Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
MAO and COMT Inhibitors – Treatment of Movement Disorders
-
Slides Parkinson Disease and other Movement Disorders CNS Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
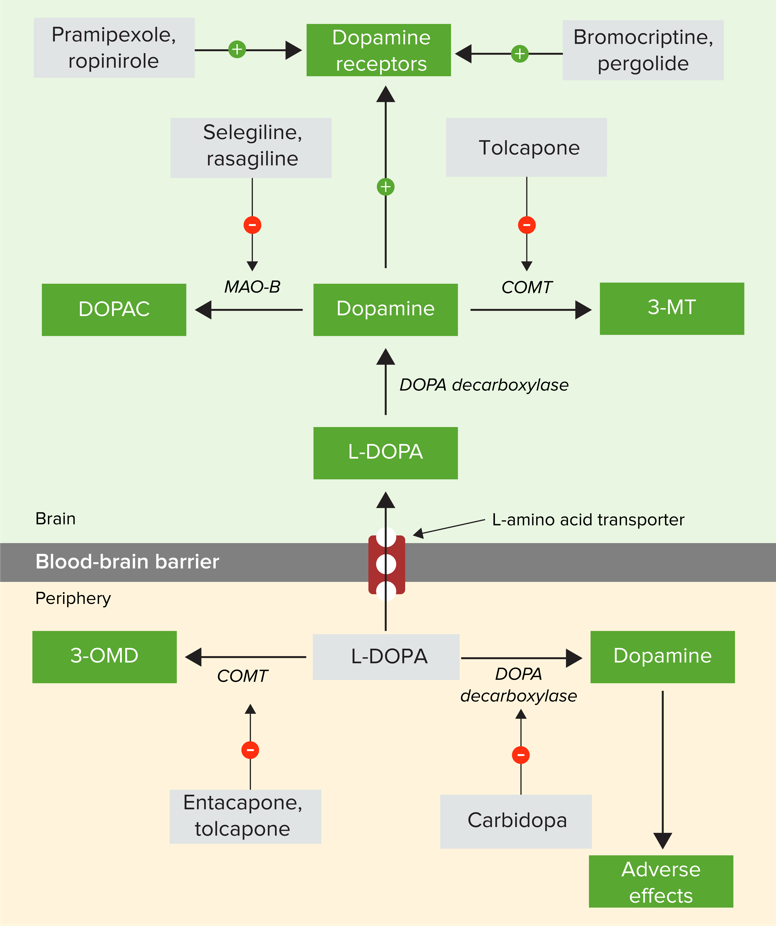
00:01 Let's talk about MAO inhibitors. We covered MAO inhibitors when we talked about antidepressants. 00:09 Selegiline is one of the MAO inhibitors that we use in Parkinsonianism. 00:14 Selegiline, and the new rasagiline is a selective MAO-B inhibitor. It is used in combination with L-DOPA. 00:22 On its own, it's not a particularly great drug. So, we almost always use it with L-DOPA. 00:27 Side effects can include anorexia, nausea and vomiting. In this particular drug, you'll have more nausea than the other medications. 00:38 Postural hypotension and dyskinesias like all of the other medications. It is also implicated in serotonin syndrome. 00:47 This is an important thing to remember that despite the fact that it's an anti-Parkinsonian drug, a lot of physicians forget that it is a MAO inhibitor. And a very common therapeutic mistake is to combine this with the serotonin specific reuptake inhibitor for the treatment of depression. 01:09 COMT inhibitors are quite numerous. We'll talk about one called tolcapone or Tasmar. 01:16 Now, COMT is one of the ways that we breakdown L-DOPA inside the tissues. 01:22 By blocking the COMT, you increase the levels of L-DOPA. Now, 3-MT also, which is a metabolite, competitively inhibits L-DOPA within the cell itself. So, by inhibiting this arm of breakdown, you actually have a much greater activity of L-DOPA than you initially would have predicted otherwise. 01:46 It is used in combination with levodopa, carbidopa. One of the things that you have to recognize is that this medication prolongs "on time". So, Parkinson's disease is a unique disease because you have on and off time where people are very hypokinesic and they don't move very much. 02:05 And then they're active and you know, it seems like they come to life. That's what we call "on time". 02:11 Using this drug prolongs that "on time" quite nicely. 02:16 Side effects. I'm beginning to sound like a broken record here, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, postural hypotension and dyskinesia. 02:26 Not surprising there. 02:28 Now, there're some very special considerations I want you to think about when we're using tolcapone. 02:33 Number 1, we have to reduce the dose of levocarbidopa. Number 2, we have to monitor liver function test, and in some areas, in some states like California, we have to get consent before using this medication. 02:48 One thing that all patients will complain about is an orange urine. It's nothing to worry about. 02:53 It just happens to be the metabolite of the drug.
About the Lecture
The lecture MAO and COMT Inhibitors – Treatment of Movement Disorders by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course CNS - Pharmacology. It contains the following chapters:
- MAO Inhibitors
- COMT Inhibitors
Included Quiz Questions
Which medication most significantly increases the risk of serotonin syndrome when administered with selegiline?
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
- Atypical antipsychotics
- Dopamine agonists
- First-generation antihistamines
- Benzodiazepines
What is most accurate about tolcapone, in comparison to entacapone?
- Tolcapone has a longer half-life.
- Tolcapone has a reduced risk of depression.
- Tolcapone has less liver toxicity.
- Tolcapone has a longer 'off time'.
- Tolcapone has less blood-brain barrier penetration.
What is a concerning side effect of tolcapone?
- Liver toxicity
- Breast cancer
- Urinary infections
- Acute renal failure
- Psychosis
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |