Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Vision: Structure and Function of the Eye
-
Slides 02 Vision NervousSystem.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
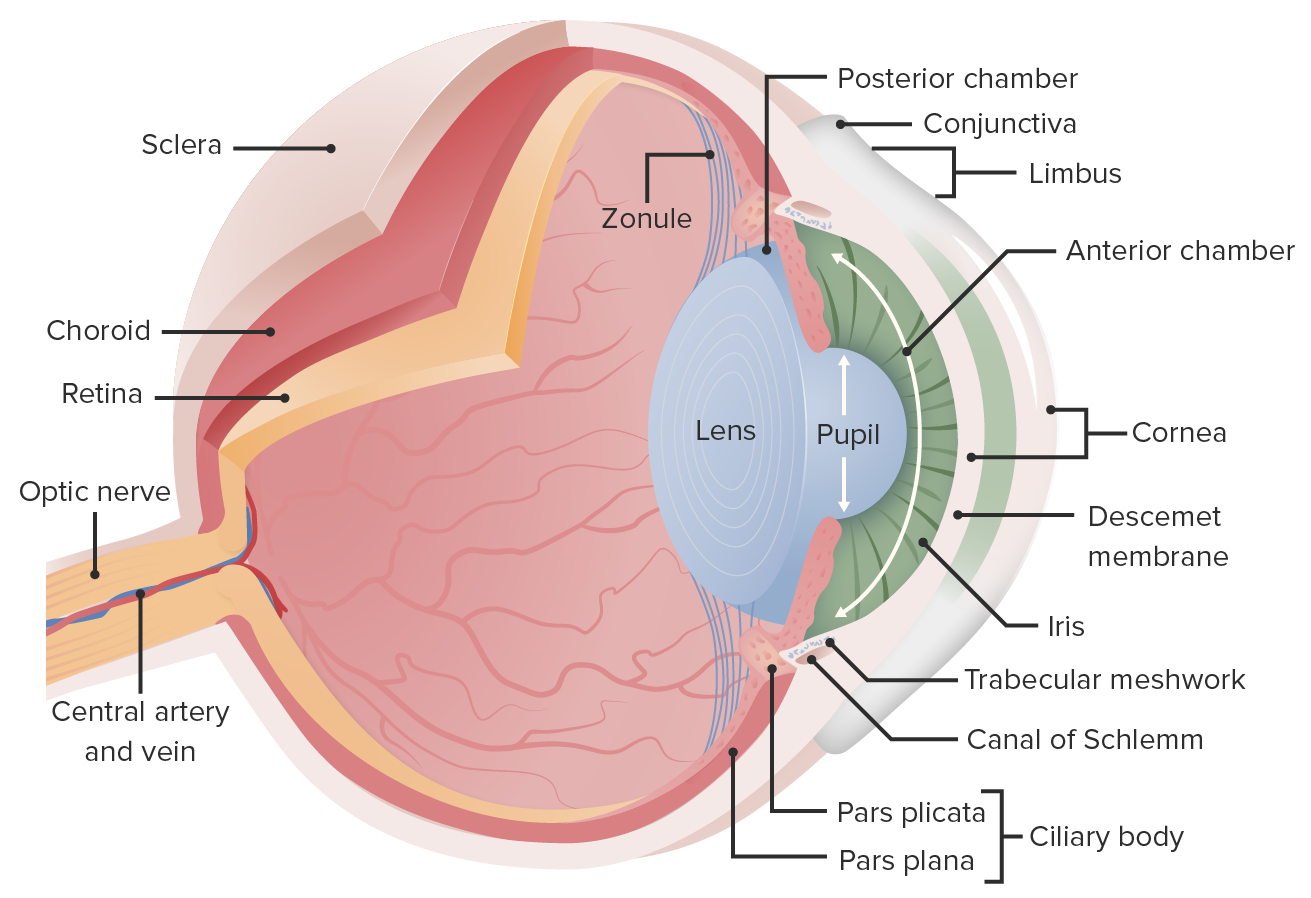
00:02 Vision. We will go through a number of different structures and functions of the eye. 00:10 The most important of which, is to try think about what the eye needs to function correctly. 00:16 It is gonna need to have light. 00:18 It’s gonna need to have bright enough light to be able to get that image to the back of the eye. 00:23 And lot of that depends upon how open the eye is to let in the light in. 00:30 Besides that, the other thing that’s gonna be very important is the frequency of that light. 00:36 Now remember light has two properties in physics. It is both a photon, a particle, as well as a wavelength. 00:45 So we have to keep both of those intension as we move forward trying to discover how we’re going to collect that and then interpret it in the brain. 00:57 Going over some of the structures will be helpful in this initial process. 01:03 We have an anterior chamber that has fluid associated in it and a cornea. 01:09 The reason why you need to have this fluid in this anterior chamber is because the cornea is avascular, meaning that it doesn’t have any blood flow going to it. 01:19 And that is important for us in the vision sense because if you have a red blood cells travelling through the cornea, you would get light would not be able to penetrate some of the heme molecules. 01:30 So in this case it doesn’t have any blood vessels, but you still have to bathe it with fluid. 01:36 so that those structures don’t die. 01:41 The iris will help control the pupil diameter. 01:45 You have the posterior chamber in which the fluid is starting from and eventually moves through the pupil into the anterior chamber. 01:55 This process is ongoing. 01:57 You’re always making new fluid from the ciliary epithelium into the posterior chamber travelling to the anterior chamber. 02:07 That is a constant process always flowing in that direction. In fact it develops a pressure. 02:13 So people often times measure an intraocular pressure. And that should be somewhere between about 8 to 22 millimeters. 02:21 If it’s too high, they start to get worried about glaucoma. 02:27 The lens of the eye is going to help focus the image onto the back of the eye or the retina. 02:36 These zonule fibers are what pull the lens either stretching it or making it less stunt so that you can get that focused image to the right spot. 02:49 You also have other structures towards the back of the eye such as the retina. 02:53 The retina is going to have our photoreceptive cells in it. 02:58 There’s a couple special spots like the fovea, which only have cones in it. 03:05 We’re gonna go through rods and cones quite a bit when we talk about eye structure function relationship. 03:11 You also have the optic disc. The optic disc is where the optic nerve leaves from. 03:17 So there are actually no photo receptors in the optic disc. It’s a blind spot if you want to think of it as such. 03:24 You will not see any images in this spot because this is where the nerves are travelling back to the brain. 03:32 Finally, everyone always thinks about the connective tissue. 03:36 The sclera is the kind of what you usually think of as the whites of the eye. 03:40 It’s that part of the eye that is going to be connective tissue and allow you to move your eye around so you can focus at different things.
About the Lecture
The lecture Vision: Structure and Function of the Eye by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Neurophysiology.
Included Quiz Questions
Into which chamber of the eye does the ciliary body secrete fluid?
- Posterior chamber
- Anterior chamber
- Vitreous chamber
- Sclera chamber
Where in the eye is a blind spot located?
- Optic disc
- Fovea
- Retina
- Choroid
- Cornea
Which of the following regions of the eye has the highest number of cone cells?
- Fovea
- Retina
- Optic disc
- Zonule fibers
- Choroid
Which of the following is considered a normal intraocular pressure?
- 13 mmHg
- 7 mmHg
- 5 mmHg
- 26 mmHg
- 24 mmHg
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |