Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Tissue Typing, Immunosuppressive Drugs and GVHD
-
14 Slides Transplantation Immunology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
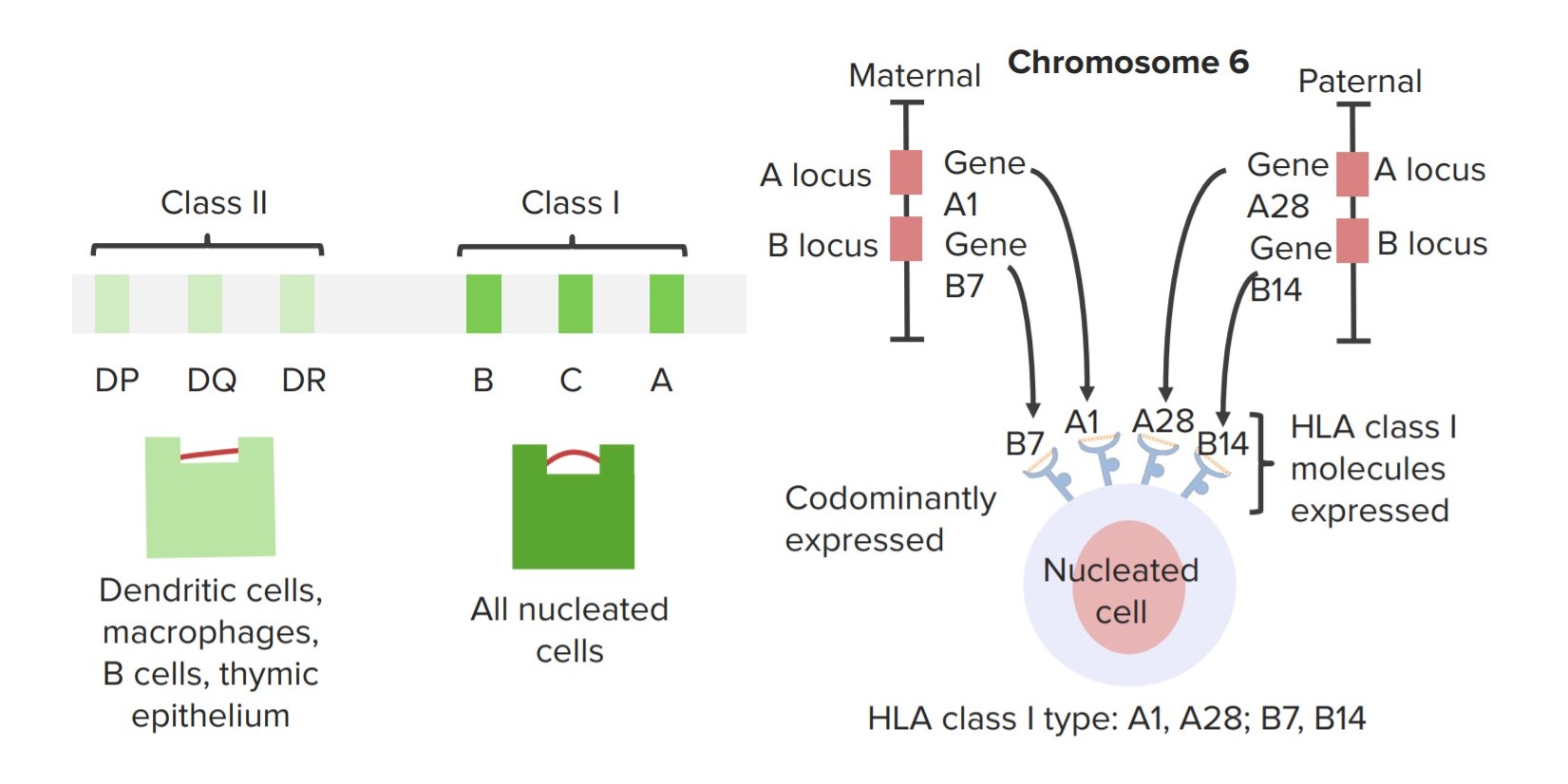
00:01 This need to match the MHC between the donor and the recipient necessitates tissue typing of the donor and the recipient. This patient has developed renal failure and needs a kidney transplant. He has been typed for HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-DR. 00:25 And as we can see, this particular individual is HLA-A2, A5, B7, B13 and DR2, DR1. 00:34 Here we have a number of different patients that are awaiting a transplant. 00:41 They are placed on a register with many others. 00:44 Each of whom are likely to have different HLA types as shown on this slide. 00:51 When tissue typing occurs, a potential donor is HLA typed and each kidney is sent to a hospital where a good HLA match patient is waiting to have the graft transplanted. 01:08 A blood sample from the donor is also sent to the hospital. 01:13 In the cross match, donor B-cells are mixed with recipient’s serum. 01:18 In this case, preformed antibodies are binding the donor cells. 01:23 This transplant cannot take place. 01:27 However here we see that the recipient has no antibodies against donor cells and the transplant can go ahead. 01:36 Preformed anti-donor antibodies can result from pregnancy, blood transfusion, or indeed a previous transplant. 01:47 Let’s look at the mechanisms of action of immunosuppressive drugs. 01:51 These are almost always required, because it’s almost impossible to get an identical match between the donor and the recipient unless there is an identical twin. 02:01 There is almost always some mismatch as regards the MHC. 02:08 Here we can see an anti T-cell receptor antibody that is used to block the interaction between the T-cell receptor and the MHC. 02:19 The drugs, cyclosporine and FK506 inhibit the calcineurin signaling pathway. 02:30 CTLA4-Ig interferes with the co-stimulatory interaction between B7 and CD28, thereby preventing co-stimulation and activation of T-cells. 02:48 Both of these approaches, using cyclosporine, using FK506, using CTLA4-Ig, using anti T-cell receptors, at the end of the day they have the same effect. 03:00 They block the activation of T-cells and block the subsequent production of interleukin-2. 03:06 Antibodies against the interleukin-2 receptor can be used to prevent T-cell stimulation by this particular cytokine. 03:19 Therefore signaling through the IL-2 receptor leading to lymphocyte activation will be blocked. 03:27 The immunosuppressive drug rapamycin inhibits mTOR which is involved in the signaling process. 03:36 And therefore, there is prevention of proliferation of the lymphocytes. 03:41 And finally, azathioprine and mycophenolate can also interfere with the proliferative process and act as immunosuppressive drugs. 03:52 One normally thinks about the recipient rejecting the graft, but the opposite situation can occur when an individual is being given a hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. 04:04 This can result in graft versus host disease. 04:09 In this situation, you have an individual, perhaps a patient with leukemia that is being treated with radiation or with cytotoxic drugs that is damaging their own immune system. 04:22 They are then given a transplant of hematopoietic stem cells, perhaps from a bone marrow. 04:28 Could be from cord blood, could be from peripheral blood. 04:32 These cells are of course immune system cells that are being used for the transplantation. 04:40 And the donor T-cells can recognize the foreign MHC on the recipient cells, leading to the death of those cells and causing graft versus host disease.
About the Lecture
The lecture Tissue Typing, Immunosuppressive Drugs and GVHD by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Transplantation Immunology. It contains the following chapters:
- Tissue Typing
- Mechanisms of Action of Immunosuppressive Drugs
- Graft versus Host Reaction
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following immunosuppressive drugs directly inhibits mTOR signaling?
- Rapamycin
- Cyclosporine
- Tacroliums
- Muromonab-CD3
- Methotrexate
Which of the following regarding tissue typing and graft survival is MOST ACCURATE?
- Recipients without preformed donor-specific antibodies have a higher chance of graft survival.
- Recipients with preformed donor-specific antibodies have a higher chance of graft survival.
- Recipients with preformed recipient-specific antibodies have a higher chance of graft survival.
- Recipients with preformed recipient-specific antibodies have a lower chance of graft survival.
- Recipients without preformed recipient-specific antibodies have a lower chance of graft survival.
Which of the following best describes the cause of graft versus host disease?
- Donor white blood cells within the graft tissue recognize the recipient as foreign.
- Host white blood cells within the graft tissue recognize the recipient as foreign.
- Host white blood cells within the graft tissue recognize the donor as foreign.
- Host white blood cells recognize the graft tissue as foreign.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
He is very entusiasthic at teaching, and makes very clear examples. I love him.