Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Quick Review: Examination of the Motor Neurons
-
Quick-Review-Examination-of-the-Motor-Neurons.pdf
-
Reference List Physical Examination.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
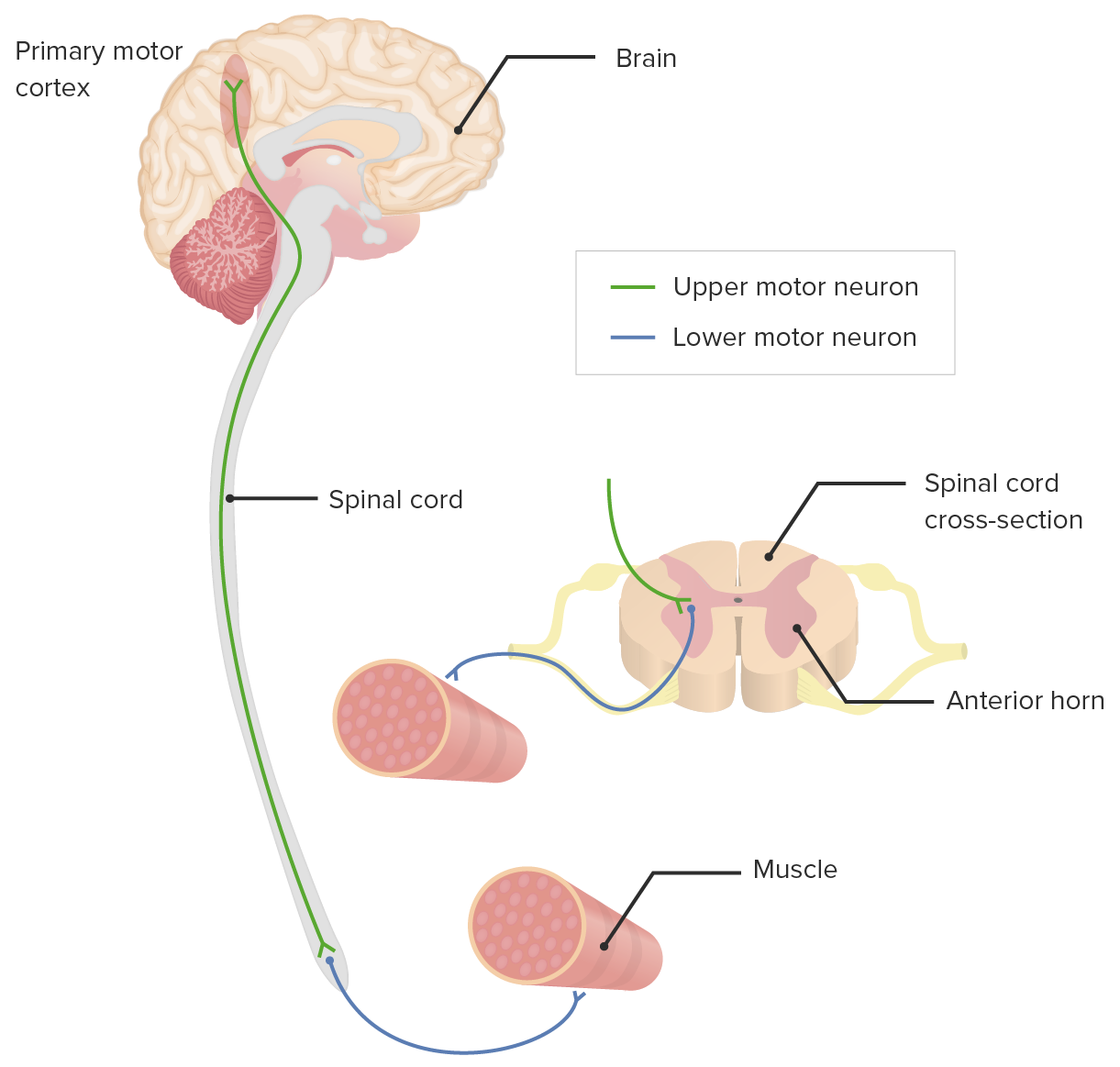
00:01 So we've covered a lot of content in this lecture, Let's do some quick review. 00:07 So one of the things I really was trying to highlight was distinguishing on physical exam between upper motor neuron which are, it's the neuron that starts up here in the cerebral cortex and sends its axon down the cortical spinal tracts versus the lower motor neuron with its nucleus in the interior horn that then goes out via nerve roots and the peripheral nerves. 00:27 Both of them are going to have weakness. 00:29 So that's not going to be sufficient to help to identify what kind of problem there is, though it will help you to localize exactly which muscle group is involved. 00:37 Muscle tone in upper motor neuron disease should be hypertonic and potentially rigid. 00:42 Whereas, patients with lower motor neuron disease will be flaccid. 00:45 I will just mention this here is that someone with an acute stroke will also be flaccid, even though that is an upper motor neuron problem, the rigidity and the hypertonicity can develop days to weeks later Fasciculations should be found in those with lower motor neuron problems. 01:04 And then deep tendon reflexes will be hyperreflexic or hyporeflexic, depending upon the type of neuron involved. 01:13 Which pairing is incorrect? C6 and wrist flexors, or is it C8 and the finger flexors? C5 and the biceps reflex, T1 and the interosseous muscles? Or is it C7 and the triceps reflex? So it's always challenging to memorize these things, but I really find that it's very important to lock this content into your memory. 01:42 So in this case, the answer is C6 and the wrist flexors because it's the sixth nerve root that actually causes wrist extension. 01:50 Everything else is correctly paired. 01:57 All of the following are associated with upper motor neuron disease except: Clonus, Hoffman sign, Spurling sign, The Babinski or the extensor plantar response, or Lhermitte's sign. 02:16 Well, the only example on this list that we would actually associate with a lower motor neuron problem and in particular, radiculopathy would be spurling sign also known as the foraminal compression test, which is looking for a cervical radiculopathy. 02:30 Everything else would be findings that you may identify with an upper motor neuron problem.
About the Lecture
The lecture Quick Review: Examination of the Motor Neurons by Stephen Holt, MD, MS is from the course Examinations of the Neck and Back Region.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |