Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
-
Slides Autoimmune Disease.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
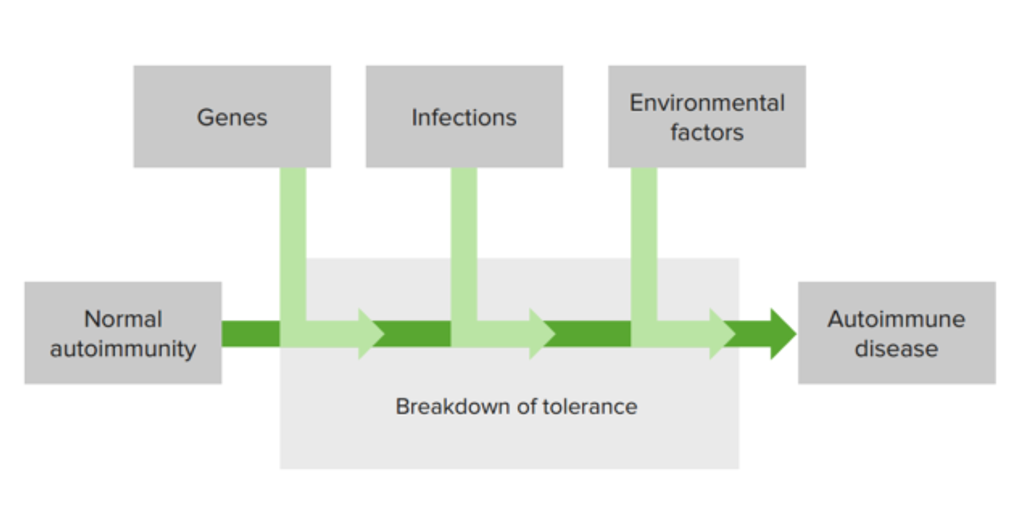
00:01 Turning now to a disease that is not an organ specific disease like type I diabetes or the thyroid autoimmune diseases, but is a rheumatological condition - rheumatoid arthritis. 00:16 In rheumatoid arthritis, there is advanced symmetrical involvement of joints of the hands. 00:23 The proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints are typically affected in rheumatoid arthritis. 00:31 And as you can see on the right hand side, there’s a radiograph of the hand of a patient with advanced rheumatoid arthritis illustrating cartilage loss and bone erosion; very typical of rheumatoid arthritis. 00:48 Like all autoimmune conditions, the disease develops because of the inheritance of a number of susceptibility genes. HLA being one but several others have been implicated. A failure of immunological tolerance and up-regulated lymphocyte activation of autoantigen specific lymphocytes. Environmental factors include infection and smoking. One of the specific things about rheumatoid arthritis is that there is a particular enzyme modification that is occurring, that is referred to as citrullination. And this modification of an amino acid in the sequence of a variety of proteins leads to the development of autoantibodies, and T and B-cell responses to self antigens within the joint of the patient with rheumatoid arthritis leads to the development of pathology. 01:53 Within the joint, Th17 cells, Th1 cells and plasma cells producing autoantibodies will cause damage to the synovial membranes. There are rheumatoid factor autoantibodies which are autoantibodies against the Fc part of IgG. So this is an autoantibody against another antibody. And these rheumatoid factors can be either IgM or IgA or IgG rheumatoid factors. 02:25 But they all recognize exactly the same antigen. 02:28 That antigen is actually the Fc part of an IgG molecule. 02:32 Little bit hard to get your head around that, I know. 02:34 But just think about it; an antibody is a glycoprotein molecule just like anything else. 02:39 It can act as an antigen. 02:41 And in this case the Fc part of IgG is the antigen being recognized by autoantibodes. 02:47 And there are also autoantibodies present to citrullinated proteins and peptides. 02:53 The result is synoviocyte activation, the production of cytokines and inflammation, causing the destruction of both cartilage and the underlying bone.
About the Lecture
The lecture Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune Disease. It contains the following chapters:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Acute Rheumatic Fever
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is the most specific antibody found in patients with rheumatoid arthritis?
- Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies
- Anti-carbamylated protein antibodies
- Antinuclear antibodies
- Anti-double strand DNA antibodies
- Rheumatoid factor antibodies
Which best describes citrullination?
- A specific amino acid conversion in a protein
- Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene mutation
- Failure of tolerance to self-antigens
- Targeted damage to specific joints
- Alteration in specific gene sequences
Which of the following patterns of joint involvement is more characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis?
- Proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints.
- Cervical and upper thoracic intervertebral joints
- Lower thoracic and lumbar intervertebral joints
- Progressive cartilaginous destruction of pelvic acetabulum
- Asymmetric involvement of large joints
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Detailed the disease's pathophysiology in a precise format that was easily understood.