Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Myocardium
-
Slides Structure-Function Relationships Cardiovascular System.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
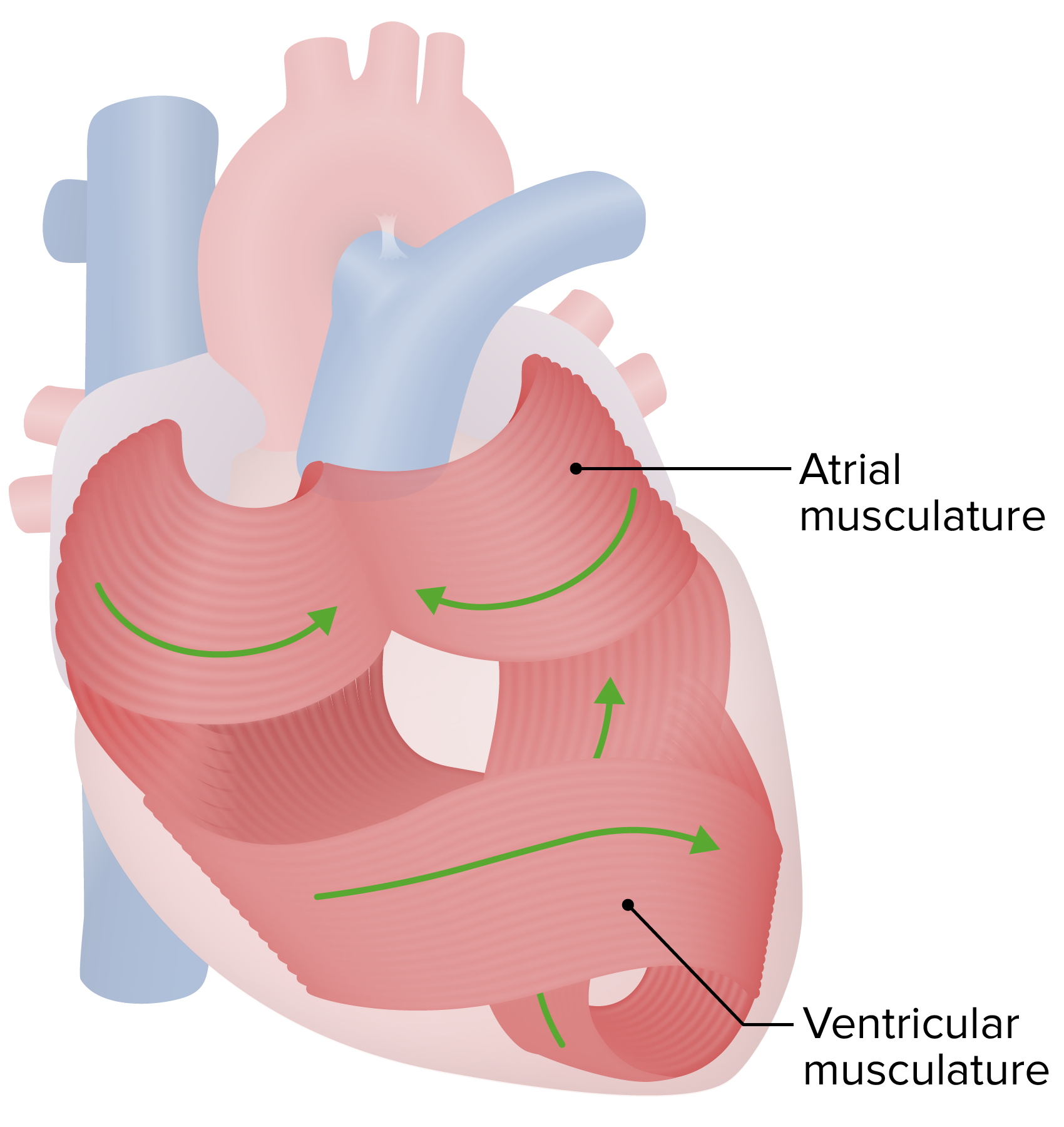
00:01 Welcome back to some of the conduction system in a bit. 00:04 But let's work our way back up here to the myocardium. 00:07 So myocardium really a great structure too. 00:10 It's got to contract and relax, contract and relax in a recurrent fashion. 00:15 How is this happening? So we have myocardium. 00:17 Here's what it looks like in real life. 00:19 And histologically, which I get to look at everyday down the microscope, it's there. 00:24 So the pinkness that's there, the vast majority of that is myocytes. 00:30 You see the blue dots, those are the nuclei of the myocytes. 00:34 And the cardiac myocytes constitute about 25-30% of the total cellularity of the heart. 00:41 They comprise 80-90% of the volume of the heart. 00:45 But if we count the individual cells, they're only about 20-30%, they're just big compared to... 00:52 Oh and then, the cardiomyocytes are connected one to another. 00:56 This is how we get a coordinated contractile wave. 00:59 And they're connected physically, mechanically, and also biochemically through the intercalated disc. 01:07 That allows us to have a nice contractile wave from cell to cell to cell. 01:11 So we can see that disk lining up. 01:15 Now the other cells that are present within the heart are endothelial cells. 01:19 There are roughly three capillaries for each cardiomyocyte. 01:22 That's how metabolically active that cell is the cardiomyocyte, we have to have a lot of capillaries to keep it happy. 01:29 So actually, the greatest number of cell type within the heart is probably endothelium. 01:35 But also with the fibroblasts, you can't just have muscle, you actually have to have an extracellular matrix to kind of pull against. 01:42 So there are a lot of fibroblasts that are in there as well. 01:46 And then, what's shown on the slide is kind of the wear and tear pigment associated with being a heart muscle or heart cell for a lifetime. 01:55 And we get oxidized lipid, oxidized glycoprotein that can no longer be degraded accumulates in the lysosomes of the cardiac myocytes. 02:04 And it's a recognizable entity called lipofuscin. 02:07 It's not particularly pathologic, but it does mean that the heart has been going through a bit of wear and tear. 02:14 Alright, here's a schematic of what we're dealing with. 02:17 And cardiac myocytes are not boxcars, they're actually kind of branching structures that are tightly intimately associated one with another. 02:26 Again, they have to actually maintain a signal cell to cell to cell. 02:30 So they have to have a lot of gap junctions that connect laterally as well as the intercalated discs at the end of cardiac myocytes connecting cardiac myocyte to cardiac myocyte. 02:40 So I have just shown you the intercalated disc in this particular cell. 02:44 And again, facilitating cell-cell mechanical and electrical and biochemical coupling. 02:51 Here's what's at the intercalated disc. 02:53 So, you see two cardiac myocytes, one in the upper right hand corner, one in the lower left hand corner and there is a gap between them. 03:01 And that is connected by a number of proteins that are responsible for mechanically linking but also electrically linking cell to cell. 03:12 So if there is a signal on the left hand side that says contract, there is a calcium current that gets into the right hand cell through the gap junctions that says contract. 03:23 And now we have a cell linked to the earlier contraction wave and we get a nice wave of contractility up along the ventricles. 03:34 What does this look like in real life? So this is a transmission electron micrograph that is showing you the intercalated disc. 03:42 Other rather dense structures within them are desmosomal proteins. 03:46 There are also within them gap junction proteins that allow the transmission of a calcium current.
About the Lecture
The lecture Myocardium by Richard Mitchell, MD, PhD is from the course Structure-Function Relationships in the Cardiovascular System.
Included Quiz Questions
Cardiomyocytes are coupled end-to-end by which of the following structures?
- Intercalated disks
- Gap junctions
- Z-lines
- Fenestrations
- Nodes of Ranvier
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |