Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Chronic Pancreatitis: Definition, Diagnosis and Etiology
-
Slides Pancreas and Biliary Tract.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
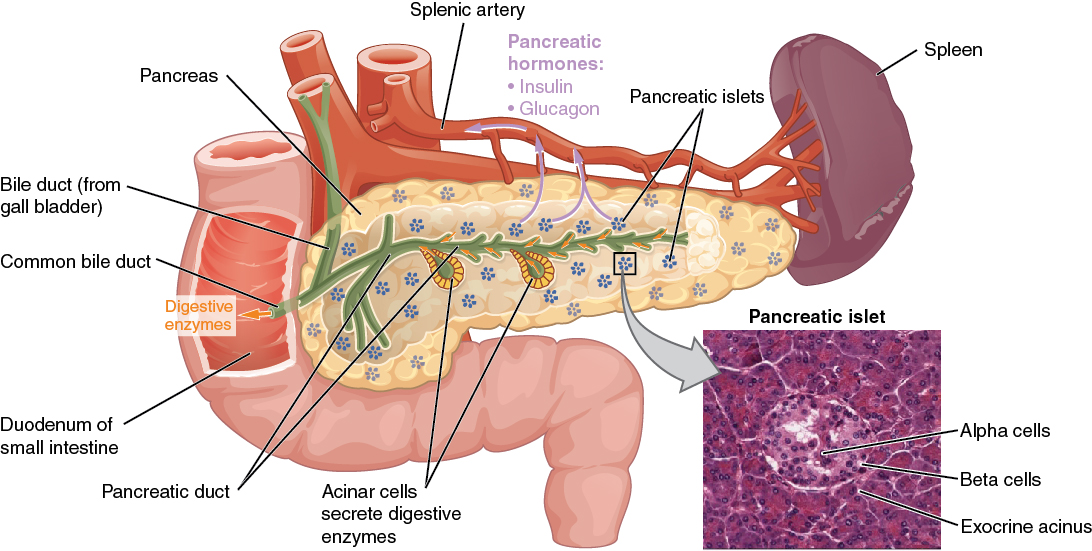
00:01 Chronic Pancreatitis. 00:03 Chronic Pancreatitis. Remember, chronicity means obviously increased duration of injury. 00:12 Is it possible that you might have acute, acute, acute, acute? Or should I say a number of acute bouts of pancreatitis and at some point you have to call it chronic pancreatitis? Isn’t that pretty much the same reasoning that we gave or we transitioned from what’s known as your pyelonephritis acute type into chronic pyelonephritis? Recurrent, recurrent, acute. 00:39 One definition, but let’s go further. 00:42 So the persistent inflammation of the pancreas where now it’s irreversible histologic changes, and without a doubt, the pancreas is completely exhausted to the point where the patient doesn’t have either the exocrine enzyme activity nor have the endocrine activity. 01:02 So for example, what was the name of the enzyme that’s more specific for pancreatic damage that you’re going to use? Lipase. 01:12 In chronic pancreatitis, if it’s persistent inflammation and there’s enough damage taking place in the pancreas, please understand that now the lipase and amylase is unreliable. 01:25 What about that glucose, endocrine? So if insulin is not present, your patient most likely is presenting with hyperglycemia. 01:34 Cardinal symptom, recurrent abdominal pain, recurrent abdominal pain. 01:39 Classic triad, with chronic pancreatitis, no doubt you’re going to find saponification. 01:46 Saponification means pancreatic calcification. 01:49 Next, without a doubt, because you don’t have the lipase to properly break down my triglyceride, you’re going to end up finding lipid in my stool. Welcome to steatorrhea. 02:03 And because of destruction of pancreas, loss of insulin, there will be hyperglycemia welcome to acquired type of diabetes mellitus. 02:13 Also, results in weight loss and malnutrition, be careful with that though because as a differential, you should also be thinking about pancreatic cancer, right? But what I’m saying is you can find weight loss and malnutrition taking place even with chronic pancreatitis. 02:29 and the symptoms here will give exactly that and I’ll give you pancreatic cancer and what you’re looking for. 02:35 Okay. Etiology of chronic pancreatitis. 02:37 Alcohol. 02:39 Here once again. Yes. 02:41 Because you have an alcoholic, sure that alcoholic is having an acute pancreatitis. 02:46 Is he gonna stop? Is he or she going to stop drinking? Chances are pretty slim that he or she will not. 02:53 They’ll continue drinking. “Ouch again!” Another acute bout. 02:57 “Oh, yet again an acute bout.” You keep having recurrent bouts of acute pancreatitis. 03:03 By definition, isn’t that persistent inflammation? By definition, isn’t that chronic pancreatitis? It correlates with the amount and duration of alcohol with pancreatitis. 03:14 Hereditary: Increased risk of pancreatic cancer with hereditary type of chronic pancreatitis. 03:21 Obstruction: We’ve talked about pancreatic divisum. 03:26 There might be issues with trauma or maybe even ductal disruption. 03:31 We talked about things such as your pancreatic stones or a gallstone which has made its way down to the pancreas. 03:41 The space occupying lesion here once again could be a tumor and that will be obstructive. 03:47 Common differentials or differentials that you want to keep in mind depending as you who your population is.
About the Lecture
The lecture Chronic Pancreatitis: Definition, Diagnosis and Etiology by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Pancreatic and Biliary Tract Diseases: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is a histologic feature of chronic pancreatitis?
- Calcifications
- Granuloma formation
- Lipofuscin accumulation
- Destruction of the exocrine pancreas and preservation of the endocrine pancreas
- Destruction of the endocrine pancreas and preservation of the exocrine pancreas
Which of the following signs and symptoms is NOT related to chronic pancreatitis?
- Constipation
- Epigastric tenderness
- Steatorrhea
- Malnutrition
Which metabolic abnormality is associated with chronic pancreatitis?
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Hypercalcemia
- Hypophosphatemia
What is the cardinal symptom of chronic pancreatitis?
- Recurrent abdominal pain
- Chronic diarrhea
- Intermittent fever
- Chronic constipation
- Jaundice
Customer reviews
3,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
1 |
2 customer reviews without text
2 user review without text