Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Atelectasis
-
Slides Atelectasis.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
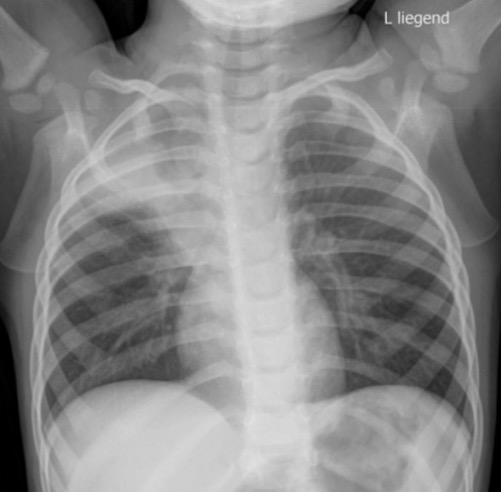
00:01 So let's talk a little bit about Atelectasis. 00:03 Atelectasis is one of the most common findings seen on a chest x-ray, because a lot of radiology is about pattern recognition. 00:10 Let's go through some patterns that will help you identify atelectasis. 00:13 Let's take a look at this case here, so we have an opacity involving the right upper lobe and the right lower lobe. 00:22 It appears to have very sharp margins, so this is an example of atelectasis. 00:27 Atelectasis is a loss of volume that results from incomplete expansion or collapse of the lung parenchyma. 00:33 It causes an increase in density or "whiteness" of the affected space similar to that caused by consolidation. 00:39 Atelectasis has very sharp margins and it usually displaces the fissures, mediastinal structures, and hemidiaphragm towards the side of atelectasis. 00:50 Again, because it does represent a loss of volume. 00:53 Atelectasis can really involve any portion of the lung. 00:57 It ranges from the entire lung to just a very small subsegmental portion. 01:01 If only a very small portion is involved, then you may not see the result in loss of volume. 01:06 So there are three major types of Atelectasis. 01:11 There's obstructive atelectasis, compressive and cicatrization. 01:15 Obstructive Atelectasis is caused by something obstructing the flow of air into the region of interest. 01:21 Compressive Atelectasis is caused by an adjacent mass, effusion, or pneumothorax that prevents air from flowing into the surrounding alveoli. 01:30 And Cicatrization Atelectasis results from adjacent scarring that pulled on the lung parenchyma, and again compresses the alveoli preventing air from entering them. 01:39 So on this case, we have an example of compressive atelectasis. 01:45 There is a very large pleural effusion which is compressing a portion of the lung and resulting in loss of air from the alveoli surrounding it and causing compressive atelectasis. 01:55 So the white portion in the middle here is the area of atelectasis or the compressed lung, and the surrounding low-density is the pleural effusion. 02:04 So let's talk a little bit about round atelectasis. 02:11 This is really a combination of cicatrization and the compressive atelectasis. 02:15 It usually occurs in patients that have underlying pleural disease such as asbestos exposure or possibly a pleural effusion. 02:22 What the pleural effusion does is it causes adjacent compressive atelectasis and the visceral pleura folds in on itself, and then pulls the adjacent lung in due to surrounding fibrous adhesions. 02:33 As the effusion shrinks the compressed lung remains trapped while the surrounding lung aerates. 02:39 So this is an example of round atelectasis. 02:43 This is done in lung windows and you can see here, a small pleural effusion and then a rounded area of what appears to be consolidation which actually represents atelectasis. 02:55 What is Subsegmental Atelectasis? This is actually one of the most commonly seen types of atelectasis on a chest x-ray. It's also called plate-like or discoid atelectasis. 03:06 And it results in linear opacities which often abut the pleura. 03:09 It's a cause of collapse of the air spaces that are smaller than a single bronchopulmonary segment. 03:16 And one bronchopulmonary segment, just to review, is a portion of a lung that?s supplied by a tertiary bronchus. 03:21 So it?s a very small segment of the lung. 03:23 This is an example of what subsegmental atelectasis looks like and it can be caused by a variety of different things such as hypoventilation, bronchial secretions, asthma, aspiration or obstruction. 03:35 We actually often see this in patients that are coming in that have abdominal pain, because they're just not taking a very deep breath and that results in subsegmental atelectasis.
About the Lecture
The lecture Atelectasis by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Thoracic Radiology.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the characteristic of subsegmental atelectasis?
- The collapse of air spaces that are smaller than a bronchopulmonary segment
- Adjacent pleural effusion
- The involvement of a large segment of the lung
- Patients with underlying lung diseases
- It is very uncommon
Which of the following is NOT a feature of atelectasis?
- A shift of the trachea is opposite to the side of atelectasis.
- The lesion has sharp margins.
- The affected area has an increased density.
- Fissures and mediastinal structures displace towards atelectasis.
- The loss of volume is due to incomplete expansion or collapse of the lung parenchyma.
Which type of atelectasis results from adjacent scarring?
- Cicatrization
- Compressive
- Obstructive
- Restrictive
- Mixed
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
The explanations are very clear and followed step-by-step. Also there are a lot of cases and until the end of the lecture you see enough of the same pathology to have an idea. Love it!