Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Invasive Bacterial Diarrhea
-
Slides Small and large bowel.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
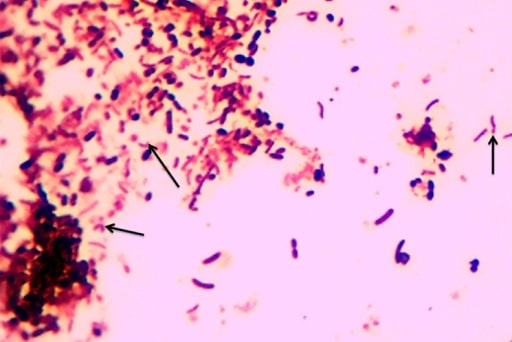
00:00 Lets talk about some important invasive bacterial diarrhea. What you can expect clinically and how you would manage your patient effectively. Shigella. Now, shigella is rather interesting. 00:11 And the reason for that is because there is certain recommendations that are made by CDC. 00:16 But without going into too much detail, lets just make sure I give you just enough so you know what's going on. Number 1, bloody diarrhea with fever and bacteremia. Well you've heard of something called shiga toxin or shigella dysenteriae type I which very much behaves like EHEC or Enterohemorrhagic E.coli associated with HUS. 00:38 Fluorquinolones or third generation cephalosporin are first line due to the high amount of ampicillin resistance. 00:45 Salmonella typhimurium is the most common in US. Associated with poultry, non-bloody diarrhea. Treatment of mild symptoms may lead to prolonged carrier state and here your management would be ciprofloxacin. 01:00 Parahemolyticus, ingestion of undercooked shellfish as I mentioned earlier. 01:06 Because the disease is usually self-limited, antibiotics are normally not given. 01:10 But if cases are severe, doxycycline, fluoroquinolones and macrolides have shown some ability to shorten symptom duration. 01:19 And we have the E.coli or EHEC and hemorrhagic. And at this point I would think that you have O157:H7 memorized. Undercooked beef is what you're thinking about. Bloody diarrhea in a child, hemolytic uremic syndrome. Uremia to you should mean renal failure. In a child next step of management, my goodness you choose Hemodialysis, next step of management, HUS. Forever more? Thank goodness no. 01:50 The child comes back to be perfectly normal. That's what makes me happy. 01:53 When a child gets sick, that's not nice. Antibiotic therapy not necessarily effective hence the hemodialysis. 02:01 Staph. aureus, here we have extremely rapid, rapid,rapid type of diarrhea that we talked about. 02:10 Enterocolitis with positive stool culture. Yersinia enterocolitica. Chronic enteritis. Can mimic your Crohn's. 02:19 Could be associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Treatment here is your co-trimoxazole. 02:26 Campylobacter jejuni. Extremely common and mimics once again your ulcerative colitis. 02:36 We have vibrio vulnificus. Raw shellfish or wound infection. I was talking to you about this earlier when I was referring to the gulf. So vulnificus gulf, if you want to call it gulfnificus, that might perhaps help you. And the wound infection is what happens here. It enters and take a look, I told you mortality increases to the point where this is exactly what happens. Necrotizing fascitis in cirrhotics. Vulnificus.
About the Lecture
The lecture Invasive Bacterial Diarrhea by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Small and Large Intestine Diseases: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
A patient presents with bloody diarrhea, and Shiga-like toxin is identified. An initial treatment of ampicillin did not decrease the symptoms. The doctor discusses the possibility of aplastic anemia and suggests the use of an antibiotic to treat virulent strains. Which antibiotic is the doctor referring to?
- Chloramphenicol
- Repeat dose of ampicillin
- Nitrofurantoin
- Azithromycin
- Amoxicillin
What is the MOST common species of Salmonella in the US?
- Salmonella typhimurium
- Salmonella enteritidis
- Salmonella paratyphi
- Salmonella bongori
- Salmonella typhi
A patient loves seafood and has shellfish for his dinner. He develops fever and vomiting. What is the probable cause?
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Vibrio cholerae
- Shigella
- Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
- Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli
A patient consumes an undercooked beef burger. Over the next few days, he has multiple episodes of bloody diarrhea. Which organism is the probable cause?
- O157:H7 strain of Escherichia coli
- Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
- Salmonella
- Shigella
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
A patient develops flask-shaped ulcers with hepatomegaly. He loves chicken to be part of his diet. The Widal test shows high titers. What is the probable organism?
- Salmonella
- Bacillus cereus
- Campylobacter jejuni
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli
A patient presents with increased creatinine levels and low platelets along with bloody diarrhea. Which organism is the probable cause?
- O157:H7 strain of Escherichia coli
- Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
- Campylobacter jejuni
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Salmonella
Which disease does Yersinia enterocolitica infection mimic?
- Crohn's disease
- Ulcerative colitis
- Ischemic bowel disease
- Colon cancer
- Pseudomembranous colitis
Which of the following complications is associated with Vibrio vulnificus in a patient with cirrhosis?
- Necrotizing fasciitis
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Necrotizing lymphadenitis
- Necrotizing pancreatitis
- Necrotizing granulomas
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |