Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
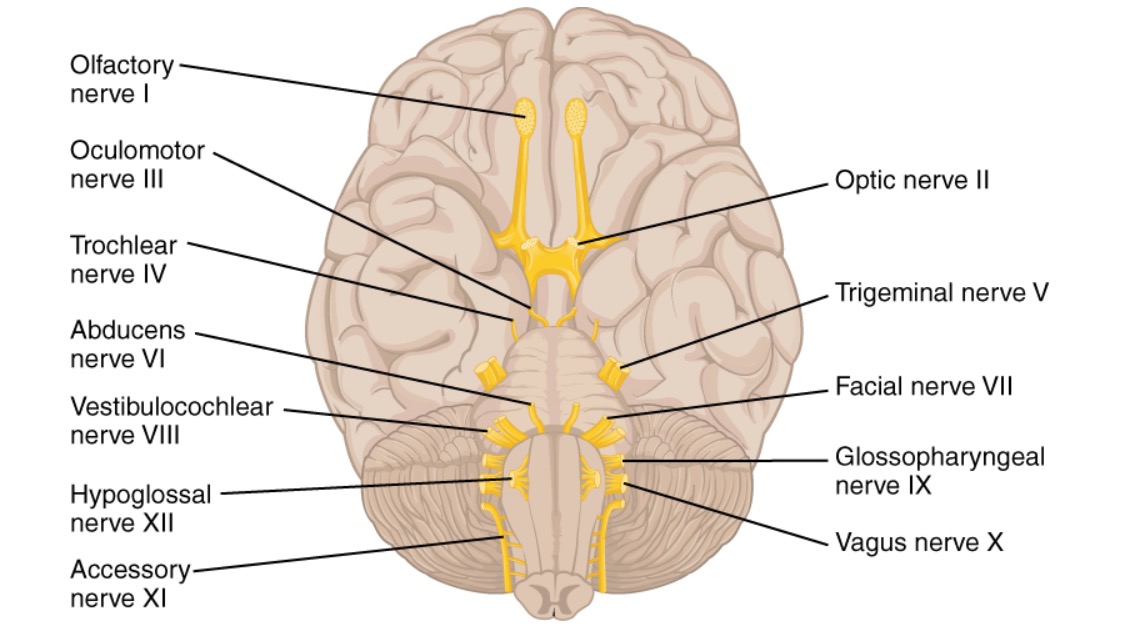
Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory Nerve
-
Slides 8 CranialNerves 2 BrainAndNervousSystem.pdf
-
Reference List Anatomy.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:00 The accessory nerve has one functional component. This is going to be general somatic efferent. 00:12 It is also transmitted through the jugular foramen. 00:20 With respect to somatic efferent or motor control, the accessory nerve innervates two muscles. 00:26 One is the sternocleidomastoid that is now highlighted in red. The second muscle innervated by the accessory nerve is the trapezius which is now highlighted in red. Clinical considerations for you to remember about the accessory nerve would be that injury to this nerve could result in shoulder pain. 00:53 Individual could have difficulty or impairment of abduction at the shoulder because the trapezius would be unable to rotate the glenoid cavity superiorly to promote abduction of the shoulder above the horizontal. 01:09 The last clinical consideration would be due to paralysis or paresis of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. 01:19 As a result, there could be weakness in the turning of the chin to the opposite side. Some causes of these clinical considerations would be penetrating or blunt injury to the distribution of the accessory nerve or a tumor could encroach upon that and cause a disruption of its ability to innervate the sternocleidomastoid or the trapezius or both.
About the Lecture
The lecture Cranial Nerve XI: Accessory Nerve by Craig Canby, PhD is from the course 12 Cranial Nerves and Their Functions.
Included Quiz Questions
Which condition would be caused by cranial nerve XI palsy?
- Impaired shoulder abduction above 90 degrees on the side of the lesion.
- Shoulder droop on the contralateral side of the lesion.
- Difficulty turning the head to the side of the lesion.
- Impaired adduction at shoulder level on the contralateral side of the lesion.
- Impaired adduction at shoulder level on the side of the lesion.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |