Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Renal Cysts and Renal Cell Carcinoma
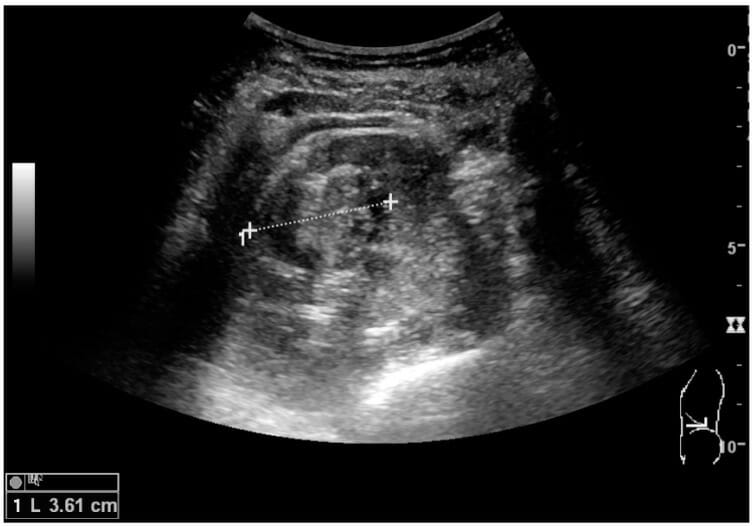
00:01 So let's talk a little bit about renal cysts. 00:03 Renal cysts are very commonly seen as an incidental finding. 00:06 Many times there are simple renal cysts, and they're just incidental finding that don't need any further work up. 00:12 However, they can raise the suspicion of malignancy if they have any of the following imaging characteristics. 00:19 So if they have thick walls, if they have thick septations within them, or if they measure high density on a CT. 00:26 So any of these three characteristics would raise the suspicion of malignancy and would need further work up. 00:30 So this is an example of a simple renal cyst. 00:33 This is the coronal CT image of the right kidney and you can see a very thin walled, low density lesion within the upper pole of the right kidney. 00:43 Again on the ultrasound image, you see anechoic lesion. 00:48 So a lesion that has no echoes within it. 00:50 It appears totally black part of the right kidney. 00:53 And this is an example of a simple cyst. 00:55 So a cyst is a fluid filled lesion that has very sharp margins. 00:59 The density measurements are about negative 20 to about positive 20 Hounsfield units. 01:04 And that's about the standard measurement of water. 01:07 On ultrasound they appear anechoic or totally black. 01:11 Renal cell carcinoma is a very important malignancy to recognize in the kidneys. And it can be any solid renal mass that's found in an adult. They often extend into the renal veins and they can also extend to the IVC. 01:24 If they metastasize then they can commonly go to the lungs. 01:27 They can be evaluated on a contrast enhance CT but if it's a very small or indeterminate lesion, then it is really best evaluated on MRI. 01:36 So if you see what looks like a solid mass on either ultrasound or on CT, and you're not able to characterize it any further, the next step really would be MRI. 01:43 So let's take a look at a CT urogram. 01:46 A CT urogram is actually an evaluation of the entire renal collecting system and it uses three different phases after the patient drinks a liter of water. 01:54 Three different phases of a CT scan so it's performed in a non-contrast, the portal venous and then a 10 to 15-minute delayed phase. 02:02 Renal cell carcinomas are low density lesions that are usually present within the kidneys and you can see here in the left kidney, this is the portal venous phase scan and you can see a low density lesion within the left kidney which enlarges the entire left kidney and it extends into the IVC here and into the renal vein. 02:21 These lesions have to be excised and when they have venous invasion associated with them that can really complicate the excision. 02:27 So let's take a look at this ultrasound image. 02:30 What do you see here? You can see the arrow pointing to an abnormality is an echogenic focus within the right kidney and this is a sagittal ultrasound image. 02:48 The echogenic focus if you look carefully here does result in shadowing behind it. So this represents a calculus. 02:56 There is no associated hydronephrosis in this patient, so this is a non-obstructing renal calculus which is very commonly found and often seen as an incidental finding. 03:04 If hydronephrosis is present however, the referring physician needs to know immediately because the renal collecting system may need to be decompressed to prevent renal injury. 03:13 Here's another case. 03:15 This is an ultrasound image and take a good look at this findings. 03:20 So what is that lesion there that's within the kidney? So this is an example of a renal cell carcinoma. 03:32 This is a sagittal ultrasound image that shows a solid rounded mass. 03:36 It's located within the mid to lower pole of the kidney and it's highly suspicious for renal cell carcinoma. 03:42 So you can see the difference between something like this and that anechoic cyst that we saw. 03:46 This is more of an echogenic lesion. 03:48 If you look inside of it, it's somewhat heterogeneous and it has definite internal echoes while a cyst will not have any echoes and appears totally black. 03:57 So in this lecture we've reviewed the common imaging findings of hydronephrosis and nephrolithiasis which are two of the most common findings seen within the kidneys. 04:05 We've also reviewed the imaging characteristics of renal cell carcinoma which is an important to do not miss finding.
About the Lecture
The lecture Renal Cysts and Renal Cell Carcinoma by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Abdominal Radiology. It contains the following chapters:
- Renal Cysts
- Renal Cell Carcinoma
Included Quiz Questions
What feature raises suspicion of malignancy in a renal cyst?
- Thick septations
- Thin wall
- Low density
- Clear fluid
- Smooth margin
Where does renal cell carcinoma most commonly metastasize to?
- The lungs
- The other kidney
- The colon
- The pancreas
- The bladder
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |