Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Group 5: Other Antiarrhythmics – Antiarrhythmic Drugs
-
Singh-Vaughan Williams classification.pdf
-
Slides Group 5 Other Antiarrhythmics Antiarrhythmic Drugs.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
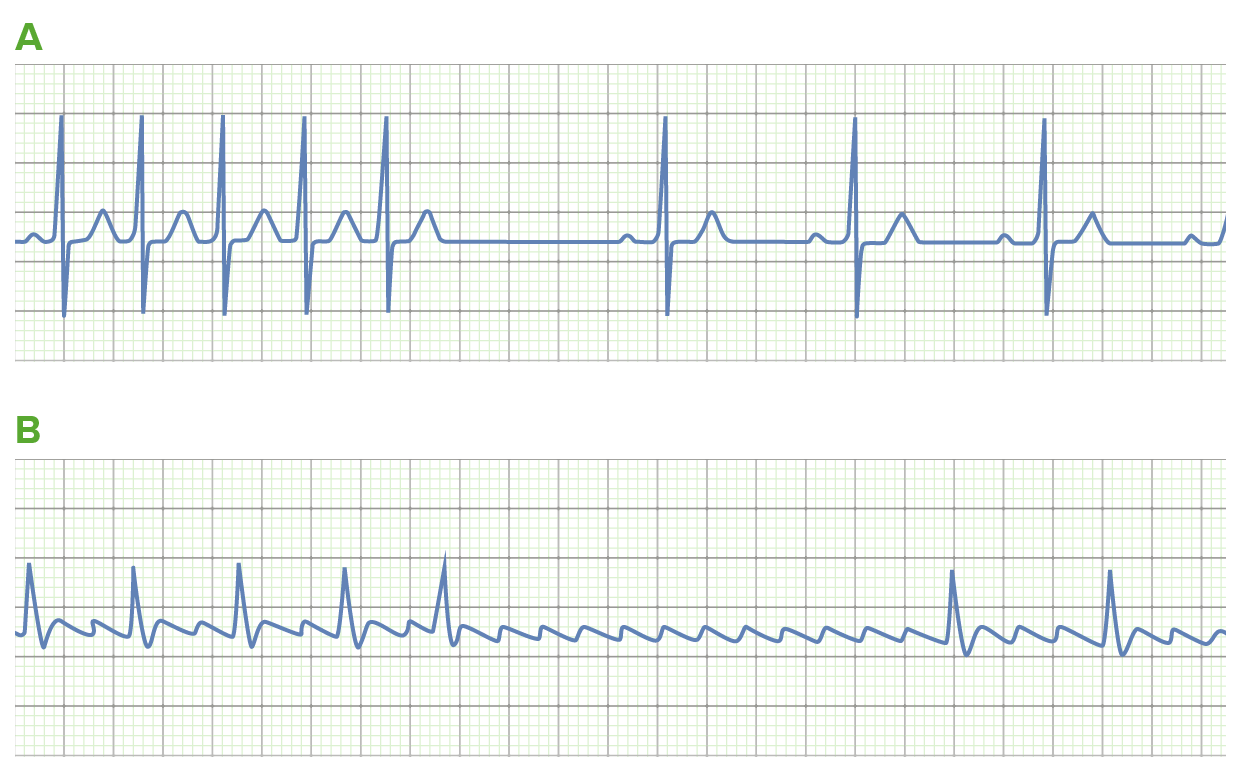
00:01 Let's talk about the group 5 drugs. Let's start with adenosine. So adenosine is actually an endogeneous compound. 00:09 We actually have adenosine in our bodies. Now adenosine acts on the purine receptor. It completely blocks conduction in the AV node. It causes quite significant membrane hyperpolarization and it increases the potassium current. 00:26 It is a very short duration of time. Now, when I say short duration I mean short duration. We think that it lasts in the blood for maybe 6 or 7 seconds because it's not broken down in the liver and it's not broken down in the kidney, it's actually broken down by red blood cells. Now one of the major side effects of using adenosine is chest pain. 00:50 When we are talking about adenosine, I do want to mention one thing. How you give this drug is really important. 00:57 And as you go on to your clerkship and work on code teams you have to know that adenosine has to be given IV push with a follow up. 01:06 So you take your adenosine syringe, you get it ready. When you are told to give it you give it and you push it hard as you can into the IV line. Then you take a saline flush and you flush it after that. You need to get that drug into the heart as quickly as possible because it has such a short duration of action. The other thing I am going to warn you about is that the patients will complain of chest pain like you've never seen. So the first time I ever gave adenosine as a medical student. I push this adenosine, the patient had a supraventricular tachycardia with a heart rate of around 175 and the monitor went flat for about 6 seconds. And I tell you, if you are standing there as a medical student, and you cause a flat line on a patient, the patient is looking at you, the nurses think you killed the patient, and you are standing there as the only person and then all of a sudden the patient starts to complain of severe chest pain. 02:02 This is chest pain like no other, it's the wrath of God kind of chest pain that these patients complain about and then the heart rate comes back. And then it comes back very slowly. That's what it's like giving this drug but you can save lives because it's very effective. Let's move on to magnesium. Magnesium, obviously you know it's a divalent cation, but it actually is great at depressing ectopic pacemakers. And it is the drug of choice for a rhythm called torsades de pointes. 02:39 And i'll explain torsades de pointes later. Potassium is actually an antiarrhythmic too. It also will depress ectopic pacemakers but it also can be proarrhythmic. It can also cause a reentry arrhythmia. In fact the KGB used to use potassium to kill people that they just didn't like and it was a very easy way to get rid of patients or enemies of the state without actually having any kind of identifiable problem when they do autopsies. So potassium kills and in fact it's now a restricted drug, or vial of liquid I suppose you could call it, in most intensive care units. 03:19 Always measure your potassium levels because each class of these drugs, whether it's class I or class III are kind of dependant upon the potassium level and having altered potassium levels can actually induce more arrhythmia in conjunction with some of these medications.
About the Lecture
The lecture Group 5: Other Antiarrhythmics – Antiarrhythmic Drugs by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Cardiovascular Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which statement best describes the antiarrhythmic action of adenosine?
- Blocks conduction time through the AV node, interrupting the reentry pathways through the AV node.
- Increases conduction through the AV node, interrupting the reentry pathways through the AV node.
- Slows conduction time through the SA node, interrupting the re-entry pathways through the SA node.
- Increases conduction through the SA node, interrupting the re-entry pathways through the SA node.
- Increases conduction through the SA node, interrupting the reentry pathways through the AV node.
Magnesium has an antiarrhythmic effect because it...?
- ,,,depresses ectopic pacemakers.
- ...increases the heart rate.
- ...reduces potassium levels in the heart.
- ...enhances the fast sodium current.
- ...induces calcium accumulation in cardiac cells.
What is the first line of treatment in a conscious patient with recurrent episodes of torsades de pointes?
- Magnesium sulfate
- Procainamide
- Verapamil
- Amiodarone
- Esmolol
What is the most appropriate step in the management of a patient who has a flat line on the ECG monitor immediately following the administration of adenosine?
- Close observation
- Intravenous atropine
- Cardiac defibrillation
- Chest compression
- Temporary pacemaker
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
LOL That adenosine mental image will NEVER leave me ajajajajajaja
1 customer review without text
1 user review without text