Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Folate Deficiency
-
Slides Macrocytic Deficiency.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
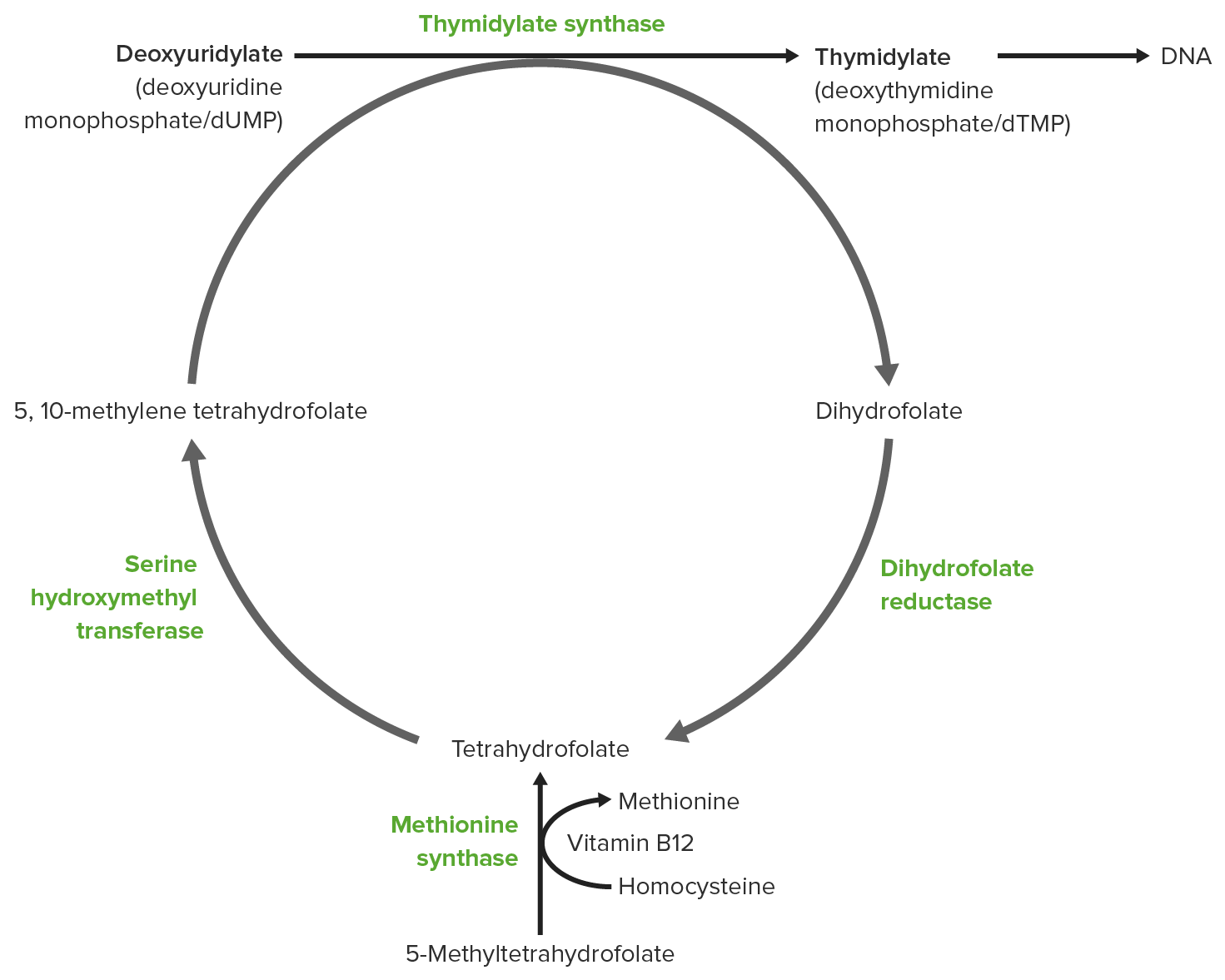
00:01 Before we move on though, I'd like to make sure that we’re clear about folate deficiency. 00:04 Folate deficiency, most common, alcoholics. 00:07 With alcohol don’t forget number of anemias, right? You can have your megaloblastic anemia. 00:13 You can have a non-megaloblastic anemia. 00:16 We’ll talk about that in a second. 00:17 Also with alcoholics you may have sideroblastic anemia which is a microcytic anemia. 00:22 I have mentioned that a few times. 00:23 Pregnant women, absolutely. 00:26 One of the major prenatal vitamins, right? Folate. 00:28 And what if the mother is deficient of folate and the fetus becomes deficient of folate? Now we have NTD, right? Neural tube defects such as spina bifida, maybe anencephaly, encephalocele and so forth. 00:44 Elderly once again, poor diet. 00:46 You’ll never know as to what happens. 00:47 Give me some drugs that we talked about already? Good. 00:51 Methotrexate, trimethoprim. 00:52 I walked you through in great detail. 00:54 Now, we can just fly through it. 00:56 Give me the name of the enzyme that it inhibits? Dihydrofolate reductase, DHFR. 01:05 Jejunal malabsorption, sure, such as celiac disease. 01:08 Okay, so big time. 01:10 If it’s B12, where are you being reabsorbed? Terminal ileum. 01:14 Hence, maybe Crohn’s more so. 01:18 And if it’s jejunal, that will your folate, folate. 01:21 And celiac disease can affect you anywhere, huh? Anywhere. 01:25 Remember blunting of the villi? Now just like we did at B12, we’ll do this with folic. 01:29 In folic acid, do remember that picture that I showed you where you’re taking up the methyltetrahydrofolate, you need to give up that methyl and what do you need to -- Well, who accepts that B12? Excuse me. 01:41 Give away. 01:42 Who accepts that methyl? The B12. 01:43 So green vegetable and meat products. 01:47 Polyglutamate converted to monoglutamate by intestinal conjugases. 01:50 Know that, please. 01:52 Conjugases are big time important when you’re dealing with folate. 01:57 So if for whatever reason, these conjugases are not present, your brush border enzymes, the conjugases. 02:03 Please understand that you’re not able to properly absorb your folate resulting in folate deficiency, megaloblastic. 02:11 The monoglutamate reabsorbed in jejunum. 02:14 So whenever you think folate, think glutamate. 02:17 And anytime you reabsorb, you have to be in the form of mono, mono, mono. 02:21 What does that mean? For example, what’s the only type of sugar “that you can take up”? Monosaccharide. 02:29 What’s the only type of protein that you can take up? Monopeptide, clear? Amino acids. 02:34 This is monoglutamate. 02:36 Next. 02:38 Supply, big time different, three to four months for folate in the liver. 02:43 How long for B12? Years. 02:45 So that’s why it's very important in a pregnant lady to make sure she is properly being supplemented with folate, folate, folate amongst other things as well.
About the Lecture
The lecture Folate Deficiency by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Macrocytic Anemia – Red Blood Cell Pathology (RBC).
Included Quiz Questions
What is the most common cause of folate deficiency?
- Dietary deficiency
- Celiac disease
- Drugs
- Malabsorption syndrome
- Pregnancy
Which of the following enzymes is mainly responsible for the absorption of folic acid in the form of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate monoglutamate?
- Intestinal conjugase in jejunum
- Intestinal conjugase in ileum
- Pepsin in the stomach
- Secretin in the stomach
- Cholecystokinins in the duodenum
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |