Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Alcoholic Hepatitis
-
Slides GD liver disease.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
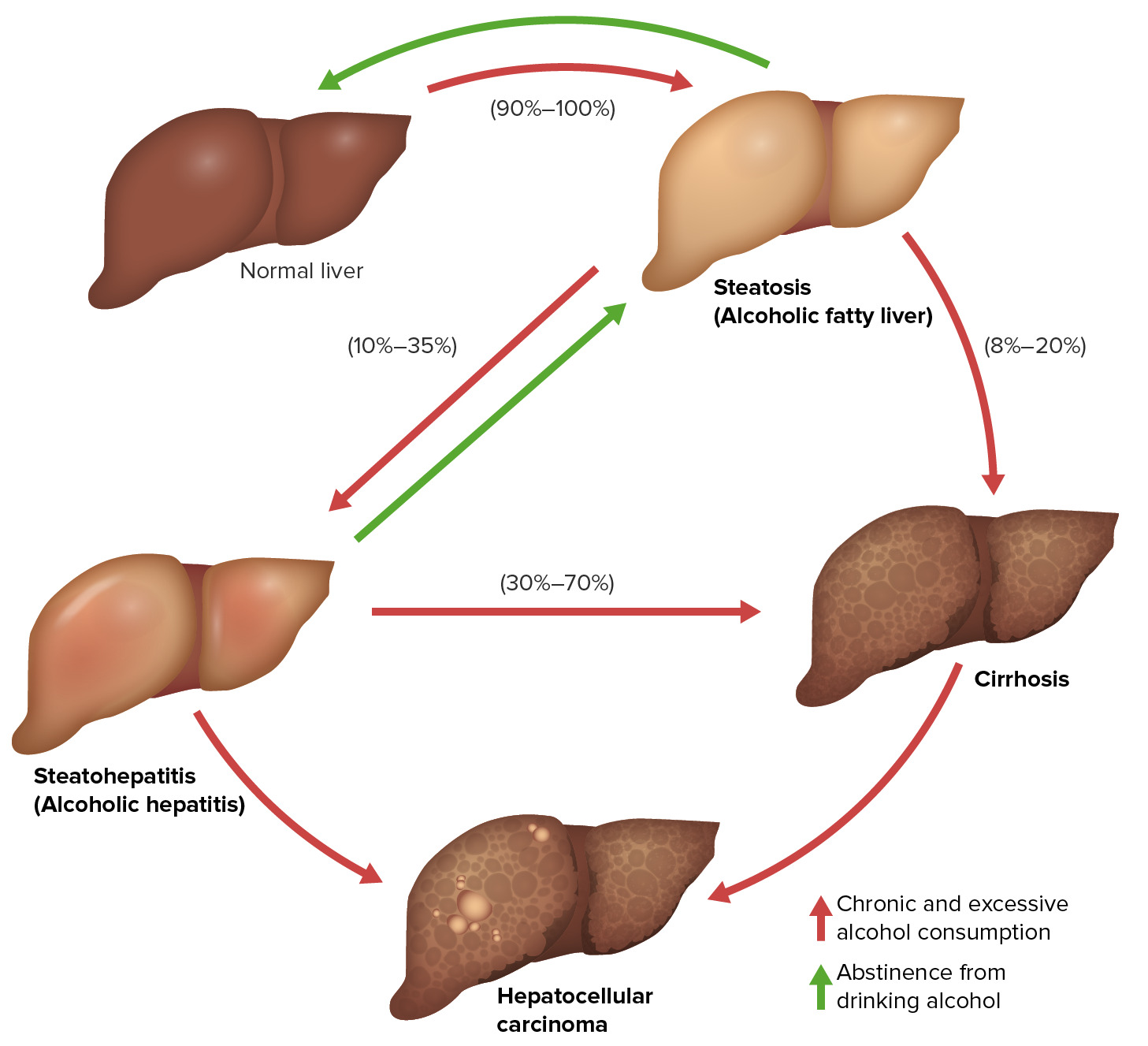
00:01 Alcoholic Hepatitis. 00:04 Signs and symptoms include, fever, weight loss. 00:07 Anorexia and abdominal pain. 00:10 Jaundice ascites and hepatosplenomegaly Worst case scenario, once the liver starts undergoing dysfunction, Now, you lose the ability to properly metabolize your ammonia, huh? And where is this Ammonia headed to? Brain. 00:26 What do we call this? What am I doing? I like Youtube but I'm not waving at you, I can't help it. 00:31 This is resting, flapping tremors. 00:34 This is a sign for Hepatic Encephalopathy. What with this that I just did. 00:40 Asterixis. 00:42 Also, bladder gland enlargement may be associated. 00:47 The diagnosis here, you will be using your transaminases to your advantage. 00:52 I'm going to give a little bit more information so that you can get your question right as well. 00:56 First, What is a Keutlopneumonic that I've heard. 01:00 As you know, I'm not a huge pneumonic man. 01:02 I mean strategically, sometimes it can be fun. 01:05 But much of this information is so that you can really excel on your exam is by understanding the material. 01:11 But you toast to alcohol. 01:14 AST 2:1 ratio. 01:17 So, you're reading the stem, you're reading the case, and you find your AST to be 300, and you find your ALT to be 150, do not waste time clicking on a button. Going through the plethora the milleu of all those labs when you know that 300 and 150 are at a 2:1 ratio. 01:38 Right? Most likely, your patient is suffering from Alcholohol Hepatitis. 01:43 Next, what else may happen? Fever, huh? Leukocytosisitis. 01:49 What does "itis" mean? Inflammation. 01:51 Anytime there is inflammation, no doubt you have a fever. 01:55 and most likely would have some type of Leukocytosis and increase on WBC count. 02:01 Don't focus upon that. That the one thing it will give you mabye they'll give yout the AST/ALT ratio. Almost always will. 02:09 And once your liver starts being injured, Woudl you tell me what are the two other functional tests or two important liver function tests that will assess the functionality of your liver. 02:25 Here is one of them, PT. 02:27 So, PT which is normally should be from 11 to 15 seconds. 02:32 It starts getting prolonged. Why? The liver is being damaged. 02:38 And what about the bilirubin? Mixed picture. 02:41 What do I mean by mixed? By that we mean, if the enzyme is being damaged in the liver, what can hyperbilirubin anemia please? unconjugated hyperbilirubin anemia. 02:52 What if the export mechanism is affected with Alchoholic Hepatitis, you don't have a problem with enzyme per se. 03:00 Then you would have, conjugated or direct hyperbilirubin anemia. 03:05 Mixed picture. 03:07 Pay attention to your mixed picture and what kind of damage is taking place within your liver. 03:14 Biopsy. 03:15 What is these Mallory bodies that you want to know? The Mallory body is an intermediate set of keratin filament remember? In basis sciences, we talked about in basics, how you can accumulate certain things in organs. 03:31 This is not triglyceride. 03:33 I told you, I am not going to cover the biochemistry of Hepaticsteatosis. 03:39 There you accumulate triglycerides. 03:42 Here, specifically under Hepatitis, caused by alcohol, you're going to find Mallory bodies. 03:49 And in our discussion, it is important that you know the Mallory body, and I even showed you a picture. 03:55 These are intermediate Cytokeratin filaments. At least take the operative word Cytokeratin, cytokeratin, cytokeratin. 04:02 Next. 04:04 We have neutrophilic infiltration with a background of... 04:08 there could be a little bit of fibrosis taking place. 04:11 So you might have a cirrhotic type of picture just a little bit in the background. 04:16 Remember, what does Cirrhosis mean to you? Fibrosis. 04:19 Anytime that you have injury to any organ, of course, Fibrosis is going to be involved. Almost, always. 04:28 Except for the brain, right? Except for the brain. 04:34 Continuing forward. Discriminate function. 04:37 Something called the Maddery score. 04:40 You want to keep this in mind. More so for for step2 CK. 04:43 and what you are doing here is your taking a look at the PT. 04:47 I'm not going to walk you thorugh this too much but you do have formula there. 04:50 Plus your bilirubin. 04:52 At least know the term: Maddery score for Alchoholic Hepatitis. 04:56 And because you expect your PT to be prolonged, and maybe bilirubin to be elevated, understand the concept first, ok. 05:05 Then if you want to come back and memorize the formula, you do that later, not now. 05:09 Understand the concept first. 05:11 The concept is: Prolonged PT because of liver damage and your bilirubin will be elevated. 05:17 If you find your score to be increased, Used to determine the need for steroid therapy. 05:22 is the clinical application of a concept that you've learned and or continue to learn. 05:30 Corticosteroids improve short term mortality, anti-inflammatory. 05:35 And we have something called Pentoxyfylline decreases incidence of a very important topic that we'll cover later. 05:42 And I have specifically extracted HRS which stands for Hepatorenal Syndrome. 05:50 as a separate topic. 05:51 Because students always seem to get that confused and you can't afford to do that. 05:56 Point is, here is the drug to decrease the incidence of it. 06:01 Adequate nutrition is critical. Remember, if the liver is damaged, my goodness! You end up causing all kinds of issues especially, glycemic control and company. 06:12 Abstinence is crucial. 06:14 Why, why, why? If abstinence is not exercised very patiently, there's every possibility that he or she is going into end-stage liver disease. 06:26 Easier said than done though, huh?
About the Lecture
The lecture Alcoholic Hepatitis by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Liver Diseases: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
The accumulation of which cellular structure leads to the formation of Mallory bodies?
- Intermediate cytokeratin filaments
- Mitochondria
- Lysosomes
- Golgi apparatus
- Ribosomes
Which of the following is NOT a histopathological feature of alcoholic hepatitis?
- Extrahepatic cholestasis
- Mallory-Denk bodies
- Steatosis
- Neutrophilic infiltrate
- Few fibrotic bands
What affects the brain in hepatic encephalopathy?
- Ammonia
- Nitrogen
- Urea
- Creatinine
- Oxygen
A patient is diagnosed with alcoholic steatohepatitis. What bilirubin levels are expected in this patient?
- Mixed hyperbilirubinemia
- Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia
- Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
- Delta hyperbilirubinemia
- No hyperbilirubinemia
What components are considered in the Maddrey score?
- PT and bilirubin levels
- APTT and bilirubin levels
- AST/ALT ratio and PT
- Transaminase levels and bilirubin levels
- Serum albumin and PT
What is the purpose of calculating the Maddrey score in patients with alcoholic hepatitis?
- It helps determine the need for steroid therapy.
- It helps assess the response of steroid therapy.
- It helps assess the liver functionality.
- It helps assess the duration of steroid therapy.
- It can determine the chance of the patient developing malignancy.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Clear explanation and differentiation. Eliminates confusion and is concise but complete