Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
DPP-4 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Analogues — Diabetes Medications
-
Slides DiabetesMedications EndocrinePharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
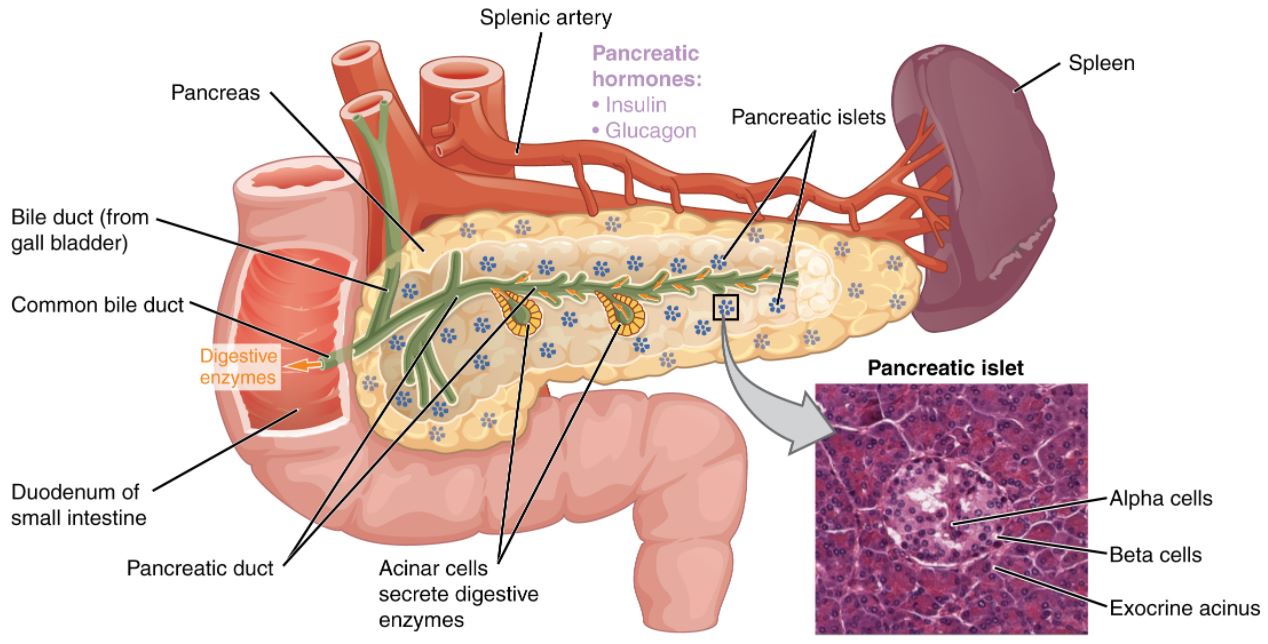
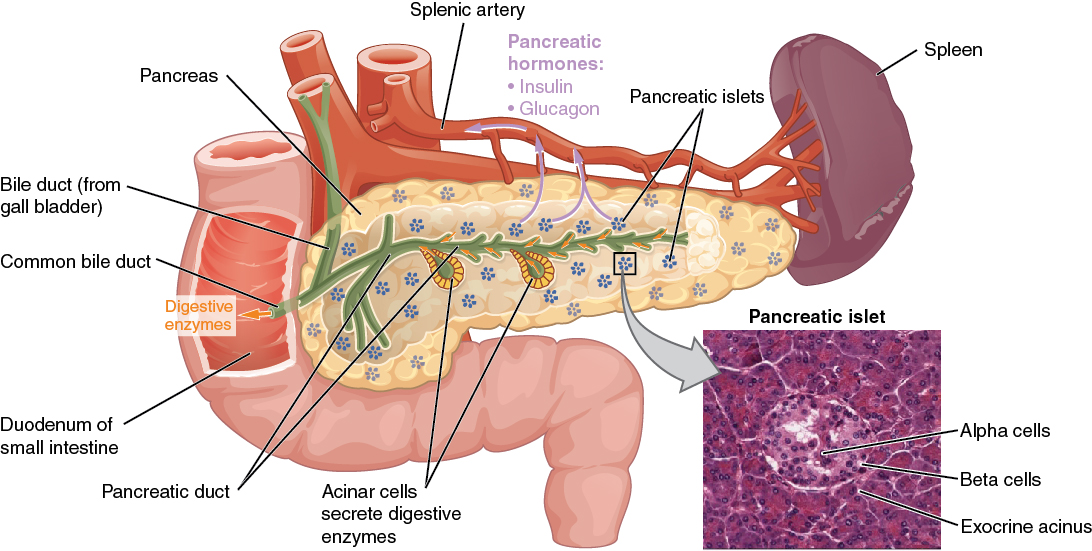
00:01 Let's move on to incretin based therapies. Now before I talk about the actual drugs, I want to talk about what incretins are. 00:09 So let's imagine you have an orange, and you decide to eat it, and it goes into your stomach. 00:15 Well your stomach and your small bowel will release something called incretins. These incretins act on the pancreas in two ways, not one way but two ways. First, it will act on the beta cells to actually increase the amount of insulin that you release into the body. 00:33 This decreases sugar levels. The other action is that it works on alpha cells, to decrease glucagon secretion and once again decrease sugar levels. Now this is an important distinction between these drugs and other drugs. 00:48 Because the amount of alpha activity with the incretins is much greater than the other medications or the other hormones. 00:57 A DPP4 is kind of like pacman because it goes in and eats the incretins. So it's kind of our built in mechanism to get rid of incretins once we no longer need them. A DPP4 inhibitor, gets rid of pacman, right. 01:13 So DPP4 inhibitor now allows more incretins to do its job for a longer time. So there is a couple of advantages to this particular method. First, it's a very natural way of affecting your systems because you're taking advantage of internal systems to bring down the sugar, rather than say artificially stimulating a cell to secrete insulin. 01:36 You're using incretins which are a naturally produced hormone and you're letting them do their job for a longer time. 01:42 The other advantages that the DPP4 inhibitors almost have no hypoglycemic risk. Now a GLP-1 analogue is an analogue of incretin. 01:55 So, DPP4 inhibitors and GLP-1 analogues are working through the incretin pathway. They are slightly different in terms of where they're acting on the pathway but they both have the same effects. 02:09 Net effect, improved glucose control. 02:13 Now let's just take a look at the various drugs in each of the drug class. If you notice and if you pay attention, the DPP4 inhibitors end in -gliptin. So there's saxagliptin, sitagliptin, linagliptin, and so on. 02:26 When you take a look at the GLP-1 analogues, they end in -tide. So there is exenatide, liraglutide, etc. 02:34 Now, the other thing I want to mention is that the GLP-1 analogues are injections, whereas the DPP4 inhibitors are pills. 02:46 Now, the DPP4 inhibitors have a neutral weight effect and they're very very well tolerated. They reduce the hemoglobin A1c by about 0.9 % if you take all the trials and put them together. I should mention though, that if you have an A1c that is 10.5, the amount of reduction that you will get from your DPP4 inhibitor is going to be up to 2 %. 03:09 If your A1c is 7.5, the amount of reduction you're going to get is probably 0.5 %. 03:15 So, your amount of reduction is proportional to where you're starting. So the higher your starting A1c, the more A1c reduction you are going to get. Generally speaking these are once a day tablets. There are actually subcutaneous forms that are given once a week however. They are rarely associated with pancreatitis but the risk is there. 03:37 You can get occasional nasopharyngitis with these medications. 03:42 In terms of the GLP-1 analogues, these are the drugs that end in -tide, they may actually cause weight loss. 03:48 So there is one study that looked at one of the GLP-1 analogues, and showed that 30 % of their patients, lost 3 kg and they kept it off. It reduces hemoglobin A1c anywhere from between 0.9 % and 1.5 %. So as an average I just put down 1.3 %. 04:08 Remember as I said before these are injections, and these medications are actually increased with more GI symptoms than the DPP4 inhibitors. Be aware, that these medications can be a associated with a very aggresive form of pancreatitis. 04:24 So monitor your patients closely when you start them on these medications.
About the Lecture
The lecture DPP-4 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Analogues — Diabetes Medications by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Endocrine Pharmacology. It contains the following chapters:
- DPP4-I's and GLP-1 Analogues
- DPP4-I's and GLP-1 Analogues – Adverse Events
Included Quiz Questions
Which statement most accurately describes the mechanism of action of incretin?
- Acts on the pancreas to reduce blood sugar
- Acts on the kidney to reduce blood sugar
- Acts on the small bowel to reduce blood sugar
- Acts on the pancreas to increase blood sugar
- Acts on the pancreas to increase blood lipase levels
What is the difference between DPP-4 inhibitors and GLP-1 analogs?
- DPP-4 inhibitors increase the level of incretins and GLP-1 analogs are incretin mimetics.
- GLP-1 analogs are mostly pills and DPP-4 inhibitors are mostly injections.
- GLP-1 analogs increase the risk of pneumonitis and DPP-4 inhibitors increase the risk of GI upset.
- GLP-1 analogs decrease HbA1c by 3% and DPP-4 inhibitors decrease HbA1c by 1.5%.
- GLP-1 analogs act on DPP-4 to increase levels of incretins.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
I was so confused when I read this in my book. Thank you for simplifying this medication process and making it understandable and easy to remember!
The "pacman" thingy is a stick forever in my brain. Thank you! I like how you presented and simplified incretins and DPP4Is