Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Cannabinoids: THC and CBD – Drugs of Abuse
-
Slides Cannabinoids THC CBD.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
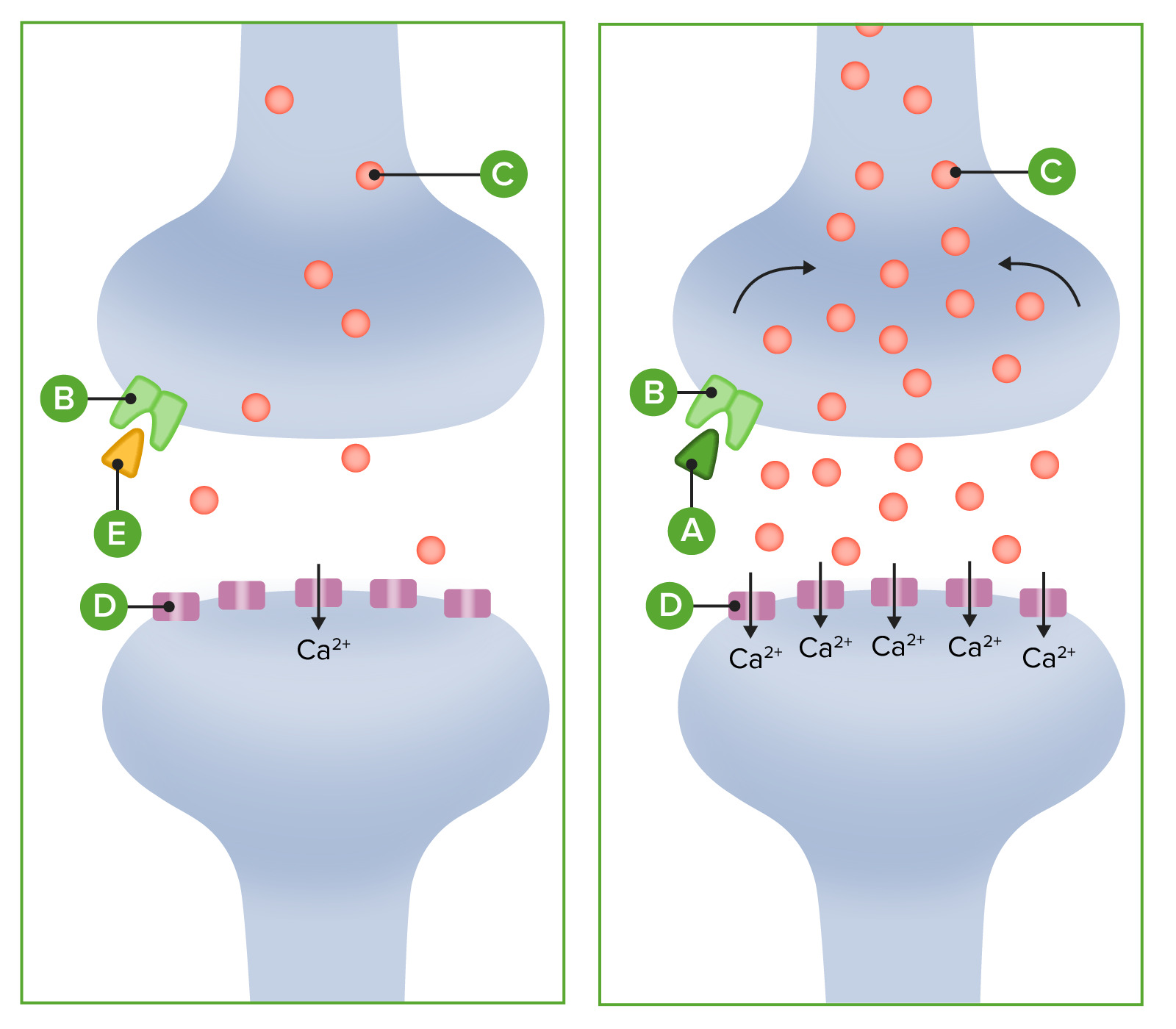
00:19 Marijuana smoke contains some of the same carcinogens as cigarette smoke, but the overall cancer risk may vary depending on factors like frequency of use and inhalation patterns. 00:29 There are 83 to 85 different cannabinoids in one joint. 00:36 So try doing a study with 85 drugs, it's almost impossible. 00:40 Now in terms of those cannabinoids, let's go through some of them. 00:44 Here's a partial list of the cannabinoids that are present in a joint. 00:47 Let's start off with THCA and THC. THCA is the terpene that is carboxylated. 00:55 And if you decarboxylate it, you'll get the active form which is THC which stands for tetrahydrocannabinol. 01:02 Now this particular product is considered to be the primary psychoactive agent in a joint. 01:09 Here's the structure of it and you can see that it has a structure that's quite similar to a lot of androgynous products in the human body. 01:18 Now, prenatal cannabis exposure causes impaired neurodevelopment and neurocognitive function in those children. 01:28 It also is associated with increased numbers of neuropsychiatric disorders. 01:33 So certainly, prenatal exposure in pregnant woman - sorry, from pregnant mothers, can cause significant long-term disabilities in those patients. 01:43 The primary port of entry or port of activity of the THC is the CB1 receptor. 01:50 The CB1 receptor induces anandamine and arachidonoylglycerol synthesis. 01:56 So what this does is it works through a G-protein. 01:59 Now the G-A-I protein is the most commonly expressed Gai protein in the brain so that the cannabinoid system and the Gai proteins associated with it are very, very commonly seen in the brain, they're almost a ubiquitous thing. 02:15 This causes depolarization, induced suppression of inhibition, it's a double negative. 02:23 Normally, you'd have an inhibition so it causes suppression of that inhibition, right, which is a retrograde signaling process which results in a reduction of GABA-mediated neurotransmitter so you have reduced calcium ion entry. 02:37 Now what that essentially does is it causes a suppression in most cerebral activities and it causes an increase in confusion. 02:46 It's found also in the liver, it's also found in other areas in the body. 02:50 In the liver, it can cause a increase in lipogenesis. 02:56 Now what happens if the THC is consumed in a tincture? So remember in - earlier in the lecture, I was kind of mixing up the words THC and TCH. 03:07 And here's why. If you have THC in the tincture, the Delta THC is transformed into 11-hydroxy TCH. 03:17 So it's a slightly different compound because of alcohol. 03:20 It will take 1 to 3 hours longer to metabolize. 03:24 The onset of hours is roughly 2 hours later and the TCH is 4 to 5 times stronger. 03:32 Now, the other thing that's going to change in the tincture is that the CBD portion is 33% effective, so there's a real change in the way that this product is working. 03:44 The next in the series of cannabinoids that I wanna talk about is CBD and CBDA. 03:49 Now, CBDA is the terpene associated with CBD. You have to de-carboxylate CBDA in order to get CBD. 03:59 CBD is the most commonly used of the products within the cannabinoid family. 04:03 It's something that is being used by the cancer and chronic pain patients for pain control and it is sometimes used for nausea control. 04:11 In general, when persons are being given medicinal cannabinoids, we are giving it to try and enhance the effects of CBD and minimize the effects of the THC. 04:21 Now, the cannabinoids are very popular in the epilepsy area. 04:27 And in fact, one of the most commonly used drugs in the CBD family was Epidiolex. 04:33 Epidiolex was actually used in the treatment of epilepsy and it was relatively effective. 04:40 In fact it was a very promising drug I would say. 04:42 Side effects include somnolence, decreased appetite, surprisingly; diarrhea, fatigue, malaise and some sleep disturbance. 04:51 Other side effects included a little bit of decreased mental acuity later on in the studies. 04:57 Now, it was also used for certain types of diseases like Lenno-Gastraut syndrome and Dravet syndrome. 05:05 Another agent that came out was Sativex which contains both CBD and THC. 05:11 It was used in central neuropathic pain in patients with - who were suffering from multiple sclerosis. 05:17 It was used in cancer related pain and it was also used to treat spasticity in patients who had multiple sclerosis; quite effectively I might add. 05:26 The pharmacology behind these products and CBD in particular, they are indirect antagonists of CB1 and CB2 receptors. 05:36 They are a GPR55 antagonists. 05:40 They are expressed in the caudate nucleus of the brain and they're also expressed not surprisingly in the putamen. 05:46 Now, most drugs that are working on the caudate nucleus are also gonna work in the putamen so that doesn't surprise us too much. 05:52 So I wouldn't consider it a wide-ranging or ubiquitous area of action. 05:58 It also works on serotonin 1A receptors. It is a partial agonist of that receptor, so it gives you some antidepressant effects. 06:06 It gives you some and seal the effects and it comes - gives you some neuroprotective effects. 06:12 The pharmacology in the opioid receptor area is complicated. 06:17 It is a u-opioid, k-opioid and a δ-opioid allosteric modulator of those receptors. 06:24 It also works on PPAR-gamma protein to cause agonism. 06:29 And finally, it works on intracellular calcium release. 06:34 There is some inhibition of the fatty acid amide hydrolase or FAHH enzyme in the body. 06:41 The metabolism is through Cytochrome 2C19 and cytochrome 3A4. 06:46 So, we are concerned about this as you are probably aware because any drug that goes through 3A4 may have an interaction with other agents including, say the antifungal's or some of the statins. 06:58 The pharmacological profile of cannabis oils can vary due to differences in cannabinoid content, terpene profiles, and production methods. 07:07 This variability presents challenges for dosing and predicting effects, highlighting the importance of standardized products in medical applications. 07:15 Studies have shown that cannabis use can affect cognitive processing speed and reaction time. 07:20 These effects can be more pronounced with higher THC content and may persist for hours after use, which is particularly relevant in medical settings. 07:31 The effects of CBD oil and other cannabis products can vary due to factors such as differences in product composition, individual metabolism, and dosage. 07:40 This variability underscores the need for standardization in production and more controlled clinical studies. 07:46 Long-term cannabis use may have effects on cognitive function, but the extent and reversibility of these effects can vary. 07:54 Some studies have shown changes in memory, attention, and executive function with prolonged use, particularly when use begins in adolescence. 08:03 The efficacy of cannabinoids, including CBD oil, varies depending on the condition being treated. 08:07 While some studies have shown promising results for conditions like epilepsy and chronic pain, more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness compared to traditional medications for many conditions. 08:21 Another cannabinoid that we see is CBN. CBN is a non-psychoactive compound within the family. 08:28 It is found in aged cannabis and in oxidized liquid forms. 08:33 So if the oil for example has been oxidized, you'll see more CBN. 08:38 It's a partial agonist of the CB1 receptor. It's a selective agonist of the CB2 receptor. 08:44 And can be a metabolite of THC. 08:48 It is not listed as a scheduled product, but it may be used as an analog of THCs, so we're not sure where this is gonna fall in the armamentarium. 08:58 CBG is another cannabinoid that we see in the - in a joint for example. 09:04 It is a metabolic precursor of THC. It has strong Alpha-adrenergic agonist activity so it works in the sympathetic nervous system. 09:14 It is a moderate serotonin agonist and it is a low affinity CB1 antagonists. 09:21 So, very complicated mechanisms of actions, we don't really know what that is going to mean for patients. Another cannabinoid is THCV. 09:31 It is, again a non-psychoactive agent. It's found in aged cannabis, outdated or oxidized liquid forms. 09:38 It's a partial agonist of the CB1 and CB2 receptors. 09:42 It's actually more selective in CB2. It can be a metabolite of THC so that's kind of interesting. And it's not listed as a scheduled product, but it may be listed as an analog of THC in some countries.
About the Lecture
The lecture Cannabinoids: THC and CBD – Drugs of Abuse by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Toxicology.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the primary psychoactive agent in a cannabis joint?
- Tetrahydrocannabinol
- Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid
- Cannabidiol
- Cannabidiolic acid
- Cannabinol
What is the main active metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)?
- 11-hydroxy-THC
- Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid
- Cannabidiolic acid
- Cannabidiol
- Cannabinol
What best describes the general medicinal use of cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in cannabis drugs?
- Enhanced CBD effect, reduced THC effect
- Enhanced THC effect, reduced CBD effect
- Enhanced CBD and THC effect
- Reduced THC and CBD effect
- No difference in CBD or THC effect
What is an FDA-approved treatment for seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome?
- Epidiolex
- Sativex
- Tetrahydrocannabinol
- Cannabidiolic acid
- Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid
What is one of the main enzymes involved in the metabolism of cannabidiol?
- CYP3A4
- UDP-glucuronyl transferase
- Glutathione S-transferase
- Cytochrome b5
- CYP1A1
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |