Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Acute Headaches: Venous Sinus Thrombosis
-
Slides 08 Headache Neuropathology I.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
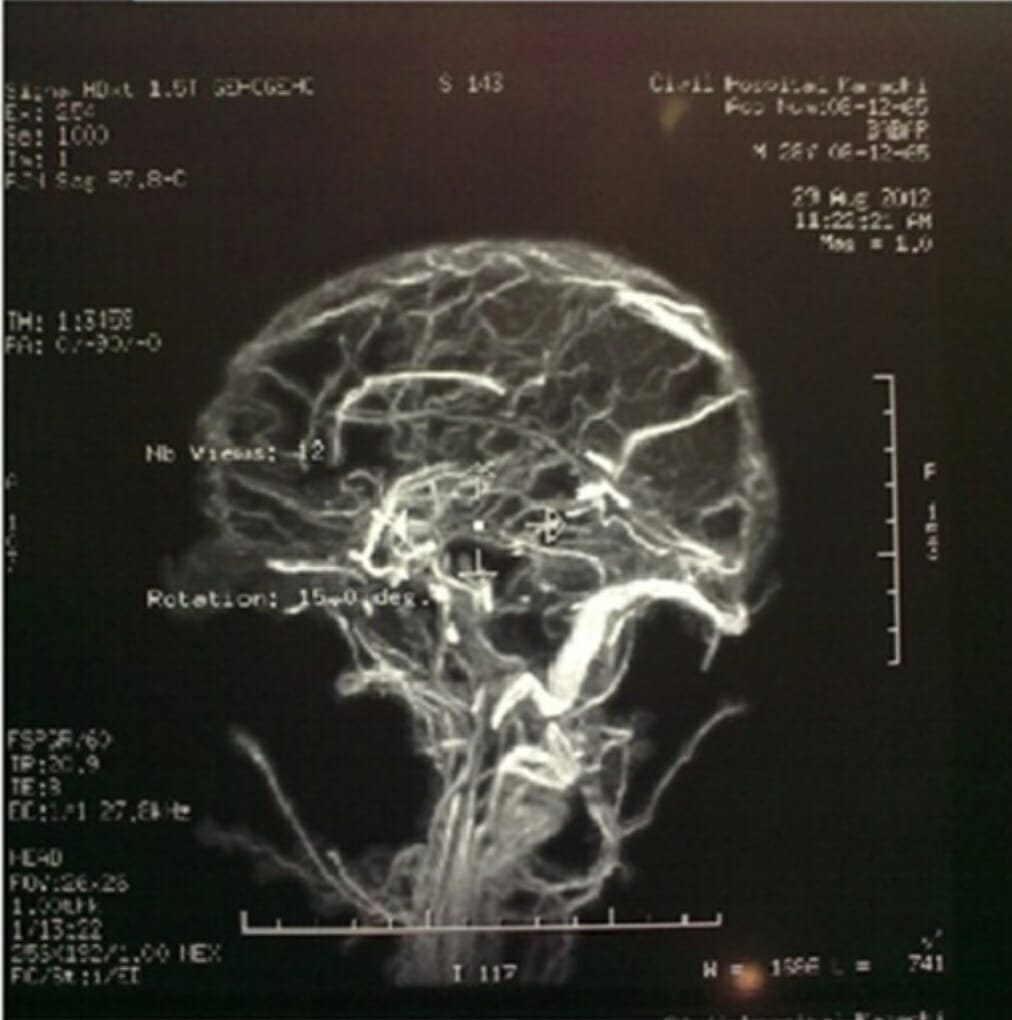
00:01 Continuing the discussion of acute headache, we have venous sinus thrombosis. 00:05 Headache with abrupt onset that lingers. 00:09 Diffuse, but occasionally localized near vertex. 00:13 In other words, sagittal sinus, and centro-parietal areas, the transverse sinuses. 00:19 Please make sure that you’re familiar with the two sinuses that might be affected with venous sinus thrombosis. 00:26 Allow the name to speak to you, transverse and sagittal. 00:31 Papilledema is going to be prominent. 00:34 More common during pregnancy and immediate post-partum. 00:37 Once again, when you think of thrombosis, you should be thinking estrogen, pregnancy, post-partum. 00:44 Others in terms of possible etiologies, hypercoagulable states, ENT infection also may predispose. 00:53 In other words, look at the name, topic is venous sinus thrombosis resulting in acute headache. 00:59 The name of the game is, what causes thrombosis in these sinuses, sagittal sinus, transverse sinus? Diagnosis: MRI imaging. 01:12 Begin IV heparin followed by oral anticoagulation. 01:15 In other words, well, depending on the etiology, be careful though. 01:19 If venous strokes occur, cerebral venography with local administration of fibrinolytics may be needed so that you can properly identify and manage your patient with venous sinus thrombosis. 01:36 You’ll notice that on your venogram that, on imaging, and you don’t find any of your blood vessels that you normally should in this area. 01:50 Then as what this picture is showing, specifically, absent right transverse sinus. 01:56 Why? Because every thrombosis is blocking the proper circulation. 02:05 Summary of your venous sinus thrombosis: Hypercoagulable states, pregnancy. 02:12 For the most part, you’re thinking about estrogen, and we talked about how local infection may occur as well maybe after an ENT type of procedure. 02:21 Preventive medicine: identify predisposition. 02:24 Signs and symptoms: This is important here, bilateral dull headache, maybe perhaps a visual disturbance. 02:29 Remember, papilledema because this is a venous sinus thrombosis. 02:34 Differential: In this female, perhaps, pregnant lady, reproductive age; differential, pseudotumor cerebri, migraine. 02:44 Pseudotumor cerebri, you’ll also find papilledema. 02:47 However, on image, pseudo means what? False. 02:51 So there’s no tumor, no evidence of a tumor. 02:54 Diagnostic workup includes MRI, and MRV. Therefore, you can confirm the diagnosis with a venography. 03:02 Treatment: anticoagulation, heparin; in the hospital setting, warfarin. 03:08 In other words, anticoagulation.
About the Lecture
The lecture Acute Headaches: Venous Sinus Thrombosis by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Headache – Pathophysiology.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the best test to evaluate a patient with a headache due to a suspected venous sinus thrombosis?
- MRI/MRV
- CT with contrast
- Lumbar puncture
- Non-contrast CT
- Ultrasound
What is the most appropriate treatment for a patient with a headache due to venous sinus thrombosis?
- Anticoagulation
- Triptan medication
- Calcium channel blockers
- tPA
- Aspirin
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |