Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Colon Polyps
-
Slides Small and large bowel.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
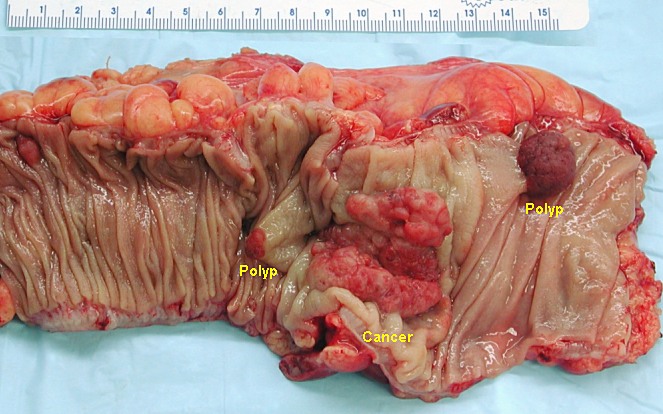
00:01 Let' go into colon polyp. The polyps begin with benign. 00:05 First benign, meaning to say very low risk of going on to malignancy. 00:10 Hyperplastic polyp, just like when found in the stomach, would be in fact would be benign. 00:15 And then you can have what is a hamartomatous polyp. 00:17 What is the definition of hamartoma? Absolutely nonneoplastic. 00:22 By definition. And I have mentioned this to you before, but with the Peutz Jeghers polyp, by definition, even though it is a hamartoma, you will think of this as being a tumor marker. 00:34 So even though this is nonneoplastic, your patient may then go on to develop breast cancer, colorectal cancer, maybe ovarian cancer if she´s a female, so on and so forth. 00:45 Peutz Jeghers. 00:47 Inflammatory polyp reaction to inflammation, especially common in ulcerative colitis. 00:53 So more or less, your benign polyp but every once in a while, you can always have the tendency of going on to malignancy. 01:02 Let us now talk about neoplastic polyps. 01:05 We will begin with the one that we, well, it still will be adenomatous, however, there are two major types that you wanna keep in mind. 01:14 The tubular, so you are doing a colonoscopy. 01:18 When you are doing a colonoscopy, now you'll find a finger-like projection. 01:21 A tube. And you call this pedunculated or stock, all the same thing. 01:28 Tube. Stock. Sitting on a pedestal. Pedunculated, if that helps you. 01:33 The chance of going on to colorectal cancer, a malignancy, extremely rare or decrease risk, were tubular, because if you are thinking about invasion, think of it this way, if you move down the tube the neoplastic cells do. It could. It could, right? It has to invade through the submucosa, mucosa and then that is a lot of invasion. 01:55 Lower risk, but it could. Whereas if you have a polyp that was flatter, flat, meaning it was strictly pasted into the mucosa, this is the villain. 02:08 The villous polyp. The villous adenoma. 02:12 You also call this a sessile. 02:14 And this is the one in which there is an increase and high risk of then going on to malignancy because how easy is it for flat adenoma to hurriedly invade? Quite easy! Quite easy. 02:28 If you have mixed and serrated as well, but the two, for sure that you are paying attention to include tubular and villous.
About the Lecture
The lecture Colon Polyps by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Small and Large Intestine Diseases: Basic Principles with Carlo Raj.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT an example of an adenomatous polyp?
- Peutz-Jeghers
- Tubular
- Tubulovillous
- Villous
- Serrated
Which of the following polyps has the highest risk of malignancy?
- Villous adenoma
- Tubular adenoma
- Tubulovillous adenoma
- Serrated polyps
- Inflammatory polyps
Which of the following polyps is benign? Select all that apply
- Hyperplastic polyp
- Villous adenoma
- Adenomatous polyp
- Hamartomatous polyp
- Inflammatory polyp
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |