Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
ECG Tracing: Definitions and Related Cardiac Timing – Electrocardiogram
-
Slides CV Physiology-Electrocardiogram.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
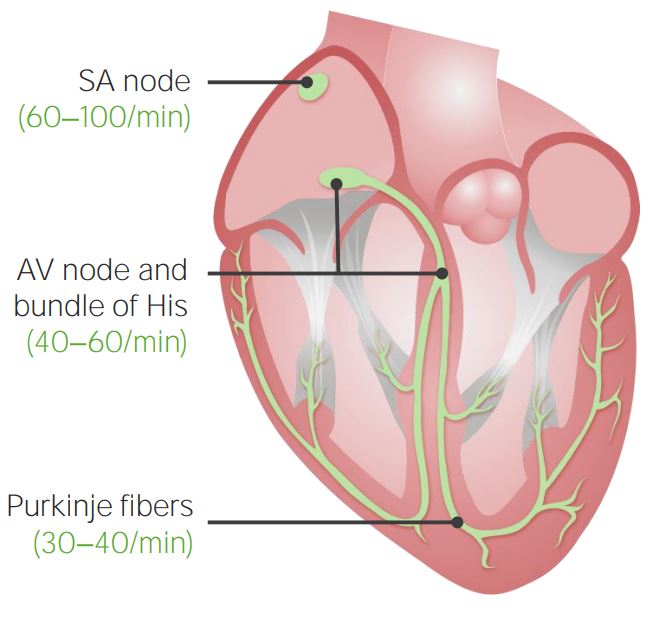
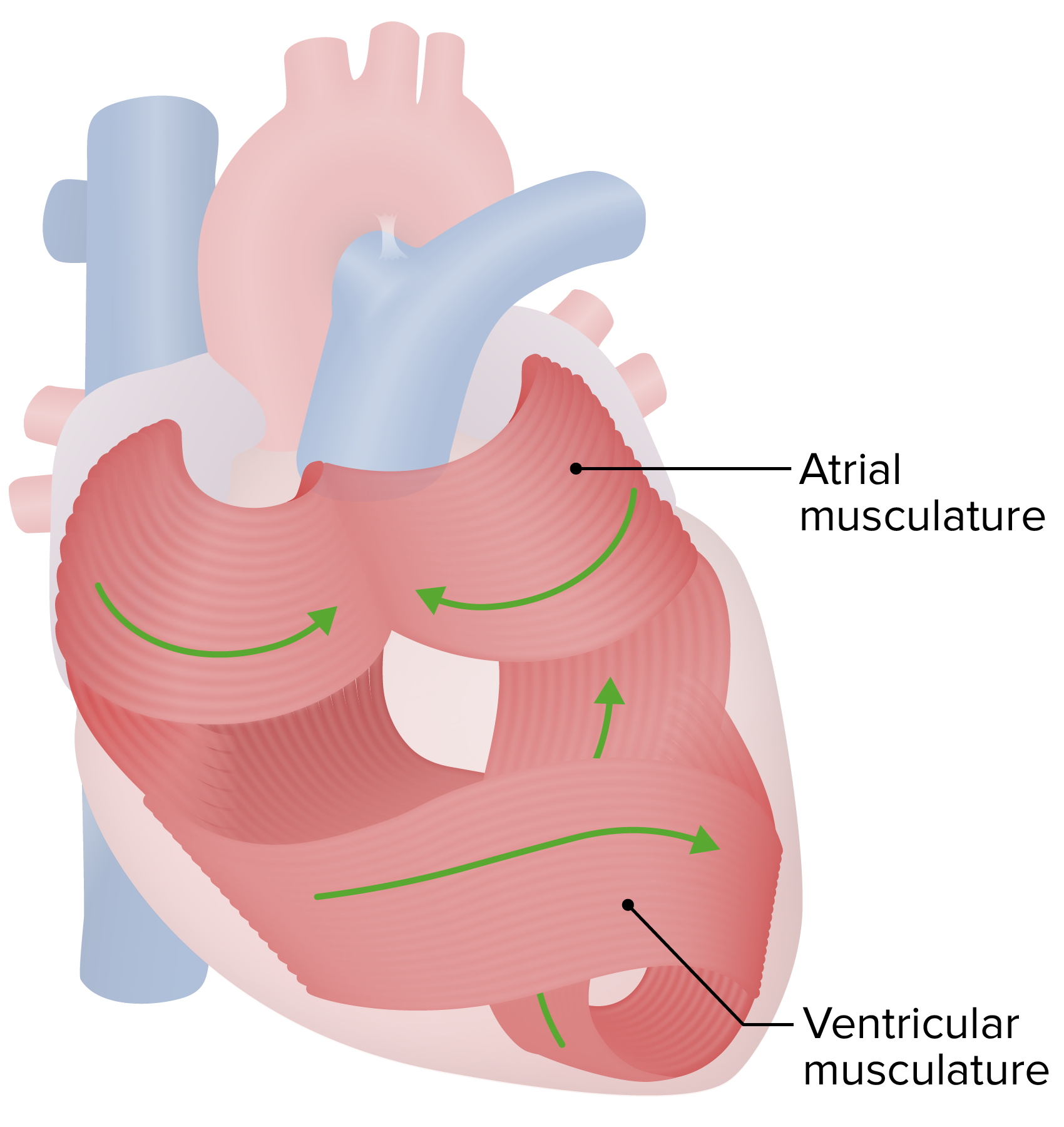
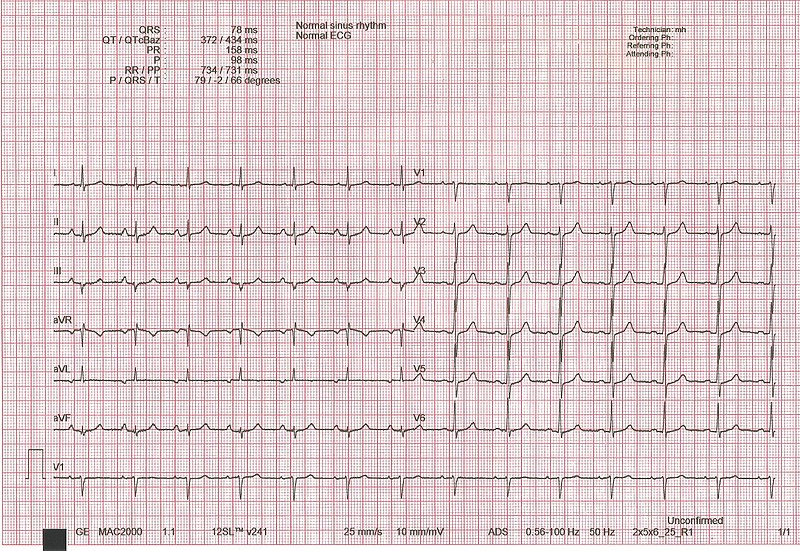
00:02 Now, it's important to go through an ECG step-by-step and name the various waves. 00:10 And you might be familiar with some of the naming of these waves, but let's go through them again, so everybody's on the same page because we have this down, then we can add pathology later on. 00:21 But until you know the waveforms, unfortunately, we can’t get to that point, and that's the fun part. 00:26 So, now you have to learn the waves. 00:29 The first is the P wave. 00:31 The P wave corresponds to atrial depolarization. 00:36 So, that’s the top part of the heart depolarizing. 00:40 The next thing we have is called the PR interval, and so that is from the start of the P wave to the start of the QRS complex. 00:52 The QRS complex is ventricular depolarization. 00:56 So, as you can imagine, the top part of the heart depolarizing is important, right? But, really, where are you pushing the blood from the top of the heart? Just to the bottom part of the heart. 01:07 Where are you pushing the blood from the bottom part of the heart? Out throughout the whole body or all through the lungs. 01:13 So, it’s a longer distance you are pushing the blood out as you go through the ventricles. 01:19 That's why the QRS complex is so important because it's pushing blood out throughout the whole body or throughout the lungs. 01:29 The next interval we have is called the QT interval and that goes from the start of the QRS complex all the way to the end of the T wave. 01:40 We have something called the ST segment. 01:43 The ST segment is from the end of the S wave to the start of the T wave. 01:49 And the final thing we have is called the T wave and the T wave is the repolarization of the ventricles. 01:59 There's another little bump after the T wave, called the U wave, but that's only prominent in pathologic findings. 02:07 So, our primary things, P wave, PR interval, QRS, QT interval, ST segment and T wave. 02:18 So, let's go through these processes even in more detail and add some intervals to them besides just the PR interval and the QT interval. 02:30 The biggest one is called the R-R interval. 02:35 And the R-R interval takes from one R wave all the way to the next R wave. 02:41 This is an important interval because this determines how often your ventricles depolarize. 02:48 What should this tell you? Heart rate. 02:52 It’s how fast the heart is beating, how many times it depolarizes. 02:57 So, the R-R interval is how you base heart rate on. 03:02 The PR interval, we already discussed, is from the beginning of the P wave to beginning of the QRS complex and that needs to be a certain duration. 03:12 If it's longer than that, then you might have an AV block. 03:18 The QRS has a certain duration that it needs to be. 03:21 If it’s too wide, you're concerned about things like premature ventricular complexes. 03:30 The QT interval is going to be very dependent upon heart rate itself. 03:34 So, how often you have depolarization versus how often it repolarizes. 03:41 The ST segment should be isoelectric, meaning that should be a flat line and it should match the same flat line that’s after the T wave and before the P wave.
About the Lecture
The lecture ECG Tracing: Definitions and Related Cardiac Timing – Electrocardiogram by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Cardiac Physiology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which part of the cardiac cycle corresponds to the ST segment?
- The interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization
- Ventricular depolarization
- Ventricular repolarization
- Atrial depolarization
- Atrial repolarization
Which electrocardiogram interval is used to calculate the heart rate?
- RR interval
- PR interval
- QRS interval
- ST interval
- T wave interval
Which of the following is the definition of the ST segment?
- End of the S wave to the beginning of the T wave
- Start of the QRS complex to the start of the T wave
- End of the S wave to the end of the T wave
- Start of the S wave to the beginning of the T wave
- End of the QRS complex to the end of the T wave
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
1 customer review without text
1 user review without text