Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Syphilis
-
Slides Dermatology Infectious Disorders.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
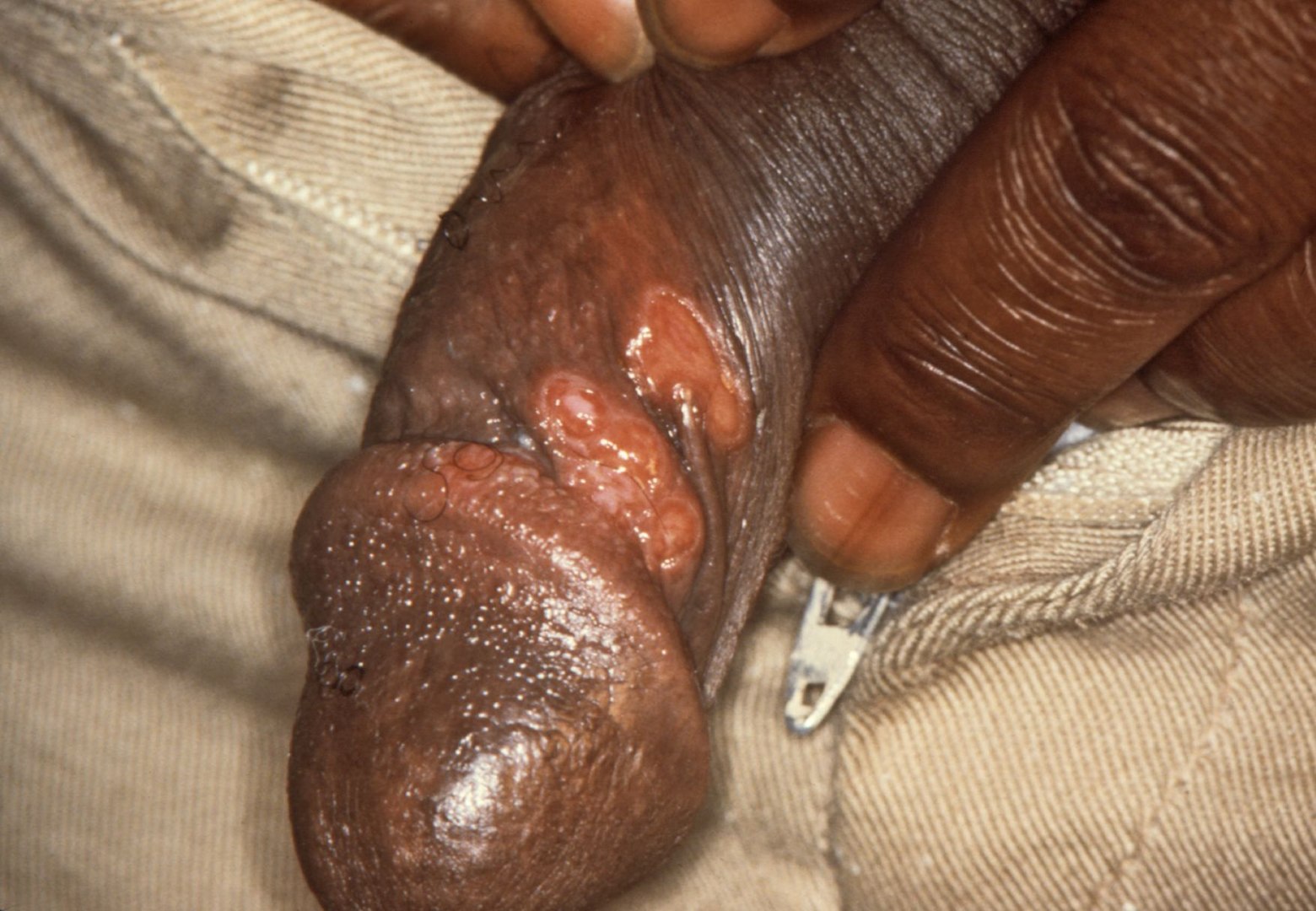
00:02 Syphilis. 00:03 A few words about syphilis when dealing with dermatology. 00:06 Infectious. 00:07 Treponema pallidum. 00:09 Diagnosis by RPR and the stages is where I want to spend a minute. 00:14 If it’s a primary chancre, remember that a chancre is painless. 00:19 A chancre is a painless ulcer in either the oral or genital region as opposed to or compared to chancroid. 00:27 A chancroid, ouch, it hurts so much so that I will be crying, referring to Haemophilus ducreyi. 00:39 So Haemophilus ducreyi will be chancroid, D and D. 00:45 And you’re crying because it hurts. 00:49 Chancre is painless and this also might be located in the genital regions or maybe perhaps around the oral regions. 00:58 The secondary: The rash should be on the palms and soles, may or may not be on the trunk. 01:03 And tertiary, may involve the bone and some of the soft tissue and this then referred to as being your necrotic type of ? Good. 01:12 Granulomas. 01:14 And you have your CNS. 01:16 Gumma is what we’re talking about for tertiary. 01:19 Remember please, secondary: Rash on the palms and the soles, don’t forget those for secondary. 01:27 For syphilis, we’re showing you penis in which you’d find your ulcer, in which in this patient, was not expressing pain because a chancre is painless. 01:41 Guess what you’re going to find? You’re going to find these spirochetes on dark field microscopy and positive for RPR. 01:49 Two to three weeks after exposure. 01:54 Occurs weeks to month after infection. 01:56 The palms and soles would be the targets if you’re referring to secondary type of syphilis and if you have alopecia, it will be like a moth-eaten alopecia and condyloma lata. 02:13 Remember lata is syphilis. 02:15 “I want a lata syphilis.” I'm just joking, but condyloma lata would be the infection on the skin that you would be looking for in syphilis, usually secondary. 02:27 If it’s late and tertiary, take a look at what happens here. 02:30 We’re talking about two years on average after infection. 02:34 It’s the gumma plus a granulomatous type of ulcer, a necrotizing type of granuloma. 02:39 This is referred to as being your gumma. 02:41 CNS involvement with dementia and confusion. 02:44 Remember tabes dorsalis could be an obvious manifestation and you could also affect your pupil and we call this being Argyll Robertson type pupil. 02:56 Aortic involvement could take place in which your patient has or undergoes endarteritis obliterans of the vasa vasorum, resulting in aortitis and therefore aortic regurgitation. 03:07 And these are all items and symptoms that we’ve discussed earlier. 03:12 Syphilis is a wonderful medical situation or clinical situation in which you can truly move from head to toe and kind of integrate the very subjects. 03:26 Management: Primary, secondary, early latent: a single dose of your penicillin. 03:32 Latent disease: You’re thinking about three doses at one-week intervals and during penicillin, patients develop what’s known as a reaction. 03:42 I want to make sure that we’re clear about this. 03:44 So let’s say that the patient is put on penicillin during a syphilitic infection. 03:50 I’m not going to spend too much time on management, but this one’s important. 03:53 It’s called Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. 03:58 So what happens is that during the penicillin therapy, an acute febrile reaction frequently accompanied by headache, weakness in the joints with 24 hours of treatment. 04:10 And what ends up happening is the fact that the penicillin is in certain patients breaking down the syphilis or spirochete so quickly, that this then causing a secondary reaction in which now you’re patient has developed, post penicillin, an acute febrile illness. 04:28 Along with this, myalgia. 04:31 When? Within one day of that treatment on average. 04:36 Most common among patients with early syphilis because of maybe the abundance of the organisms is the theory.
About the Lecture
The lecture Syphilis by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Infectious Skin Diseases.
Included Quiz Questions
A 28-year-old man presents with a painless 1-cm ulcer on the shaft of the penis with a raised, indurated margin. What test is indicated to help with the diagnosis?
- RPR (rapid plasma reagin)
- Culture of scrapings
- Skin biopsy
- Wood lamp test
- Tzanck smear
What is a manifestation seen in late syphilis?
- Gummas
- Painless ulcer
- Diffuse rash involving the hands and soles
- Nephrotic syndrome
- "Moth-eaten" alopecia
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |