Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
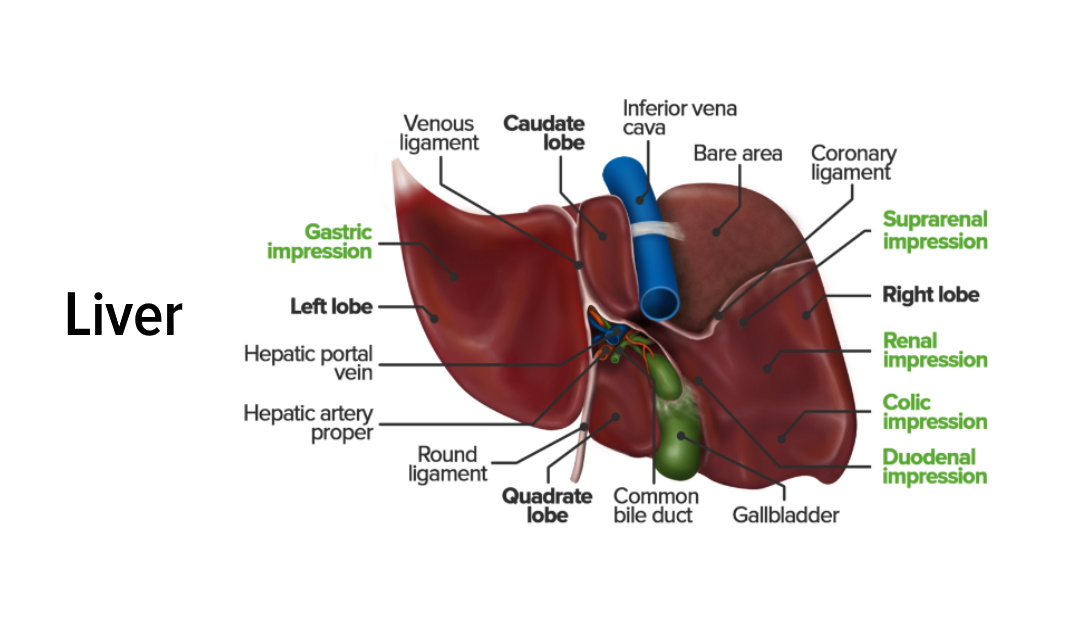
Alcoholic Liver Disease
-
Slides GD liver disease.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
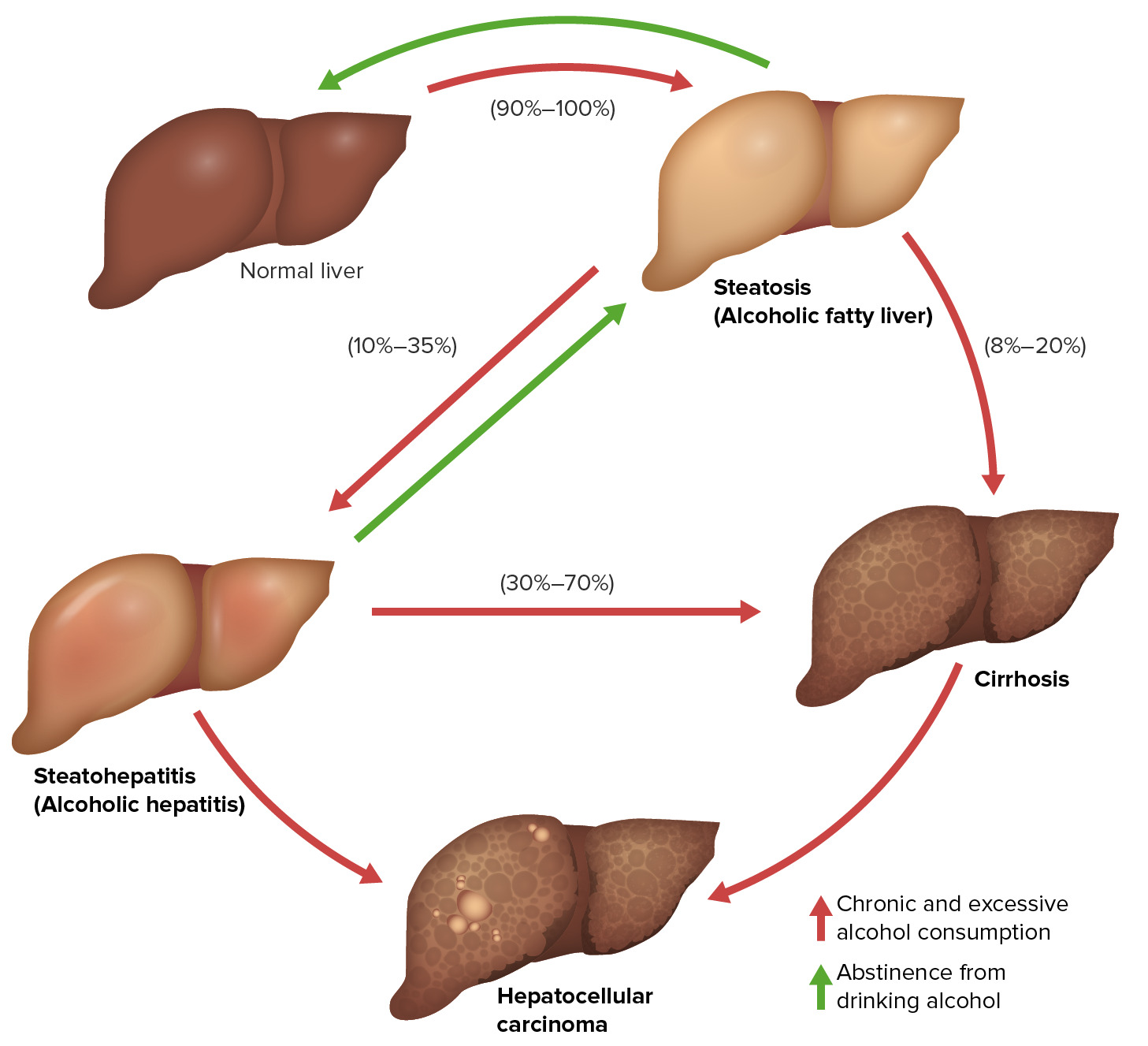
00:01 Alcoholic Liver Disease Yet, another cause of Hepatitis. 00:08 good at some point in time. 00:10 Now, with that said, a little bit of biochemistry and basics Also, what may then happen in end-stage. 00:20 Alcoholic Liver Disease, you have a patient that’s drinking beer, how much? Well, for a female, greater than 20 g per day for a woman. 00:28 Whereas for men, greater than 40 g per day. 00:30 Because of the increase amount of metabolism that males have inherently. 00:37 Long-term excessive use can cause a range of Alcoholic Liver Disease. 00:44 What I'm trying to say is this: You can have a patient who has been drinking and most of us will then cause fatty change or we call this Hepatic Steatosis. 00:57 But you could have patients that drink alcohol, Instead of having fatty change which is reversible, there is a possibility that it might go into what is known as Alcoholic Hepatitis. 01:09 So, from henceforth, when you're dealing with Alcoholic Liver Disease you can divide this into three major diseases. 01:17 and it doesn't even have to follow in steps. 01:21 You don't have to go from fatty change to Alcoholic Hepatitis to Cirrhosis. 01:25 You don't have to go from fatty change to Alcoholic Hepatitis the Cirrhosis You can have a patient who is drinking and go straight into Alcoholic Hepatitis; You've heard of Mallory bodies. 01:37 Or you can go directly into Cirrhosis, worst-case scenario. 01:42 Make sure you understand as to how much alcohol is excessive. 01:46 Risk factors. As we said earlier, A female unfortunately, would have decreased equipment to metabolize the alcohol effectively. 01:54 Therefore, she might be at risk for alcoholic liver disease. 01:57 Malnutrition, underlying viral hepatitis. 02:02 Remember, the if you have a patient of viral hepatitis in this then to you an increase in ALT and this patient, remember, a patient who has hepatitis C, who has chronic hepatitis, most likely, asymptomatic on top of that, and starts drinking, will only exacerbate the disease further. 02:21 Risk factors are important for you to understand. 02:25 Alcoholic Liver Disease. 02:27 The types and the syndromes that we will take a look at. 02:31 What I am not be covering here in great detail which we did in basics, is the accumulation of triglycerides in your liver and it's called your fatty change, you call that Hepatic Steatosis. 02:42 I'll go straight into your clinical syndromes for Alcoholic Liver Disease. 02:46 I will talk about Alcoholic Hepatitis. and I will talk about Alcoholic Cirrhosis. 02:50 Is that clear? Under biochemistry, extremely important that you know about proper alcohol metabolism and enzymes and their genetics. 03:00 For example, the first enzyme that is required for proper alcohol metabolism if you remember correctly, It's called Alcohol Dehydrogenase. 03:08 The second enzyme that you absolutely must know from even pharmacology management is then called Aldehyde Dehydrogenase, right? What’s the drug that I am referring to that inhibits Aldehyde Dehydrogenase- disulfiram. 03:22 Another topic. 03:24 A different subject. 03:25 Here, under pathology, I will walk you through the clinical syndrome of Hepatitis of Alcohol, and Cirrhosis caused by alcohol.
About the Lecture
The lecture Alcoholic Liver Disease by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Liver Diseases: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
How much alcohol can cause alcohol-induced liver damage if consumed over many years?
- More than 20 g/day for women and more than 40 g/day for men
- More than 40 g/day for women and more than 20 g/day for men
- More than 30 g/day for women and more than 50 g/day for men
- More than 50 g/day for women and more than 30 g/day for men
- More than 40 g/day for women and more than 40 g/day for men
Which of the following enzymes is involved in the metabolism of alcohol?
- Aldehyde dehydrogenase
- Acetaldehyde fumarase
- Acetaldehyde decarboxylase
- Acetaldehyde oxidase
- Alcohol decarboxylase
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |