Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Glucagon: Functions
-
Slides Endocrine Pancreas Endocrine System.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
00:02 Now what does glucagon do? The functions of glucagon are primarily it's break down glycogen. 00:11 So there's a lot of glycogen stored in places like the liver. 00:14 And this is one of the stimuli to have it break down. 00:18 It's done by activating the enzymes which break down glycogen and inhibiting the enzymes that form new glycogen. 00:30 The last thing that it does is stimulates the enzymes which do the final break down product going from glucose 6-phosphate to glucose. 00:42 Then the glucose is transported out of the cell to transporter. 00:49 Now that is the process of breaking down glycogen, releasing glycogen out in the circulation. 00:56 So this should remind you of the process of --we're not building things here with glucagon. 01:02 We're breaking down glycogen so we can use that blood glucose. 01:07 What else does it stimulate. 01:10 The enzymes associated with gluconeogenesis. 01:13 So gluconeogenesis is the process of making new glucose out of things that weren't glucose to start with like amino acids. 01:24 It also stimulates the enzymes associated with lipolysis. 01:27 So there you have fat. 01:30 You can break it down into more simple form and release free fatty acids into the circulation. 01:36 And finally it stimulates ketogenesis which is the formation of ketone bodies. 01:42 So between all four of these processes, you should think of --okay, we're breaking down glycogen so that we can get more blood glucose. 01:51 We're making new blood glucose. 01:53 We're breaking down fats. 01:54 So the free fatty acids are in the circulation. 01:57 And we're forming ketone bodies. 01:59 All of those can be used as energy substrates for different tissues of the body. 02:05 So glucagon is really preparing you so make sure you can use energy that's been stored in the body. 02:13 So you can use it for increase in metabolism. 02:18 So let's now look at this in more of a systemic effect. 02:22 The systemic view always let's us take a step back, point to the various tissues, see where the different molecules are going. 02:31 And as you're studying for your test, this is a very important thing to do, it's easy to get lost in the leaves of a tree without taking a step back to look at the branches and how their shape is. 02:43 So that is this kind of a process. 02:45 So we know we have the release of blood glucose. 02:50 Usually comes from the liver by breaking down glycogen through a number of steps and then finally releasing blood glucose. 03:01 Fatty acids are also broken down through lipolysis and moved out of adipose tissue into the circulation. 03:11 Those fatty acids are also form the basis of backdrop for ketoacids. 03:19 So here we've got increases in glucose, fatty acids and ketoacids. 03:25 All help us do what, increase our metabolism. 03:30 Because we're responding to some sort of stressful environment.
About the Lecture
The lecture Glucagon: Functions by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Endocrine Physiology.
Included Quiz Questions
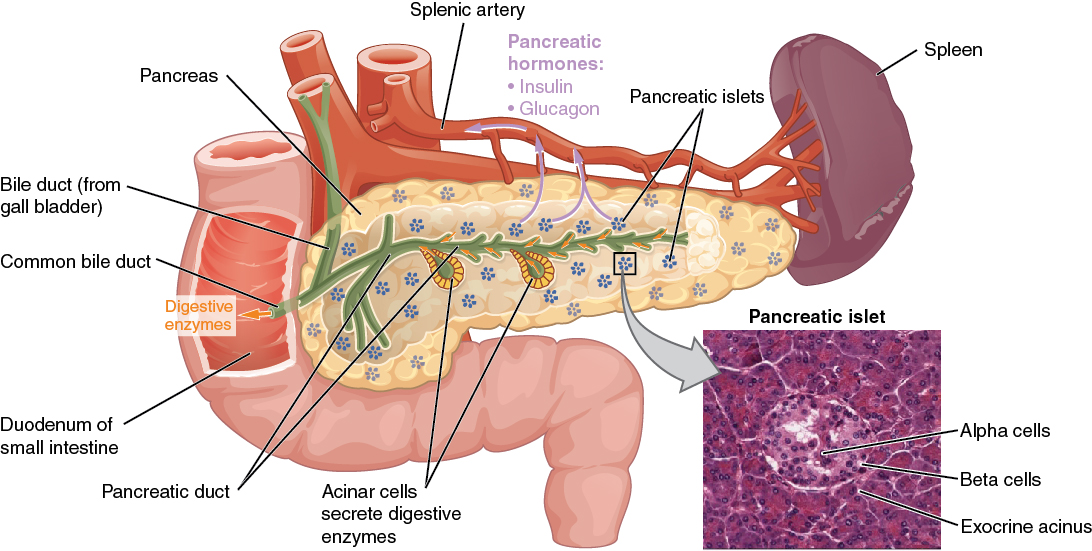
Which of the following organs serves as storage organ of glycogen?
- Liver
- Adrenal gland
- Spleen
- Pancreas
- Gall bladder
Which of the following is NOT a metabolic function of glucagon?
- Proteolysis
- Glycogenolysis
- Gluconeogenesis
- Lipolysis
- Ketogenesis
In which of the following tissues are ketoacids produced?
- Liver
- Skeletal muscle
- Spleen
- Kidney
- Ovaries
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |