Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
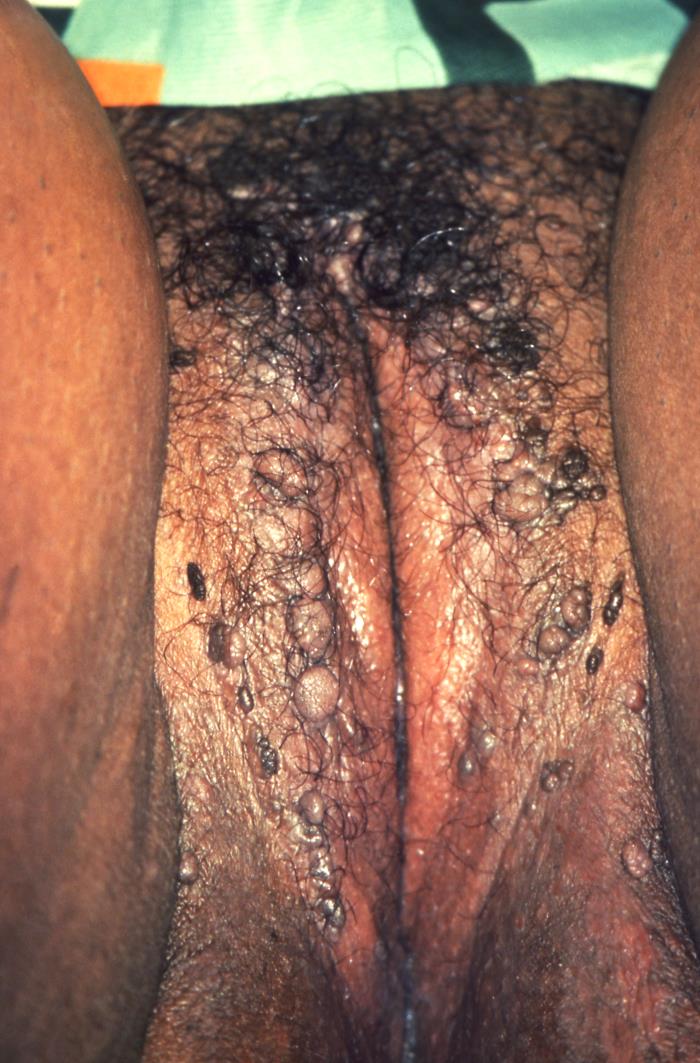
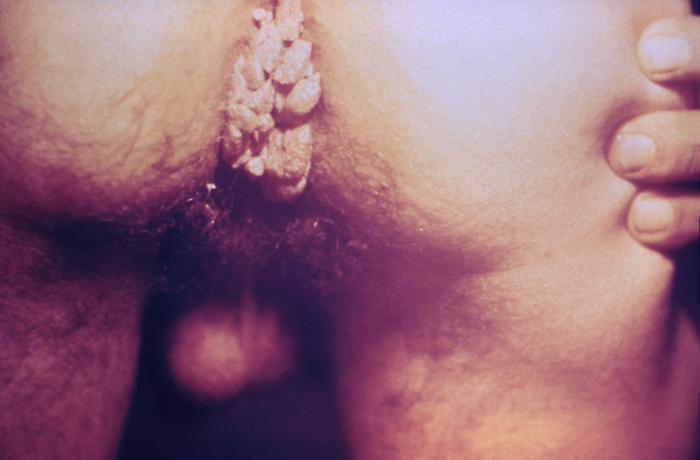
Condyloma Acuminatum
-
Slides Vulva Female Reproductive Pathology.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:01 Our topic here is still vulvar pathology. 00:04 I’ll tell you at some point when we actually leave this behind, but this is going to be an infection of the vulvar region. 00:11 This, obviously, is referring to what's known as your HPV. 00:15 And these would be the low-risk strains since we’re talking about wart. 00:16 since we’re talking about wart. 00:19 Now, the warts here are going to be quite obvious when you actually see it. 00:24 And the type of histologic picture that you’d find with HPV, and specifically, condyloma acuminata, is accumulation of koilocytes if that helps you. 00:36 The reason that I’m emphasizing or exaggerating such a pronunciation is because you cannot afford to get acuminata confused with condylomata lata. 00:46 Condylomata lata is found with syphilis. 00:50 This is condyloma acuminata or acuminatum, and you’re accumulating koilocytes if that helps you, HPV. 00:58 Branching, tree-like proliferation of stratified squamous epithelium supported by fibrous stroma is what we’re seeing here on this histologic picture. 01:09 There’s branching, tree-like proliferation of stratified squamous, underlying fibrosis. 01:15 There will be thickened epithelium with koilocytes. 01:19 Koilocytes are these cells that are appearing as being blank or pale or empty. 01:27 And then you find a peripherally located hyper-eosinophilic nucleus. 01:32 Nuclear atypia in surface cells with perinuclear vacuolization. 01:37 So there’s going to be a clear halo in which then the nucleus has been pushed out to the side, which will then appear as being darkened. 01:45 You’ve seen this in microbiology. 01:47 I just wish to reinforce something that you’ve seen already. 01:51 These would be the low-risk strains of HPV for warts, 6 and 11. 01:55 Please do not forget about condyloma acuminata with warts. 02:00 Now what you’re seeing here on gross examination is exactly what you’d expect with warts on your left. 02:05 There’s absolutely no way that you can miss this. 02:08 On the right, the condyloma acuminata, accumulation of koilocytes. 02:12 And the cell that you see there in the middle there are those clear vacuolizations or clear halo. 02:18 And the nucleus will then appear as being hyper-eosinophilic or a little bit darker. 02:24 These are koilocytes. 02:26 We should point out to you there will be another Paget's -- Excuse me. 02:29 another vulvar disease we’ll take a look at known as Paget’s disease of the vulva, and those cells will be quite different. 02:36 They will not have clear vacuoles. 02:38 It is important that you know the histologic pictures of some of these conditions.
About the Lecture
The lecture Condyloma Acuminatum by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Disorders of Vulva, Vagina and Cervix.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following histologic findings are seen with condyloma acuminatum?
- Thickened epithelium with koilocytes or nuclear atypia in surface cells with perinuclear vacuolization
- Flat cells with centrally located, spindle-shaped nuclei
- Round cells with centrally located nuclei
- Columnar cells in areas replacing squamous cells
- An increased number of squamous cells with hyperkeratosis
Which of the following virus types are associated with genital warts?
- HPV (human papillomavirus) types 6 and 11
- HSV (herpes simplex virus) types 1 and 2
- HPV (human papillomavirus) types 16 and 18
- HHV (Human herpesvirus) types 8 and 9
- HPV (human papillomavirus) types 31 and 45
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |