Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Group 4: Calcium Channel Blockers – Antiarrhythmic Drugs
-
Slides Cardiovascular drugs – Antiarrhythmics.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
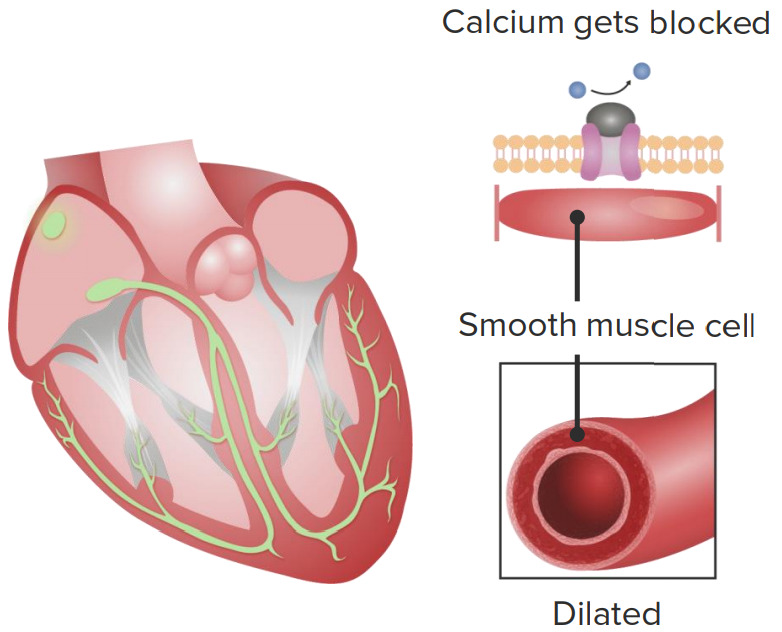
00:01 Let's move on to the group 4 antiarrhythmic drugs. These are the calcium channel blocker drugs. Now I've discussed them multiple times in our angina lecture, in our heart failure lecture, and in our hypertension lecture. 00:14 Let's talk about these drugs as they act on the AV node. Now we are going to be focusing only on verapamil and diltiazem because if you remember the other type of calcium channel blockers like nifedipine, don't really act on the heart. 00:29 These drugs act on the heart. I also want to mention too that verapamil is more cardiac active than diltiazem. 00:37 So you can think of verapamil as being a cardiac drug, diltiazem being more of a mixture of cardiac and vascular, and drugs like nifedipine being vascular drugs. Let's move on to AV nodal arrhythmia. So take a look at that action potential. 00:53 How is it different to you? Well, remember that these drugs are state and use dependant. So if you are using the calcium current a lot, for example if you have fast heart rate, then you are going to have more response to these drugs. 01:10 The AV conduction velocity is decreased. Do you remember what that is called? That's called dromotropy. The PR and ERP are increased. PR means PR interval, the space between the P wave and the R wave of the QRS complex. And the ERP is the effective refractory period. Now, nifedipine and amlodipine are not good antiarrhythmics. The other thing that happens with nifedipine and amlodipine, which are not antiarrhythmic drugs, is they cause a reflex sympathetic discharge, what we call reflex tachycardia. So these drugs should not ever be thought of as group 4 antiarrhythmics like the other calcium channel blockers, you have to think of them as just hypertension drugs and they can actually induce tachycardia because of their reflex action.
About the Lecture
The lecture Group 4: Calcium Channel Blockers – Antiarrhythmic Drugs by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Cardiovascular Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which statement regarding class 4 anti-arrhythmic agents is most accurate?
- It includes calcium channel blockers verapamil and diltiazem.
- It includes calcium channel blockers nifedipine and amlodipine.
- It includes beta-blockers esmolol and bisoprolol.
- It includes beta blocker-like agents amiodarone and sotalol.
- It includes sodium channel blockers, mexiletine, and procainamide.
Which medication is most likely to cause an unwanted increase in heart rate?
- Amlodipine
- Verapamil
- Esmolol
- Amiodarone
- Metoprolol
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |