Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Williams Syndrome
-
Slides WilliamsSyndrome Pediatrics.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
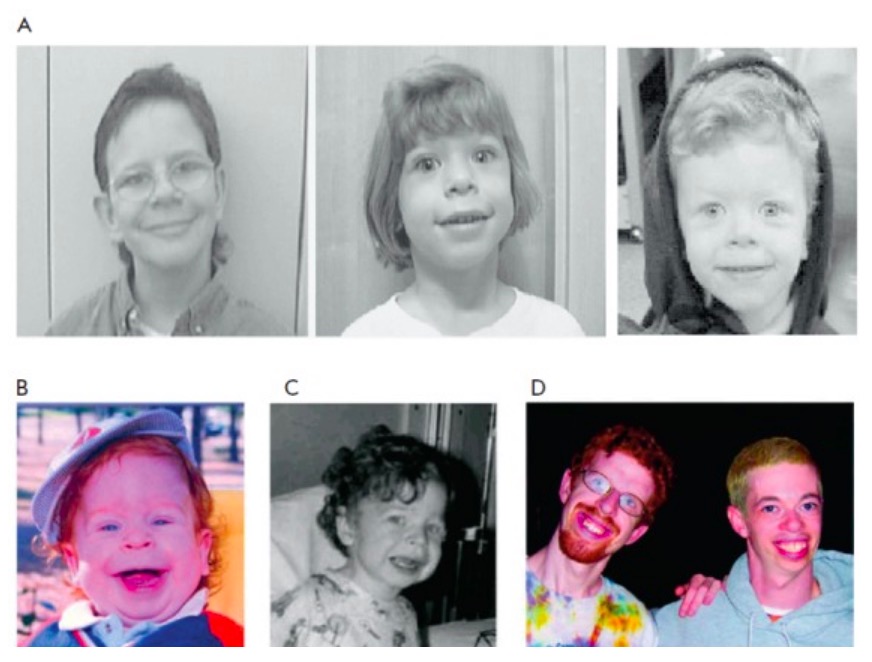
00:01 In this lecture, I'm going to discuss Willams Syndrome. 00:04 So Williams Syndrome is a microdeletion on chromosome 7q11.23 which contains the Williams-Beuren syndrome critical region or the WBSCR. 00:18 The Williams-Beuren Syndrome Critical Region contains 25 to 28 genes including: the gene ELN which codes for elastin. 00:26 The loss of this gene causes cardiovascular and connective tissue abnormalities. The loss of the gene GTF2IRD1 may contribute to the distinctive facial features of Williams syndrome. 00:37 Losses of the genes CLIP2. 00:40 and the other three in this row may contribute to characteristic behavioral abnormalities, cognitive difficulties, and learning disabilities, particularly visuospatial abilities. 00:50 The loss of the NCF1 gene is actually protective in decreasing the risk of hypertension. 00:57 This is an autosomal dominant disease that's mostly de novo mutations. 01:01 and it happens in roughly 1 in 10,000 live births. 01:04 How do these patients present? They often have short stature and they have characteristic, what we would say, 'elfin" facies. They look like little elves. 01:16 They have a transient neonatal hypercalcemia. 01:18 The cause of which is not at all understood but it can be quite severe. 01:22 So we worry about Williams Syndrome in patients who in the newborn period, present with a hypercalcemia that will gradually resolve over several months. 01:33 They can also have a congenital heart disease, most commonly supravalvular aortic stenosis like you can see in this patient. 01:42 These patients will have mild to moderate learning difficulties, not severe but mild to moderate. 01:51 They may have failure to thrive as well, difficulty growing early on. 01:55 One of the classic features of these genetic syndrome is a cocktail type of personality. 02:01 Let me explain what that means. 02:03 What that means is they're incredibly friendly, they're incredibly engaging and when you speak with them verbally, they seem very astute, but when you drill down into a subject, you discover they have not such a sophisticated understanding of any sort of depth of content of what they're speaking about. 02:22 In other words, they're like somebody you might encounter at a cocktail party, fun to get along with them, fun to meet them but maybe you don't get to know them so well. 02:31 They often have connective tissue abnormalities, elastin defects that allow them to be maybe more hypermobile. 02:40 So the cocktail party personality is interesting. 02:45 They have a lower IQ but actually have a higher verbal IQ. 02:50 Additionally, they have a lack of social inhibition which is truly remarkable. 02:56 In many ways, children with Williams Syndrome exemplify of what we should all be. 03:02 In one study of behavior of these children, researchers found that 100% of them had a kindred spirit approach, 90% sought the company of others, 87% empathized with others in pain, 84% were caring and 75% were happy when others did well. 03:23 These children engaged very well socially. 03:26 So if we suspect Williams Syndrome, how do we test? The diagnosis is based on a microarray genetic study. 03:35 If we test someone and they are positive, we should screen them for underlying abnormalities. 03:41 They require an echo to check for cardiac anomalies like the supravalvular aortic stenosis. 03:47 They require a renal ultrasound. 03:50 We need to do an eye exam on them to make sure that's normal. 03:54 They require also an auditory exam. 03:56 At birth, these infants need a calcium check and we need to watch that very closely during the first few months. 04:02 That hypercalcemia can be very challenging to manage and it's very reasonable to check them also to make sure that their thyroid hormones are normal. 04:11 So we'll do all this as a screening approach if they test positive. 04:16 So that's my brief review of Williams Syndrome in kids. 04:21 Thanks for your time.
About the Lecture
The lecture Williams Syndrome by Brian Alverson, MD is from the course Pediatric Genetics.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following lab findings is commonly associated with Williams syndrome?
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hyperphosphatemia
- Hyperkalemia
- Hyponatremia
Which of the following is not a typical finding in Williams syndrome?
- Average IQ
- Short stature
- Congenital heart disease
- Failure to thrive
- Elfin facies
Which of the following best describes the social characteristics of a patient with Williams syndrome?
- Higher verbal IQ, lower social inhibition
- Lower IQ, higher social inhibition
- Lower verbal IQ, higher social inhibition
- Higher IQ, lower social inhibition
- Lower verbal IQ, lower social inhibition
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |