Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Quiz Questions and Case Studies – Antibacterial Agents (Antibiotics)
-
Slides Antimicrobial Pharmacology Quiz Questions Case Studies.pdf.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
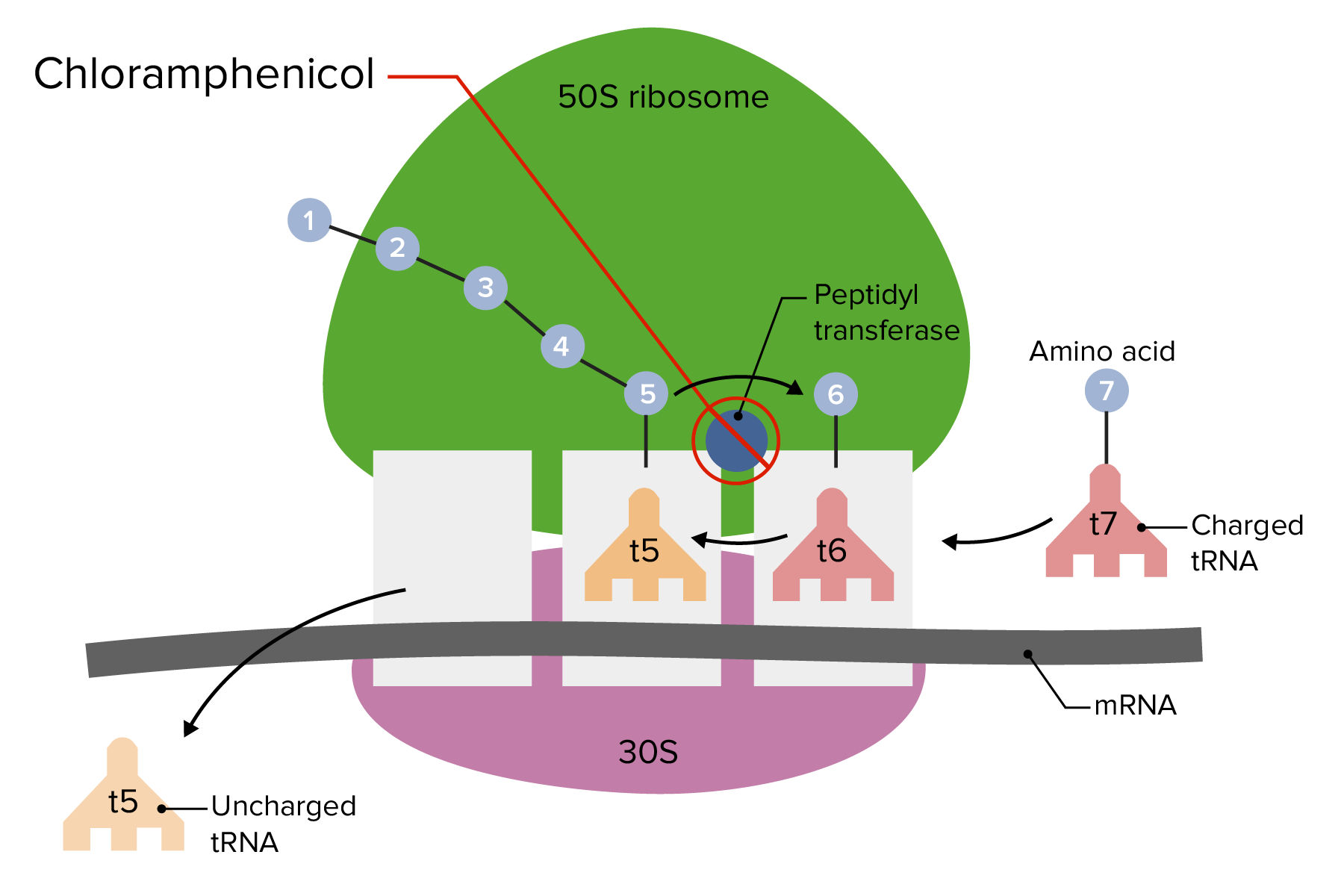
00:00 Let's ask some question about our aminogylcosides. 00:04 The following is true about aminoglycosides. 00:07 A) Aminoglycosides bind to the 30 S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. 00:14 B) Aminoglycosides have no cell wall activity. 00:18 C) Gentamicin and tobramicin are associate with vestibular ototoxicity. 00:25 Amikacin and kanamycin are associated with auditory ototoxicity. 00:31 and D) All of the above is true. 00:34 And the right answer is all of the above is true. 00:38 Let's do another question a girl with a red rash. 00:42 A 12 year old woman has severe staphylococcal skin infection after a motor vehicle accident. 00:48 She is intubated and ventilated in the intensive care unit. 00:53 She was started on an intravenous vancomycin drip. 00:56 She develops a body wide rash without wheals. 01:00 Her core temperature has climbed to 37.9 degrees Celsius. 01:04 Her blood pressure is 112/77. 01:07 Her heart rate is a 109 beats per minute. 01:10 Her white count is 23. 01:13 What is happening to this patient? A) She has a leukemic rash; the patient has had a progression of her undiagnosed leukemia with a leukemic rash. 01:23 B) Severe renal failure due to acute tubular necrosis, with a uremic rash. 01:29 C) Septic shock; the septic meningitis is now a global sepsis with severe peripheral vasodilation. 01:38 Or D) She has developed a cutaneous reaction due to the vancomycin. 01:43 Which is the right answer? Good, she has developed a cutaneous reaction. 01:52 So although a leukemic rash is a possibility. 01:54 She does not fit the clinical picture. 01:56 And it seems kind of an unlikely diagnosis. 01:59 Acute tubular necrosis is not a common reaction to vancomycin. 02:03 Sepsis is certainly an important consideration and your major differential diagnosis here. 02:08 But her heart rate is within acceptable limits for a child in intensive care unit. 02:13 And the blood pressure is actually pretty normal. 02:15 She would have a much lower blood pressure if she were septic. 02:19 The correct answer is going to be D. 02:22 She is having an acute reaction called "Red Man Syndrome", a well known side effect of high dose vancomycin. 02:31 Let's pick the true statement. 02:34 A. Tetracyclines are broad spectrum antibiotics that bind to the 50 S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. 02:41 B. Aminoglycosides are broad spectrum antibiotics that bind to the 50 S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. 02:50 and C. Macrolides are broad spectrum antibiotics that bind to the 50 S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. 03:01 Good. 03:03 Macrolides are broad spectrum antibiotics that bind to the 50 S subunit of the bacterial ribosome. 03:08 So remember tetracyclines and aminoglycosides bind to the 30 S subunit. 03:18 Let's take a look at penicillin. 03:20 Penicillin acts through the following mechanism. 03:23 A) Reduction of calmodulin B) Increasing beta-lactamase activity C) Inhibiting beta-lactamase activity D) Inhibiting the cross linking of peptidoglycan molecules or E) Substitution of the alanine terminal for the lactate terminal. 03:45 The answer is D. 03:46 Inhibiting the cross linking of peptidoglycan molecules. 03:52 Calmodulin has nothing to do with antibiotics. 03:55 Beta-lactamase activity is how bacteria becomes resistant to penicillin. 04:00 Substitution of the alanine terminal for lactate terminal is how organisms are thought to become resistant to vancomycin. 04:07 Doesn't have anything to do with penicillin per say. 04:11 Let's do another question on septicemia. 04:14 So a patient has had a known allergy to penicillin five years ago, with a severe rash and low blood pressure. 04:21 Which of the following medications would be appropriate for use in a gram-negative septicemia? Would it be A) Cefotetan B) Amoxicillin C) Amoxicillin-clavulonate D) Methicillin or E) Aztreonam Good job, you picked E. 04:49 So amoxicillin will probably will have a cross allergy with penicillin as it is so similar structurally. 04:56 Methicillin is also a penicillin. 04:58 May also have a cross-allergy. 05:00 Cefotetan is a cephalosporin and has lower likelihood of cross allergy and maybe a reasonable choice if it work for the fact that we have another choice on the list. 05:11 Cefotetan is otherwise excellent at gram negative infections, particularly septicemia. 05:18 Aztreonam is an antibiotic with no penicillin cross allergy. 05:23 And the answer is E. 05:24 Now the reason why we have this question here is to reference the lack of cross allergy of aztreonam with penicillin as a learning point, okay. 05:36 The following statements are true about vancomycin except: Vancomycin is not easily absorbed when taken orally. 05:47 It is effective for treating bowel infections. 05:51 B. Vancomycin does partially penetrate the blood-brain barrier allowing it to be an efficaceous treatment for septic meningitis. 05:59 C.Vancomycin is an effective agent against staphylococci, although recently resistant strains have been implicated in hospital breakouts. 06:07 And D. 06:08 Vancomycin is a broad spectrum antibiotic. 06:13 The answer is D. 06:15 So this is an incorrect response. 06:19 So it's the correct answer. 06:20 Remember we're asking which are true EXCEPT, so the other three are true. 06:25 So vancomycin is a large, polar molecule that does not easily cross barriers. 06:31 The transmembrane pores do not commonly let vancomycin across because it's such a big molecule. 06:37 Now we take advantage of this characteristic to use it against certain infections like bowel infections as it tends to stay in the bowel and act directly on organisms trapped in the bowel. 06:47 It is not known for crossing the blood brain barrier. 06:50 So a lot of times we may use intrathecal administration in cases of very severe meningitis with responsive organisms. 06:59 Now do not mistake its incredible effectiveness against gram positive bacteria as being a broad spectrum agent. 07:08 A broad spectrum agent is one that cross the gram positive, gram negative, anaerobe sort of barriers. 07:14 Whereas vancomycin is really a gram positive agent in it's truer sense. 07:22 There you have it. 07:23 We covered a very large topic. 07:24 I know you're going to do well in your exams. 07:27 Show them what you know.
About the Lecture
The lecture Quiz Questions and Case Studies – Antibacterial Agents (Antibiotics) by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Antimicrobial Pharmacology.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
It helps me a lot to study the topic. Well covered! EXCELLENT!