Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Breast Abnormalities in Radiology
-
Slides Breast Abnormalities.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
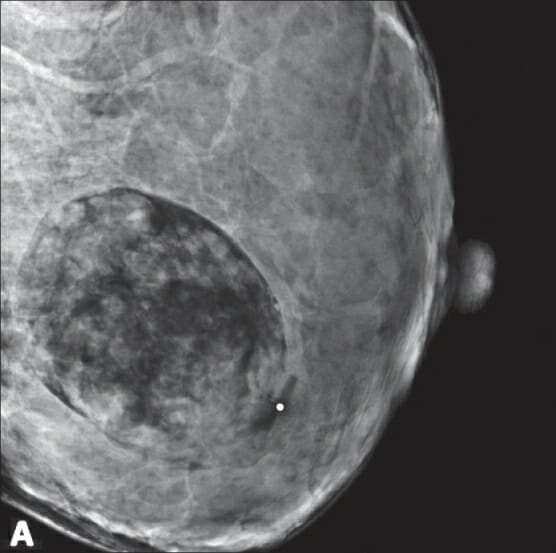
00:01 So in this lecture, I'd like to review some common abnormalities that can be found within the breast, and I'd also like to review what to do with a patient that presents with a breast symptom. 00:10 Some common imaging features of breast cancer include a mass, microcalcifications which are 5 or more punctate calcifications within a 1 cm area and architectural distortion. 00:22 So let's review some terminology, a mass is a lesion that has 75% of the margins visualized on both views of the mammogram. 00:31 A focal asymmetry is lesion that seen on two views, but 75% of the margins are not fully visualized and an asymmetry is a lesion that seen on only one view, either the CC or the MLO. 00:44 So this is an example of a mass. 00:49 We have here a CC view and an MLO view and we have a mass that's in the left upper outer aspect of the breast. 00:58 If you remember on the CC view, the top part of the CC view represents the lateral part of the breast. 01:04 You also see multiple coarse calcifications which are actually benign and they represent involuting fibroadenomas. 01:13 So these are commonly seen calcifications within the breast and when they have this appearance there's nothing to worry about. 01:19 So what do we see here? We have what's called an XCCL view and an MLO view. 01:26 This is a patient that had an abnormality seen on a screening mammogram, that came back for additional imaging. So an XCCL view is a type of CC view essentially that takes into account the lateral aspect of the breast a little bit more. 01:39 These are also spot view, so the area of the abnormality seen on the screening mammogram is further evaluated specifically. So the abnormality is right here. 01:49 This is an example of architectural distortion. 01:57 So we have spot images from a diagnostic mammogram, that demonstrate an area of architectural distortion in the right upper outer breast. 02:05 Architectural Distortion is very specific for breast cancer. 02:09 However, it's also one of the most difficult things to see on a mammogram. 02:13 And what do we see here? So here we have magnification views. 02:19 So again, this patient came in for a screening mammogram and had an abnormality seen on the screening mammogram. 02:24 The patient was called back for additional imaging of this abnormality. 02:28 So we have a magnification CC view. So again, this is the lateral aspect of the breast and then we have a magnified lateral view. 02:37 So this is the superior aspect of the breast and here we see a small portion of the pectoralis muscle, so the abnormality is circled. 02:45 This is an example of microcalcifications, so these are linear branching microcalcifications that are present in the left upper outer breast. 02:56 Again, we see a group of calcifications together, 5 or more within a 1 cm area. 03:01 So these calcifications are suspicious that need to be biopsied. 03:05 This patient would likely be given a Birads 4. 03:07 So what do you order when a patient comes in? So this is categorized into two different age groups, for patients presenting over the age of 30 and patients presenting under the age of 30. 03:21 Patients who are over the age of 30, usually get a diagnostic mammogram or tomosynthesis and a breast ultrasound. Patients who are under the age of 30, usually get only a breast ultrasound and this is because the breast is susceptible to radiation although we said that there's very little radiation that's emitted from a mammogram, you have to take into account the patient's age. 03:43 So patients who are very young usually under the age of about 25 or so, still have stem cells within their breast, which are very susceptible to radiation. 03:51 And as you recall radiation is additive. So if it's not necessary it's better to not do a mammogram and usually in the patients that are very young unless there's a very suspicious abnormality. 04:01 We prefer to avoid it whenever possible. 04:04 So what happens if a pregnant patient comes in? And these patients we would perform only a breast ultrasound. 04:12 Again, because of the adverse effects of radiation on the fetus. 04:15 How about a patient that's breastfeeding? And these patients we would perform a breast ultrasound first, because most of the abnormalities seen in a breastfeeding patient or seen best on breast ultrasound. However, depending on what the abnormality is, we may or may not do a diagnostic mammogram and tomosynthesis. 04:33 There are no adverse consequences to radiation in a patient that's breastfeeding. 04:36 The patient should be instructed to feed or pump just prior to the mammogram. 04:41 So when a patient is breastfeeding their breast tissues can appear very, very dense and it can obscure what we can see within the breast. 04:48 So the patient pumps are feeds just prior to the mammogram that clears out some of the milk that's within the breast and allows us to take a better look at what's inside. 04:56 And a patient that's presenting with an axillary lump, and gets both a mammogram or tomosynthesis and the breast ultrasound. 05:03 Although, the axilla may not be visualized on the mammogram and tomosynthesis, often times a patient that has a breast abnormality, also presents with an axillary lump. 05:13 So we wanna evaluate both the breast tissue and the axilla, when this patient comes in. 05:17 So how can you localize a breast lesion? If there's a vague or large area of concern then you can localize it by a quadrant. 05:24 So we have the upper quadrant. We have the upper outer quadrant. 05:28 The upper inner quadrant and both lower quadrants. 05:31 So the lower inner and the lower outer quadrants. 05:33 However, if there's a focal area of concern, then it's localized by an o'clock position and a distance from the nipple in centimeters. 05:40 And again, this is the standard that's used to ensure that the correct area is looked at by the radiologist. 05:45 It's also important to remember that ultrasound is usually used as an adjunct to mammography for focal areas of concern and for focal mammographic abnormalities. 05:55 It's not commonly used alone as a screening exam because it has a very high false-positive rate. 05:59 So we often see abnormalities on ultrasound that aren't really true abnormalities but just the breast tissue appearing a little bit different than the rest of the breast tissue. 06:08 So this is an example of a clock position and how to localize a mass within the breast. 06:15 It's important to see that the right breast and the left breast, are a little bit different, it's as if you were looking at the patient and each breast is a clock. 06:23 So the lateral aspect of the right breast is 9 o'clock, while the lateral aspect of the left breast is 3 o'clock. 06:29 This is often confused so it's important to review this. 06:32 So let's take a look at this mammogram. 06:39 This is a patient that presented for a screening mammogram. 06:42 So she had no abnormalities when she presented, what do you see on here? So let me just orient you again, we have the MLO views here and we have the CC views on the right. 06:55 Again, with all of radiology this is the right breast and then this is the left breast. 07:02 This is the right CC view, this is the left CC view. 07:07 So the abnormality is on the right. We can see it right here circled. 07:13 So what would be the next step when you see this abnormality on a screening mammogram? So the next step would be performing a diagnostic mammogram. 07:29 So the patient would come in for additional imaging specifically of this area. 07:33 So the patient came back and she had spot views performed of this area. 07:38 And now you can see the abnormality a little bit better. 07:41 So what would be the next step? It looks like the patient might have a mass in the breast. 07:47 The next step would be to perform an ultrasound. 07:52 Ultrasound is always performed when there's a suspected mass and this is because ultrasound is really the only way for us to see whether the mass is cystic or whether it's solid. 08:01 If you remember cystic lesions are anechoic. So they're totally black. 08:06 Solid lesions can be anywhere on a shade of gray. 08:09 They could be light grey, they could be dark grey, but if it's a solid lesion then it's obviously more worrisome. 08:14 So this is what we saw on her ultrasound. 08:18 Again, you can see that this is labeled as right breast, 12 o'clock and 7 cm from the nipple. So this is the standard labeling, this image is also labelled sag, which means that it's performed in the sagittal dimension. 08:33 So this is the abnormality here and then here posteriorly, we have the pectoralis muscle. 08:42 So this patient actually has what appears to be an irregular hypoechoic mass. 08:47 So what would be your next step? How can we figure out what this is? So the next step is an ultrasound guided biopsy. 09:01 So we would take a look under ultrasound and we would sample this lesion with a needle to see what's going on. So breast masses are almost always biopsied under image guided biopsy first. Breast imaging and breast image guided biopsy is allow for a full evaluation prior to performing surgery because if the type and extent of disease is known, then only one surgery is needed. 09:22 So prior to the advent of breast needle biopsies, a surgical biopsy was actually performed to diagnose the problem and then a second surgery was done perform to fully remove the lesion because of image guided needle biopsies now, we can actually evaluate the entire extent of disease and we know exactly what the pathology is prior to the patient undergoing surgery, which can limit the surgery to only one. 09:44 Image guided biopsies are actually very quick procedures with very few complications, so it's a great alternative to a surgical excision. 09:52 So there are 3 major types of image guided breast biopsies. 09:55 We can perform biopsies using ultrasound guidance. 09:58 We can perform biopsies using mammographic guidance and these are called stereotactic biopsies, and we can perform biopsies using MRI guidance. 10:06 So depending on which area the lesion is seen best on, the biopsies performed using that imaging. 10:13 Ultrasound guided biopsies are actually the most common because masses are best seen on ultrasound and breast cancer is often present as a mass. 10:20 This is also the easiest on the patient because it's a very quick procedure, the patient is lying flat on their back and has very few complications. 10:28 So we've gone over what to do when a patient comes in with a breast problem. 10:32 Hopefully, this will help you when patients come in. 10:35 It'll also help you let the patient know what to expect when they enter the Mammography Department.
About the Lecture
The lecture Breast Abnormalities in Radiology by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Thoracic Radiology. It contains the following chapters:
- Imaging Features of Breast Cancer
- Breast Lesions
- Breast Biopsies
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following mammographic findings is NOT a sign of breast cancer?
- Popcorn calcifications
- Mass
- Asymmetry
- Architectural distortion
- Microcalcifications
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
The steps for diagnosis and reason behind it are well explained, thank you. I will definitely recommend my other friends to have a look.