Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Herpes Simplex (HSV)
-
Slides Dermatology Infectious Disorders.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
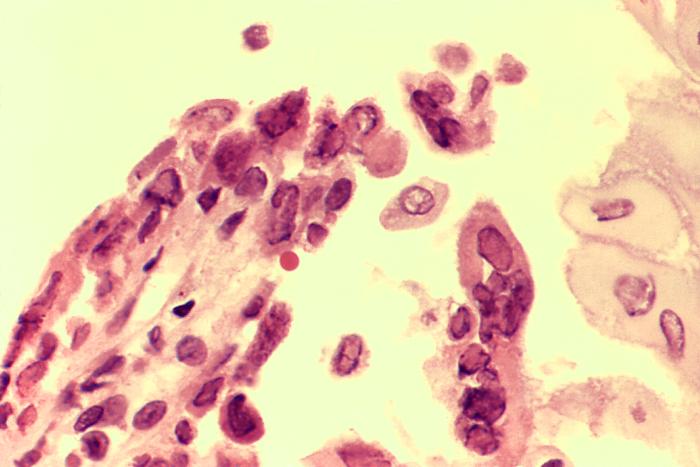
00:01 Herpes. 00:02 HSV 1, often referred to as being your sore or cold sore that you see here in this patient. 00:09 HSV 2 is associated with genital type of herpes. 00:13 Remember that HSV1 if it ever affects the brain, may result in damage or influences and affects the frontal and temporal lobe whereas if it’s HSV 2 and it affects the brain, think of TORCHES and you’re thinking about diffuse involvement of the brain. 00:31 Overlap can occur between the two viruses. 00:34 and the proportion of newly diagnosed HSV-1 genital infections has increased significantly in the last 20 years. 00:41 Small, fluid-filled vesicles as you can imagine with an erythematous type of base. 00:46 HSV 2, genital. 00:48 HSV 1, more commonly oral. 00:53 Morphology: Dew drops on a rose petal, same description that we’ve seen earlier with chicken pox. 00:59 Both of these organism come under the family of herpes. 01:02 So therefore, the vesicles remain, well, in description-wise, pretty similar. 01:08 Fluid-filled vesicles with an erythematous base tend to occur in the same area during stress or illness and often painful when actually active. 01:18 Herpes simplex. 01:22 Demographics: Up to 1 in 6. 01:25 Some would say 1 in 4 nowadays with the genital herpes, which is HSV 2. 01:30 So it’s almost like if you don’t have this, there’s something wrong with you. 01:33 It’s amazing that is it’s as high as you see here. 01:37 An even higher number have oral herpes, referring to your HSV 1 or cold sores. 01:46 As soon as you hear herpes, what are you thinking about? Tzanck smear. 01:50 And if you’re thinking about the skin, what are you going to find? What we saw earlier, multinucleated keratinocytes and we have identical to that seen with zoster, which is what, please? Reactivation of your VSV from the dorsal root ganglion, and therefore, following a dermatome type of appearance causing pain, pain, pain. 02:10 Keep things simple. 02:11 Herpes, Tzanck. 02:13 If it’s Tzanck and if it’s the skin, you can expect there to be as you see in this image, multinucleated giant cells here in the keratinocytes. 02:22 It’s important to point out that, while knowing about Tzanck smear findings is important for testing purposes, it has limited clinical utility in the present day. 02:34 Current diagnostic strategies preference PCR assays, viral culture, or serologic testing. 02:43 Management: Oral acyclovir to shorten the cycle of outbreaks, but will not cure, obviously, because it’s a virus. 02:51 Recurrence caused by reactivation of virus lying dormant in the nervous tissue. 02:59 Just like it would for VZV.
About the Lecture
The lecture Herpes Simplex (HSV) by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Infectious Skin Diseases.
Included Quiz Questions
A 24-year-old woman presents with painful, small vesicles on the vermilion border of the lower lip, and she states she has been under a lot of stress lately. What is the most likely cause of this condition?
- Herpes simplex virus
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Human papillomavirus
- Varicella-zoster
- Measles
What is the recommended treatment for painful oral herpetic lesions?
- Oral antivirals
- Oral antibiotics
- Topical antibiotics
- Topical steroids
- Oral steroids
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |