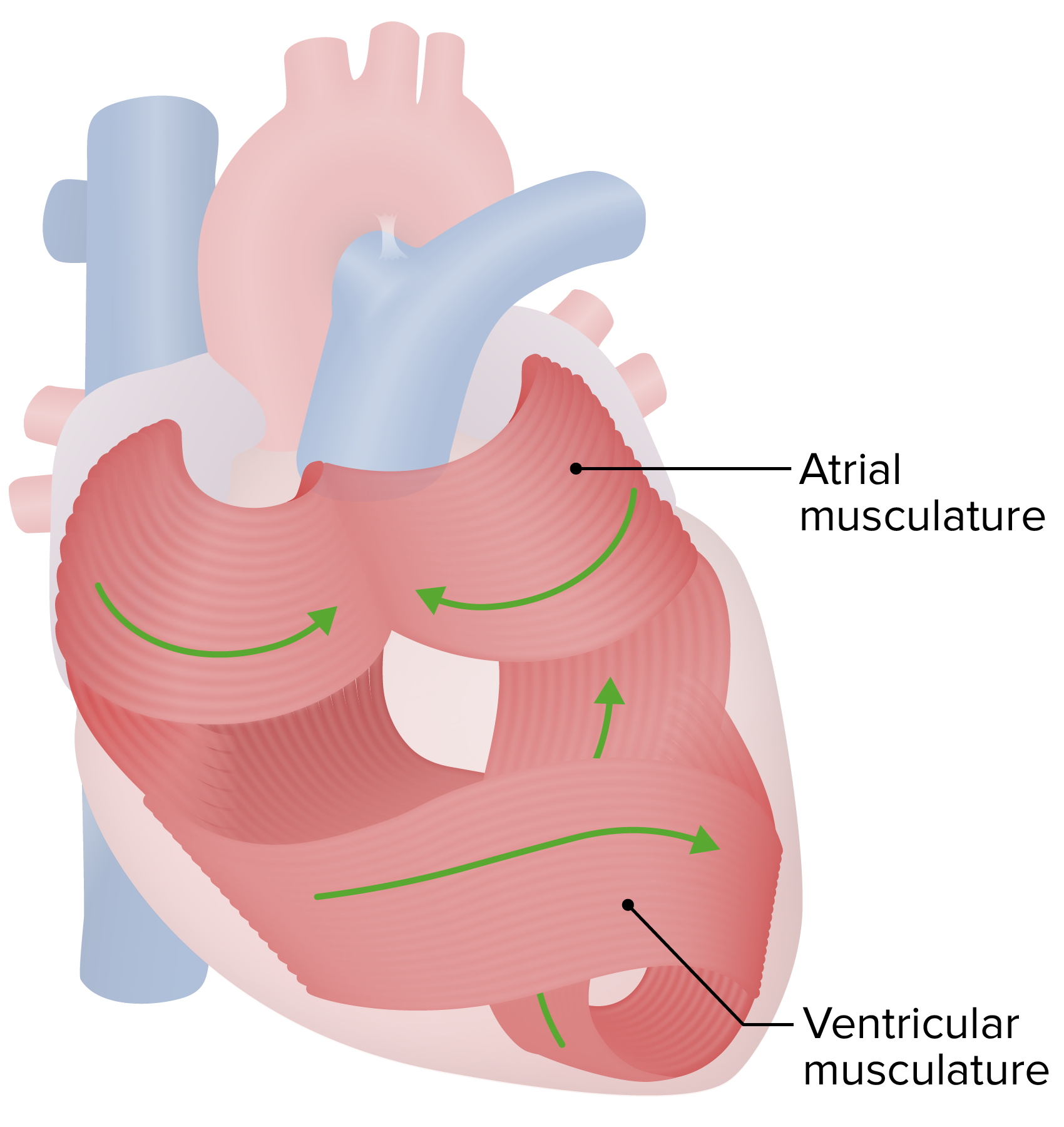
00:01 Now, we’re going to take on one of the more interesting parts of cardiac physiology. 00:07 We’re actually going to talk very much about the electrocardiogram, which is your ability to monitor what the heart's electrical properties are from outside the body. 00:21 So, in this case, what exactly is an electrocardiogram measuring. 00:25 We usually abbreviate this as ECG. 00:29 This is really pretty simple, although we try to make it into something that allows for a lot of diagnostic purposes associated with it. 00:38 It really just involves a positive and a negative electrode. 00:43 That's it. That's it. 00:44 Pretty easy, right? Positive and negative electrode. 00:48 But what does one positive and one negative electrode give us? It gives us one picture of the heart. 00:56 What we can use, though, is maybe 10 or 12 electrodes and then we can get multiple pictures of this same structure. 01:06 So, think of this like your house or your apartment. 01:10 You can look at it from the street view. 01:13 You can look at it from down the street. 01:15 You can look at it from up the street. You can look at it from down the street. 01:15 You can look at it from up the street. 01:16 You can go in the backyard, look at it from the back. 01:19 It all looks different even though it's the same apartment or house. 01:24 And that's what all these different pictures of the heart give us. 01:28 Different views of the same structure. 01:34 So, how do these single positive and negative electrodes do that? Well, basically, you're looking at a mean vector. 01:45 And the mean vector tells you in what direction the ECG is going to be traveling. 01:52 If you are traveling towards a positive pole, you're going to get a positive deflection. 01:58 If you're traveling a depolarization wave towards a negative pole, you’re going to get a negative deflection on the ECG. 02:07 It's that simple. 02:09 Now, notice that there are a lot of different vectors that are being generated as you have a depolarization. 02:17 You know, you get one going to the right, one going to the left. 02:20 We are only concerned with here the average or mean of all of those vectors. 02:27 That determines if a positive charge is moving towards a positive pole. 02:33 If that occurs, it’s a positive deflection.
About the Lecture
The lecture Electrocardiogram (ECG): Definition, Function & Basic Principles – Electrocardiogram by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Cardiac Physiology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following test is meant to create a record of the heart's electrical activity at rest?
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- MUGA Scan
- Exercise stress test
- Cardiac MRI
- Echocardiography
Which of the following statements characterizes the ECG electrical activity between a pair of positive and negative electrodes?
- It represents the average of the many depolarization vectors “seen” in the heart taken by those electrodes.
- If the depolarization wave travels toward a negative electrical pole you will get a positive deflection on the ECG.
- The ECG is not concerned with the polarity of the electrodes.
- The positive and negative electrodes can be switched without affecting the ECG.
- A single pair of positive and negative electrodes can give multiple electrical views of the heart without repositioning the electrodes.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Thank you Prof. Wilson. you made the subject to be very easy to understand.