Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Epithelium: Introduction
-
Slides 01 Types of Tissues Meyer.pdf
-
Reference List Histology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
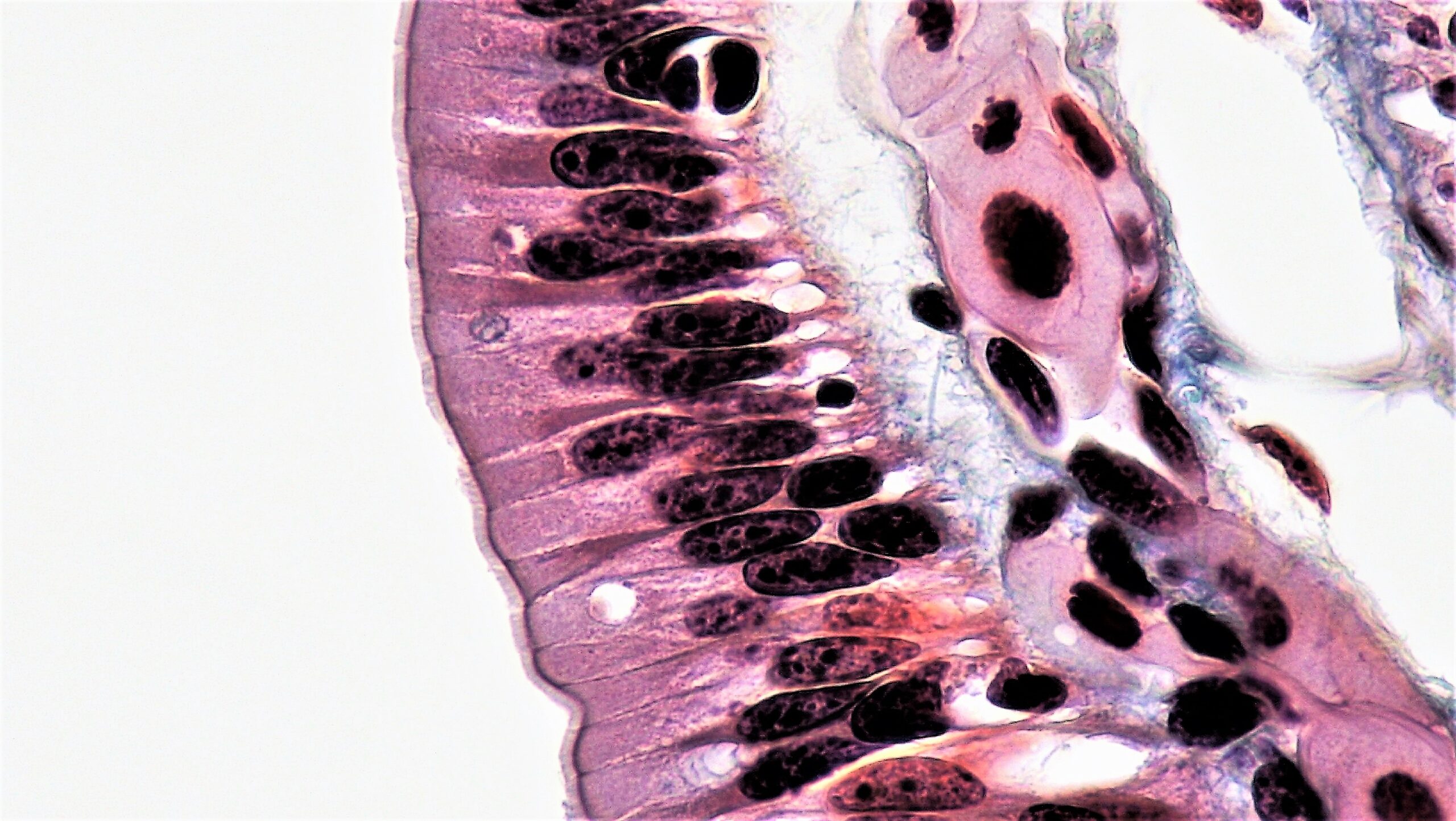
00:01 In this lecture, I'm going to talk about epithelium. 00:05 Epithelium is one of the four basic tissues of the body. 00:09 The other three are connective tissues, muscle and nerve. 00:14 Epithelium is very important to understand because it's located in most organs of the body. 00:21 And if you can identify the different sorts of epithelium, and you know the different functions of each of these epitheliums. 00:30 Then it's very important and very easy for you to understand, then the structure of organs and being able to identify different organs. 00:40 At the end of this lecture, I would like you to understand the following: Firstly, that epithelial cells are orientated in certain ways. 00:50 They're also classified or named differently depending on how they appear. 00:56 And also, in some instances their functions. 00:59 They have certain surface specializations that have a very important role in some parts of the body. 01:08 Epithelial cells are very tightly held together by junctional complexes. 01:14 And I'll explain the different types of junctional complexes. 01:18 Epithelial are also very thoughtly anchored to underlying connective tissue. 01:25 Let me just summarize what the main functions of epithelia are. 01:31 And then we'll look at the structures of the epithelia that serve these particular functions. 01:39 Epithelia cover body surfaces. A skin is an example. 01:44 Skin is the external covering of the body. It's a very specialized epithelium. 01:50 And I'll talk about skin especially in another lecture. 01:54 Epithelia lines the body cavities, such as the thoracic cavity, the pleural cavity, and abdominal cavities. 02:04 It also aligns tubes. Some of those tubes are external to the body, such as the respiratory passages, the gastrointestinal tract. And some tubes are internal, such as blood vessels. 02:20 Epithelia also forms secretory tissues or glands and also the ducts or conduits that carry the secretory product of these glands to the surface. 02:32 And they're also in special instances receptors. 02:35 And we'll learn about those in more detail when we look at the ear, and the tongue, and olfactory epithelium in the nasal cavity, and also the eye. 02:47 It's very important first of all to understand what the characteristics of epithelia are. 02:53 It has three major characteristics that really identify epithelia. 03:00 Firstly, each of the epithelial cells has an apex or a surface that's adjacent to the lumen, which is often a hollow tube. 03:11 Here, you see a section through a collecting duct in the kidney. 03:16 You don't need to understand the details of the kidney at this stage, but just have a look at this image, have a look at the sections through this tube. 03:24 Identify the lumen, and identify the epithelial cells. 03:29 They stain light pink, some you can see have a nice round nucleus. 03:35 In other instance you can't see the nucleus because the section just hasn't pass through, that part of the cell. 03:42 But these epithelia all have the surface that opens into the lumen which is the clear area in the center. 03:51 Epithelia also have lateral border, and that lateral border, has very important functions, and that's where junctional complex has occur to hold these epithelial cells very closely together. 04:05 All epithelia sit on a basement membrane. 04:11 And therefore are anchored to underlying connective tissue. 04:16 We call that underlying connective tissue, lamina propria. 04:20 And I'll be talking about lamina propria a number of times in this lecture and also in other lectures.
About the Lecture
The lecture Epithelium: Introduction by Geoffrey Meyer, PhD is from the course Epithelial Tissue.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of epithelial cells?
- Cuboidal and columnar epithelia lack an underlying basement membrane.
- They may be immediately adjacent to a cavity within an organ.
- They are held together by junctional protein complexes.
- They protect the tissues that lie beneath.
- Their functions include selective absorption.
What are the three characteristics of any epithelium?
- Each cell has an apex, lateral membranes, and the entire epithelium lies on a basement membrane.
- Each cell has two apices, 3 lateral membranes, and usually no basement membrane.
- The cells are smaller than most other cells, with lateral membranes, and have a basement membrane.
- The cells are larger than most other cells, with apical surfaces and no basement membrane.
- Each cell can produce secretions and have both lateral and basement membranes.
Which of the following is NOT one of the four basic types of tissue?
- Vascular tissue
- Epithelial tissue
- Muscle tissue
- Connective tissue
- Nerve tissue
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
3 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
I think that this lesson was very interesting and easy to understand. 5 starts out of 5.
I think that this lesson was very interesting and easy to understand. 5 starts out of 5.
professor lectures factual information relevant to epithelium in a simplified way