Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Brain Abscess
-
Slides 10 CNSInfections Neuropathology I.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
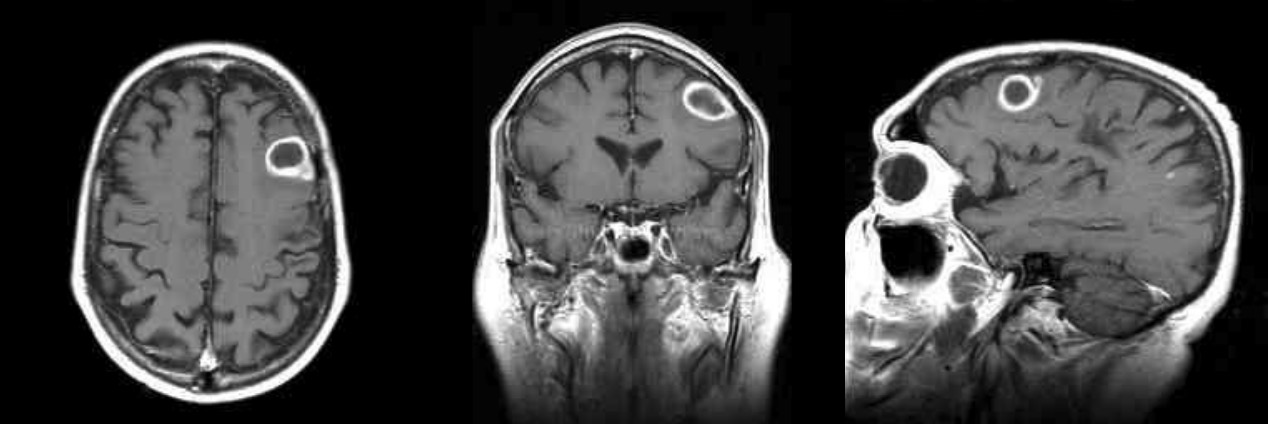
00:01 Here, we have brain abscess. 00:03 With the brain abscess, acute focal suppurative infection of brain parenchyma. 00:09 What does suppurative mean to you? Bacterial. 00:13 Under brain abscess, there might be direct seeding. 00:16 Local extension Or it could be hematogenous. 00:19 Acute bacterial endocarditis. 00:22 Or cyanotic congenital heart defects. 00:25 So anyone of these type of presentations could then result in eventual brain abscess. 00:32 Spreading. 00:34 Spreading. 00:37 Clinical features: Headache, nausea with vomiting, papilledema, focal neurologic, pretty nonspecific. 00:44 Elevated CSF, WBC count, and here we go, ring enhancing lesion on CT or MRI. 00:51 So now let’s step back for one second and at least, at least, review the three different ring enhancing lesion that we’ve seen. 00:59 Technically, two. 01:01 Toxoplasmosis, AIDS patient, immunocompromised. 01:04 Most common CNS infection in an AIDS patient, toxoplasmosis. 01:09 What if serology comes back to be negative? You still move forward with treatment because your patient has AIDS. 01:15 How long do you give therapy? Lifelong therapy. 01:18 Toxo. 01:19 Then we looked another ring enhancing lesion during active, active, infection with neurocysticercosis. 01:27 It could be ring enhancing. 01:28 But I told you most common presentation would be a calcified cyst in the brain and then we have brain abscess. 01:36 And here, we have ring enhancing lesion. 01:38 Pathogenesis, well, we’ll just walk through how maybe a patient has endocarditis. 01:44 Maybe there is a direct seeding, so on and so forth, hematogenous spread. 01:48 Edema, ring enhancing lesion, and an abscess core. 01:52 So in other words, this time, we don’t have calcifications. 01:56 So therefore, we have a ring with an abscess core. 02:01 What does an abscess core mean to you? Neutrophils, right? And what does that abscess core mean to you apart from neutrophils coming in? What kind of necrosis is this? It will be liquefactive necrosis. 02:14 Because neutrophils are destroying everything in its path. 02:18 Brain abscess.
About the Lecture
The lecture Brain Abscess by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course CNS Infections - Clinical Neurology.
Included Quiz Questions
A 15-year-old girl presents to your office with fatigue and shortness of breath. She was diagnosed with a ventricular septal defect at the age of 2. Physical examination shows pedal edema and cyanosis. Auscultation reveals a pansystolic murmur. A head CT shows a ring-enhancing lesion. What does this lesion most likely represent?
- Brain abscess
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Tuberculosis
- Toxoplasmosis
- Neurocysticercosis
What type of necrosis is seen within a brain abscess?
- Liquefactive necrosis
- Fibrinoid necrosis
- Coagulative necrosis
- Caseous necrosis
- Fat necrosis
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |