Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Acute Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Etiology
-
Slides OtitisMedia InfectiousDiseases.pdf
-
Reference List Infectious Diseases.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
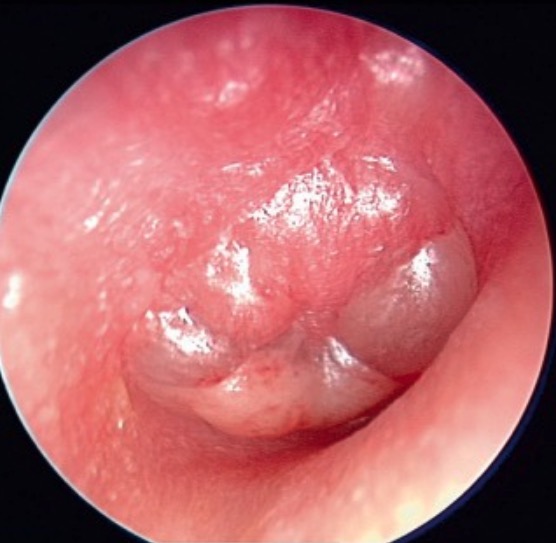
00:02 So when you’re talking about acute bacterial otitis media, this is the order of the most common causes. 00:12 Number one is Streptococcus pneumoniae. 00:16 Number two is Haemophilus influenzae. 00:20 Now remember, in developing countries, most babies get immunized against H. influenzae type B. 00:26 We don’t see that as much anymore in developed countries, but in developing countries we do see H. influenzae B and a lot of the complications, which include meningitis. 00:40 Many of the time, we don’t know what’s caused the problem. 00:44 The cultures are negative or we grow something that’s not normally pathogenic. 00:50 Moraxella is a definite cause of acute otitis media in children, but generally, it’s milder than that caused by the pneumococcus. 01:02 Strep pyogenes, group A strep, was once common. 01:06 Now, it’s uncommon. 01:08 Staph aureus is an uncommon cause of acute otitis media, except when we have to employ tympanostomy tubes because of frequent recurrences. 01:23 And there are miscellaneous causes. 01:28 So here are some of the miscellaneous causes. 01:31 Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Chlamydophila trachomatis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae in developing countries. 01:43 Every once in a while you will encounter a patient with otitis media due to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 01:51 This is usually chronic, not acute. 01:55 Mycobacterium chelonae, which is a soilborne mycobacterium, very, very unusual. 02:02 And of interest, some worms can even cause otitis media. 02:09 The most strange example I ever heard of that was a patient who had Ascaris lumbricoides. 02:18 Now, Ascaris worms are about the size of earthworms. 02:24 And this patient had a large Ascaris worm find its way up into the Eustachian tube, perforate the tympanic membrane from the inside, and the patient actually pulled the worm out of the external auditory canal. 02:48 And then the disease Granulomatosis with polyangiitis, which often causes disease in the lungs and kidneys, as well, has been a cause of otitis media, and this would be one of the reasons perhaps an adult could be diagnosed. 03:08 I’m not saying that a normal adult couldn’t have otitis media, just the antenna should be up when an adult has otitis media. 03:20 Now, if you’re looking at the severity, look no further than the pneumococcus. 03:27 It’s number one in causing bad symptoms, it’s number one in being persistent, and it’s number one in causing complications, the most serious of which is going to be bacterial meningitis. 03:42 The non-typable H. flus are milder in all of those categories and Moraxella catarrhalis is milder yet. 03:53 So the initial event is the common cold, viral. 04:00 And of interest, in kids who have actually bacterial otitis media, you can find the viruses in 50% of them. 04:14 They’re actually found in the middle ear fluid of 25% of children with bacterial otitis media. 04:25 Among the viruses that cause this, the most common is respiratory syncytial virus, influenza virus, enterovirus, the common cold coronaviruses, and rhinoviruses, another cause of the common cold.
About the Lecture
The lecture Acute Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): Etiology by John Fisher, MD is from the course Upper Respiratory Infections.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the most common initial event that leads to bacterial acute otitis media in children?
- A viral upper respiratory infection
- Bacterial sinusitis
- Bacterial meningitis
- Congenital malformations
- Foreign objects
Which of the following bacterial pathogens is the most common cause of acute otitis media?
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Group A streptococcus
- Staphylococcus aureus
Which of the following is the most common viral cause of otitis media?
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Influenza virus
- Enteroviruses
- Coronaviruses
- Rhinoviruses
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Good lecture on inflamation of mucosa over middle ear cleft