Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
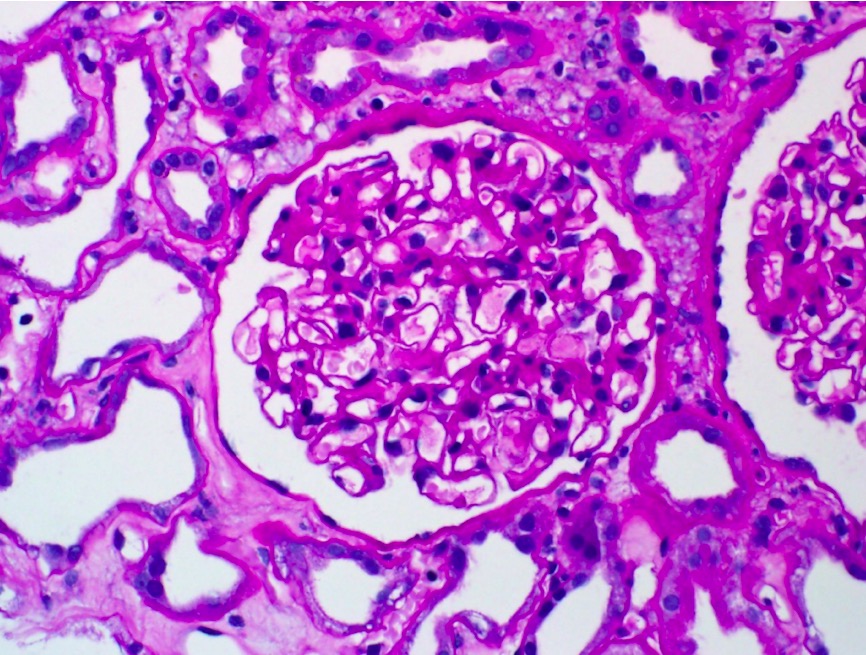
Subendothelial IC Deposition Viewed With EM
-
Slides Glomerulonephritis.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:00 Corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide. 00:02 Subendothelial deposits is what we're looking at here on electron microscopy. 00:07 Same thing, get in the habit of doing this quickly. 00:10 The more number of times you go to the protocol the better off you’ll be. 00:13 You’ll find your glomerular basement membrane paved road. 00:16 Number two, you look for the foot processes. 00:19 Well, there’s nothing underneath the foot process because this is DPGN. 00:24 Which gives you what? The title of the slide is subendothelial. 00:28 So therefore, you would find this underneath the endothelial cell. 00:31 Thin rim of normal basement membrane, it separates the epithelial side from the obviously the endothelial side. 00:41 Patient has diffused proliferative glomerulonephritis and as we talked about the prototype here, will be SLE. 00:49 If you pay attention, this is your electron microscopy with subendothelial DPGN. 00:55 As you see here on light microscopy, there’s going to be diffused proliferation. 01:01 There is going to be hypercellularity and there’s neutrophils within the mesangium. 01:05 What’s your mesangium? Basically, think of it as being the supportive infrastructure of your glomerulus, which then properly support your glomerular capillaries and all. 01:14 Also, it very much behaves like smooth muscle in which it will contract when need be.
About the Lecture
The lecture Subendothelial IC Deposition Viewed With EM by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Glomerulonephritis.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following represents the correct location of the deposition of immune complexes in diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis?
- Subendothelial layer
- Subepithelial layer
- Subendothelial and subepithelial layers
- Podocytes
- Parietal epithelial cells
Which antibody is found in SLE associated diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis?
- Anti-dsDNA
- Anti-Streptokinase
- Anti-Ro/SSA
- Anti-La/SSB
- Anti-ssDNA
What is the drug regimen used in the management of patients presenting with diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis?
- Corticosteroids and cyclophosphamide
- Corticosteroids and ciprofloxacin
- Corticosteroids and cyclosporine
- Cyclobenzaprine and cyclophosphamide
- Corticosteroids and clopidogrel
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus?
- It is the only type of nephropathy seen in SLE.
- It is associated with “wire looping” of capillaries.
- It often evolves into chronic renal failure.
- Subendothelial deposits are seen on electron microscopy.
- Ant-dsDNA antibodies are seen in this condition.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |