Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Systole and Diastole – Cardiac Cycle
-
Slides CardiacCycle CardiacPhysiology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
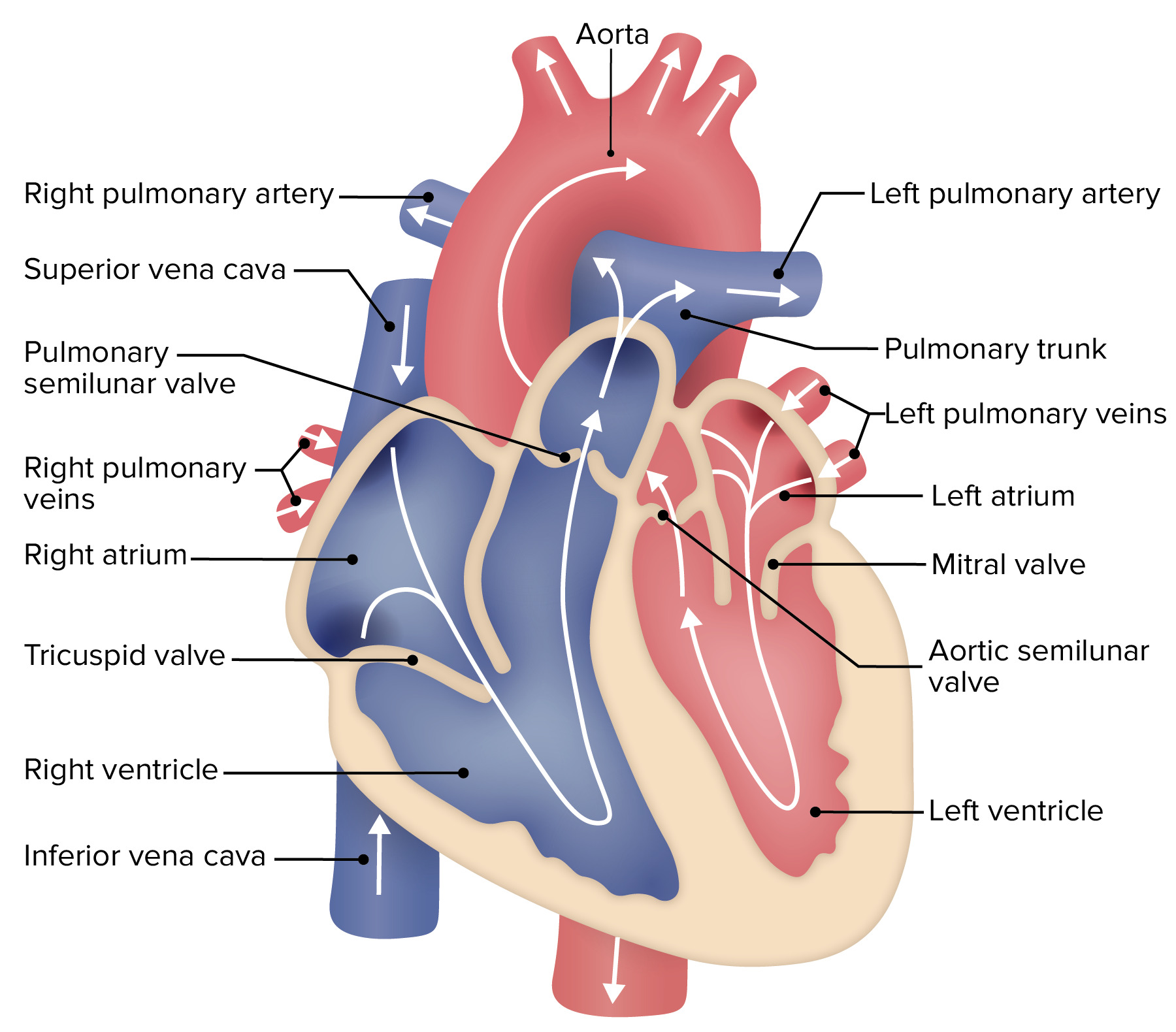
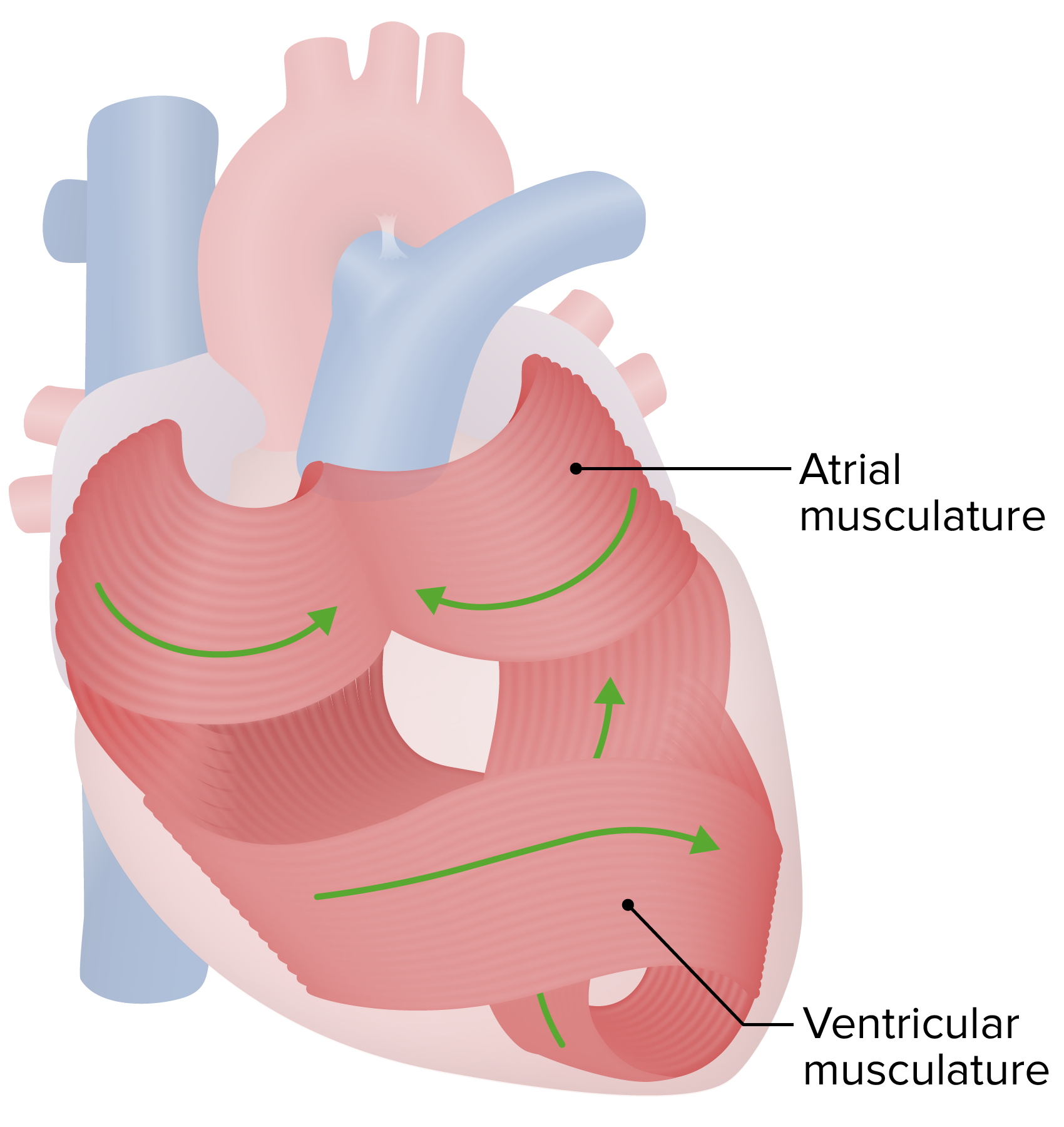
00:02 The cardiac cycle. 00:04 Here in the cardiac cycle, we need to break it down into its two most basic forms – that is systole and diastole. 00:13 So, in terms of systole, what really are we talking about? We’re talking about what's occurring with ventricular contraction. 00:20 So, contraction is one of the biggest components of systole. 00:25 Interestingly, though, also, is the ejection of blood comes along with contraction. 00:31 So, the majority of the time, during the ejection phase of the blood, there will be within systole. 00:40 However, a little bit of it translates over into diastole. 00:46 There is a relaxation phase that transitions between systole and diastole. 00:52 So, what do I mean by relaxation? It is the muscles themselves – cardiac muscle – that is relaxing. 01:00 So, it's interesting to think about, even when the muscle is relaxing a little bit, you still could be in systole, i.e. pushing blood out because blood being pushed out of the left ventricle is simply a matter of the pressure differential. 01:16 The other times in which you are in diastole are during the filling phases. 01:21 And you notice we have some numbers attached to things like ejection and filling. 01:27 That is because there's a rapid and a reduced ejection and a rapid and a reduced filling. 01:35 So, all of those kind of items come out when we look at the cardiac cycle.
About the Lecture
The lecture Systole and Diastole – Cardiac Cycle by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Cardiac Physiology.
Included Quiz Questions
What is present in both systole and diastole?
- Active relaxation
- Ventricular filling
- Ventricular ejection
- Active contraction
- Ventricular ejection & active contraction
Which of the following is TRUE regarding the cardiac cycle?
- Systole is the contraction phase and diastole is the relaxation phase.
- Diastole is the contraction phase and systole is the relaxation phase.
- Both the contraction and relaxation phases are termed diastole.
- Systole is exclusively the contraction of the atria.
- Both the contraction and relaxation phases are termed systole.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
excellent clear description told easily thanks so much understand a lot more now