Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Functional Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
-
Slides 11 Types of Tissues Meyer.pdf
-
Reference List Histology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
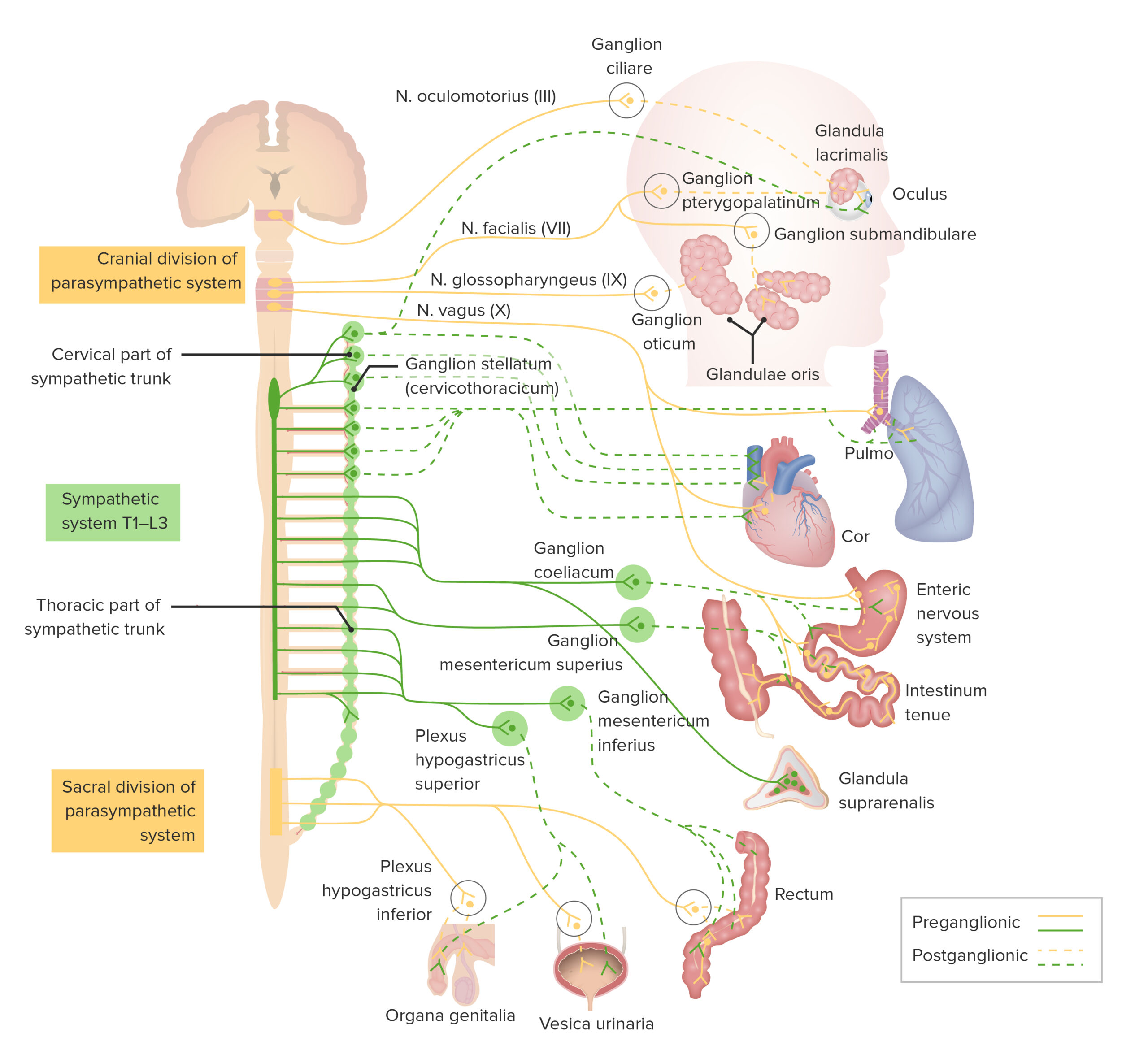
00:00 Well, it is now important to really have a look at the division of the autonomic nervous system, the parasympathetic and the sympathetic division. In this diagram, it looks rather complicated but is just a simple story that I want to try and explain. And that is let us first of all look at the sympathetic division. Sympathetic division comes from only certain spinal cord segments. They come from thoracic and lumbar areas. The thoracolumbar components make up the sympathetic vision of the autonomic nervous system. And those thoracolumbar preganglionic neurons pass to ganglia just outside the spinal cord. You can see them labelled there in a long chain running down next to the spinal cord, chain of ganglia. You can see little blue-covered neuron exiting the thorax and the lumbar region of the spinal cord. 01:15 These represent the preganglionic sympathetic neurons and they travel into this paravertebral or prevertebral chain of ganglia or other little ganglia you see in circles there and then the second order neuron or the postganglionic neuron then passes to the tissue where it does its activity where it innervates the smooth muscle or whatever the target tissue is. 01:49 Parasympathetic division is different. Neurons, the preganglionic neurons of the parasympathetic division of the nervous system exit from the cranium or from the sacral region, craniosacral. 02:03 They do not exit the spinal cord at any other location. And these preganglionic neuron travel a long way, some distance out into the organs, the viscera and there they locate the postganglionic neurons and those postganglionic neurons are located very close to the organ in which the postganglionic neuron is then going to innervate. So in simple summary, the sympathetic preganglionic neurons are short, but the postsympathetic neurons are long. In the case with the parasympathetic division, the preganglionic fibers are very long because they contact ganglion and postganglionic cells in those ganglia are very close to the organ in which they are going to innervate. 03:05 Sometimes the transmitterrs used vary in each of these types of neurons. Some can use acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter. Some can use adrenalin and therefore they are often referred to as being cholinergic and adrenergic neurons. And I only say that because I might use that term in later lectures.
About the Lecture
The lecture Functional Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System by Geoffrey Meyer, PhD is from the course Nerve Tissue.
Included Quiz Questions
Preganglionic sympathetic neurons are located in which part of the spinal cord?
- Thoracic and upper lumbar levels
- Lower thoracic and lumbar levels
- Cervical and thoracic levels
- Cervical, upper thoracic, and lower lumbar levels
- All throughout the spinal cord
Postganglionic sympathetic neurons originate in which of the following?
- Paravertebral and prevertebral ganglia
- Lateral horns of the spinal cord
- Anterior horns of the spinal cord
- Ganglia near peripheral organs
- Dorsal horns of the spinal cord
Which of the following is NOT a parasympathetic ganglion?
- Inferior mesenteric ganglion
- Ciliary ganglion
- Pterygopalatine ganglion
- Submandibular ganglion
- Otic ganglion
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
excellent presentation and clarification of both structures and function of the Nervous system. Thank you.