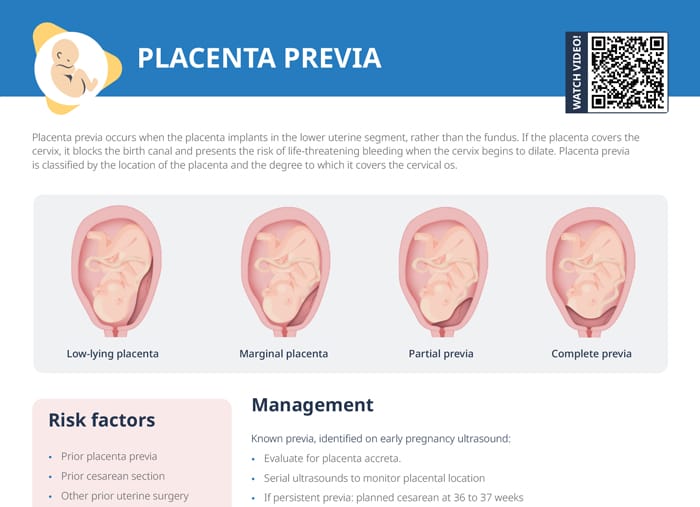
What is vasa previa?
Vasa previa occurs when fetal vessels are not fully contained and protected within the umbilical cord. Rather, exposed vessels connecting the umbilical cord and placenta run through the membranes within 2 cm of the internal cervical os.
This risks of this condition include severe bleeding and compromised oxygen supply during labor or membrane rupture, potentially causing fetal distress, hypovolemic and hypoxic injury, or fetal death.
Vasa previa vs normal
The key difference between vasa previa and a normal pregnancy is the positioning of the fetal blood vessels relative to the cervical os. In vasa previa, the vessels are exposed and at risk, whereas in a normal pregnancy, they are safely positioned away from the cervical opening.
Related videos
Vasa previa types and diagnosis
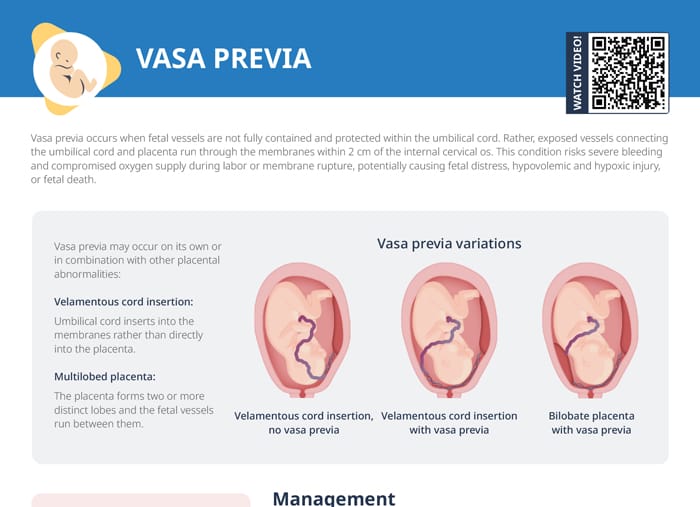
Vasa previa variations
Vasa previa may occur on its own or in combination with other placental abnormalities:
- Velamentous cord insertion without vasa previa
- Velamentous cord insertion with vasa previa
- Bilobate placenta with vasa previa
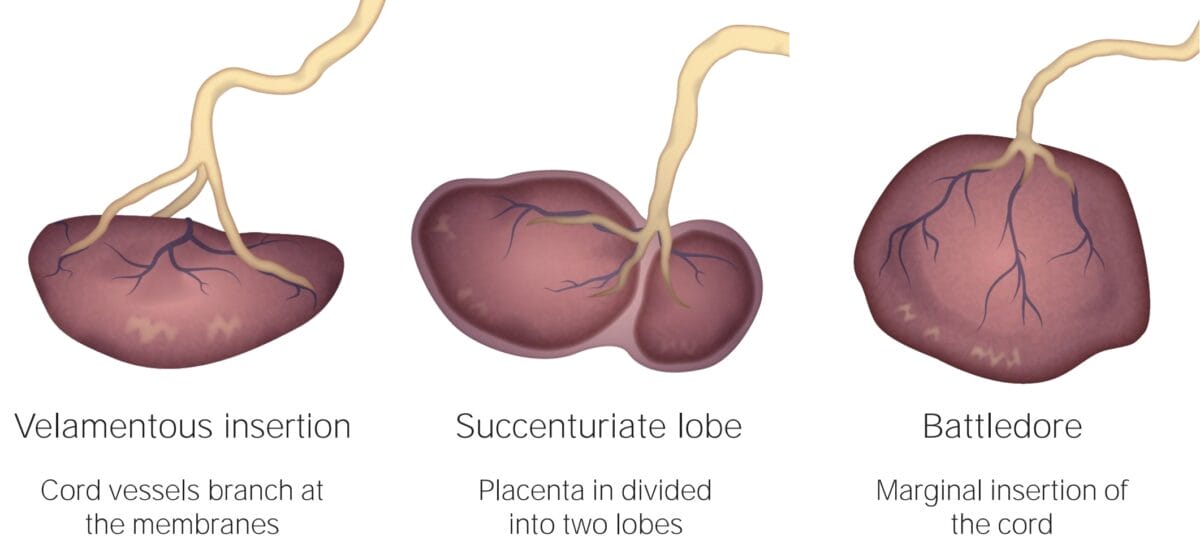
Velamentous cord insertion occurs when the umbilical cord inserts into the membranes rather than directly into the placenta. In a multilobed placenta, the placenta forms two or more distinct lobes and the fetal vessels run between them.
Vasa previa types
Vasa previa symptoms and diagnosis
The most common symptom of vasa previa is painless vaginal bleeding, often following the onset of labor or the rupture of membranes.
Vasa previa can also present with decreased fetal heart rate variability, fetal heart rate decelerations, persistent bradycardia, or sinusoidal FHR tracing.
For every client who presents with vaginal bleeding in the 3rd trimester, an ultrasound should be done to check for vasa previa.
Vasa previa ultrasound assessment
On an ultrasound, vasa previa is identified by the presence of blood vessels crossing the internal cervical os. Pay attention to the location of the placenta: Vasa previa often occurs in pregnancies with a low-lying placenta or placenta previa. As a nurse, if you suspect vasa previa on an ultrasound, it is important to promptly alert the case to the obstetrician for further evaluation and management.
Vasa previa management
After vasa previa has been diagnosed, the following measures are needed:
- Prenatal monitoring to detect cord compression
- Potentially serial cervical length monitoring at 32 weeks
- Corticosteroids for fetal lung development
- Planned cesarean delivery at 34 to 37 weeks: cesarean is recommended prior to ROM which is hard to predict → goal is to balance the risk of fetal death with the risk of iatrogenic prematurity
If the vasa previa has not been diagnosed on ultrasound during the pregnancy and a client presents with bleeding in the third trimester, implement the following interventions:
- Serial vital signs and electronic fetal monitoring
- Ultrasound to diagnose vasa previa
- Prepare client for an emergency cesarean
- Alert NICU team
Restrictions for vasa previa clients
Educate the client about the condition and precautions they can take to minimize the bleeding risk with vasa previa, including:
- Avoiding travel
- Reduced physical activity and pelvic rest
- In severe cases, bed rest or hospitalization
- Set up an emergency plan and plan for delivery early (cesarean)
- Teach about the warning signs like bleeding, pain, or fetal distress
Can vasa previa resolve itself?
Vasa previa generally cannot resolve by itself. The condition is defined by the placement of fetal blood vessels across or near the cervical os, and once these vessels have developed in this location, they typically remain there throughout the pregnancy.